- Good: -
Karp's Algorithm finds
all elements with
support level θ:
- I(x, θ) ⊆ K
- Bad: -
the
size of the output
is
1/θ
The output set can be very large
- Ideally, we want to
find the set:
- I(x, θ) = { a ∈ Σ | fx(a) > θ × N }
in an input stream using a one-pass algorithm (i.e., without storing all the values in the stream)
- Because we do not know
the number of items
N
in the stream
in advance,
finding the exact solution
is very difficult
The natural step is to relax the condition:
- The algorithm is
allow
to make some errors
- But, the
degree of the error
must be controlled
by user's specification
(The user can decide how big the error can.)
- The algorithm is
allow
to make some errors
- Solving the frequent element set
problem exactly
requires multiple passes
through the input stream.
- In order to solve the problem using a
single pass
algorithm, Manku and Motwani
relaxes the problem
by
defining the
ε-approximate frequency count
- Their algorithm is called
lossy counting algorithm
- Property of the Lossy Counting Algorithm:
- It can find all items
x
in a data stream such that:
- freq(x) > (θ) N
- The solution will not contain
any item y
with a frequency:
- freq(y) <
(θ - ε) N
for a user-chosen value ε
- freq(y) <
(θ - ε) N
- Graphically:
Frequency: some not included in solution included all included |-----------------------------|---------|-----------------| (θ-ε)N θN
- It can find all items
x
in a data stream such that:
- Furthermore:
- The lossy counting algorithm
can find an estimated frequency
for the output items
The estimated frequencies are less than the true frequencies by at most &epsilon N (where N is the total number of items in the stream)
- Graphically:
Estimated frequency of item x: actual freq(x) |<-------->| ------------------+----------+------------- ^ ^ | | freq'(x) freq'(x) + εN (computed by algorithm)
- The lossy counting algorithm
can find an estimated frequency
for the output items
- The paper "Approximate Frequency Counts over Data Streams" by
Manku & Motwani is here:
click here
- Warning:
- Different papers
propose algorithms to solve
a similar problem
- BUT,
different authors
use different notations
for tha same parameter
- I will use the notations in the paper
to represent that
parameter
Otherwise, reading the paper along with the class notes will be very difficult
- Different papers
propose algorithms to solve
a similar problem
- Notations:
- Input is a stream of values (items)
- N =
number of items in the stream
- fe =
true frequency
of the item e
in the input stream
- f =
computed (approximate) frequency
of the item
- s =
support threshold
(This parameter was called θ in Karp's paper)A frequent item x is an item that satisfy:
- freq(x) ≥ sN (s ∈ (0,1))
- ε =
user specified error threshold
- Output of Algorithm:
- All items that has with frequency greater than or equal to sN.
- No item that has with frequency less than (s - ε)N.
- Input is a stream of values (items)
- The Lossy Counting algorithm
store the counts
of input items in into
"buckets"
Warning:
- I would rather call them "windows"
because buckets
will remind you of
histograms....
- But I will keep using the terminology of the paper - just keep in mind that there is absolutely no histograms in this algorithm !!!
- I would rather call them "windows"
because buckets
will remind you of
histograms....
- Properties of buckets:
- w = the
size (width)
of a bucket
All buckets have the same width:
- w = ⌈ 1/ε ⌉
- Each bucket is numbered
The buckets are numbered started at 1
- bcurrent = the number of the current bucket
- w = the
size (width)
of a bucket
- The value of
bcurrent
can be compute as follows:
- Assume k = number of items processed so far...
- Each bucket contains
w =
⌈ 1/ε ⌉
items.
- So k items are
contained in:
- bcurrent = ⌈ k/w ⌉ = ⌈ ε k ⌉
- The Data Structure
used in the Lossy Counting algorithm
is
a
list/set of record D.
- Each element of D
has the structure:
- (e, f, Δ), where:
- e = the item
- f = the computed (estimated) frequency of the item e
- Δ = the maximum possible error in f (i.e.: fe - f ≤ Δ)
- NOTE: you will see that Δ is also equal to bcurrent, the current bucket number !!!
- (e, f, Δ), where:
- Example:
- (e=4; f=12; Δ=0):
the item 4 has
frequency 12
with an error of 0
(exact)
- (e=7; f=4; Δ=1):
the item 7 has
frequency 4
with an error of 1
I.e., its actual frequency is 4 or 5
- (e=4; f=12; Δ=0):
the item 4 has
frequency 12
with an error of 0
(exact)
- Lossy Counting ALgorithm:
/* ----------------------------------------------------- Initialization: ----------------------------------------------------- */ D = empty; // Empty list... bcurrent = 1; // First current bucket N = 0; // Number of items processed /* --------------------------------------------------- Main processing loop --------------------------------------------------- */ while ( not end of stream ) do { x = next item in stream; N = N + 1; // One more item processed /* -------------------------------- Insert phase -------------------------------- */ if ( x ∈ D ) { fx++; // Increase its count } else { insert (x, 1, bcurrent-1) into D; // Add x to D with frequency count = 1 // The maximum error Δ is set to (bcurrent- 1) } /* ----------------------------------------------------------- Delete phase: Space Reduction step... Note: this step is executed once every w insertions I.e., when one bucket fills up ! ----------------------------------------------------------- */ if ( N mod w == 0 ) { // Bucket boundary reached, cleanup the infrequent items !! for ( each element i ∈ D ) do { if ( fi + &Deltai ≤ bcurrent ) delete (i, fi, &Deltai) from D; } bcurrent++; // Start a new bucket... } } /* --------------------------------------------------- Output phase --------------------------------------------------- */ for ( each element i ∈ D ) do { if ( fi ≥ (s - ε) × N ) { Print i, fi } }
- Example:
(The parameter s is not used until the end of the algorithm) ε = 0.2 w = 1/ε= 5 (5 items per "bucket")
Input: 1 2 4 3 4 3 4 5 4 6 7 3 3 6 1 1 3 2 4 7 | | | | | | | | +-------+ +-------+ +-------+ +-------+ bucket 1 bucket 2 bucket 3 bucket 4
===================================== bcurrent = 1 inserted: 1 2 4 3 4 ------------------------------------- Insert phase: D (before removing):(x=1;f=1;Δ=0) (x=2;f=1;Δ=0) (x=4;f=2;Δ=0) (x=3;f=1;Δ=0) Delete phase: delete elements with f + Δ ≤ bcurrent (=1) D (after removing) :(x=4;f=2;Δ=0) NOTE: elements with frequencies ≤ 1 are deleted New elements added has maximum count error of 0 ====================================== bcurrent = 2 inserted: 3 4 5 4 6 -------------------------------------- Insert phase: D (before removing):(x=4;f=4;Δ=0) (x=3;f=1;Δ=1) (x=5;f=1;Δ=1) (x=6;f=1;Δ=1) Delete phase: delete elements with f + Δ ≤ bcurrent (=2) D (after removing) :(x=4;f=4;Δ=0) NOTE: elements with frequencies ≤ 2 are deleted New elements added has maximum count error of 1 ====================================== bcurrent = 3 inserted: 7 3 3 6 1 -------------------------------------- Insert phase: D (before removing):(x=4;f=4;Δ=0) (x=7;f=1;Δ=2) (x=3;f=2;Δ=2) (x=6;f=1;Δ=2) (x=1;f=1;Δ=2) Delete phase: delete elements with f + Δ ≤ bcurrent (=3) D (after removing) :(x=4;f=4;Δ=0) (x=3;f=2;Δ=2) NOTE: elements with frequencies ≤ 3 are deleted New elements added has maximum count error of 2 ====================================== bcurrent = 4 inserted: 1 3 2 4 7 -------------------------------------- Insert phase: D (before removing):(x=4;f=5;Δ=0) (x=3;f=3;Δ=2) (x=1;f=1;Δ=3) (x=2;f=1;Δ=3) (x=7;f=1;Δ=3) Delete phase: delete elements with f + Δ ≤ bcurrent (=4) D (after removing) :(x=4;f=5;Δ=0) (x=3;f=3;Δ=2) NOTE: elements with frequencies ≤ 4 are deleted New elements added has maximum count error of 3
Interpreting the content in D: Item fmanku factual ------------------------ 4 5 5 3 3 5
- Unlike Guha's efficient histogram
construction algorithm
(which is quite intuitive -
because we can clearly see that
the OPT[k][i]
values can be
easily
approximated by
a histogram),
Manku's Lossy Counting
algorithm
is not intuitive
- You should ask:
- Does it
output all the frequent elements ?
- Why does it work ??
- Does it
output all the frequent elements ?
- Therefore, we will analyze Manku's Lossy Counting algorithm more closely....
- Lemma 4.1:
- Let N =
number of items processed by the
algorithm
- Then the value of
bcurrent
at a bucket boundary
(i.e., when a new bucket is
started)
is:
- bcurrent = ε × N
- Let N =
number of items processed by the
algorithm
- Proof:
- Recall that the
width
of a bucket is equal to:
w = ⌈ 1/ε ⌉
- The program statement:
bcurrent++; // Start a new bucket...is executed once after processing exactly w = ⌈ 1/ε ⌉ items.
- Initially: (before any items are processed)
bcurrent = 1;After processing N = ⌈ 1/ε ⌉ item (i.e., at a bucket boundary), bcurrent is still equal to 1, but this is also the moment that:
1 (= bcurrent) = ε × ⌈ 1/ε ⌉ (= N)
- In general, the kth bucket
is started after processing:
Number of items processed at start of kth bucket = (k - 1) × w = (k - 1) × ⌈ 1/ε ⌉The kth bucket is ended after processing another w items, so:
Number of items processed at end of kth bucket = k × w = k × ⌈ 1/ε ⌉
- So we have this relationship at the end
of a bucket:
Number of items processed at end of kth bucket = k × ⌈ 1/ε ⌉ <==> N = k × ⌈ 1/ε ⌉ <==> N = bcurrent × ⌈ 1/ε ⌉ <==> bcurrent = ε × N
- Example:
ε = 0.2; w = 5 N = 1 2 3 4 5 6 7 8 9 10 11 12 13 14 15 16 17 18 19 20 Input: 1 2 4 3 4 3 4 5 4 6 7 3 3 6 1 1 3 2 4 7 | | | | | | | | +-----------+ +-----------+ +-----------+ +-----------+ bucket 1 bucket 2 bucket 3 bucket 4
- Recall that the
width
of a bucket is equal to:
w = ⌈ 1/ε ⌉
- NOTE:
- By the result of this lemma, we can approxiate the value of bcurrent by ε × N
- Lemma 4.2
- When an entry
(e, f, Δ)
is deleted
in the delete phase of the algorithm
when
bcurrent = k,
then:
- the number of occurences of
e
(i.e., the actual count
fe)
is less than or equal to
k
I.e.: fe ≤ bcurrent
- the number of occurences of
e
(i.e., the actual count
fe)
is less than or equal to
k
Proof: by induction
-
Base Case: bcurrent = 1
- Inserting in first bucket:
bucket 1 |<------------------------------->| N=0 N=1 ... N=w | | V V +---------------------------------+-------------------------> bcurrent = 1 ^ ^ | | | | (e, f=1, Δ=0) | | Delete phase: delete items with f + Δ ≤ 1 - Each item
inserted into D has the value
Δ = 0
In the delete phase of round 1, items e that are deleted will have a frequency of:
- fe + Δ ≤
1
(Δ = 0)
- Or: fe ≤
1
( bcurrent = 1)
- Or: fe ≤ bcurrent
- fe + Δ ≤
1
(Δ = 0)
- Hence, the base case
is true.
- Inserting in first bucket:
-
Induction Step: bcurrent = k ≥ 2
- If an entry
(e, f, Δ)
is deleted when
bcurrent = i,
the actual count of the number of occurences of
e
is less than or equal to
i,
for all i ≤ k-1
More specifically: If (e, f, Δ) is deleted in the delete phase when bcurrent = i, then:
-
fe ≤
i
for i = 1, 2, ..., k-1
- If an entry
(e, f, Δ)
is deleted
in the
delete phase
when
bcurrent = k,
then:
-
fe ≤
k
- Let
(e, f, Δ)
be an (arbitrary) entry that was
deleted when
bcurrent = k
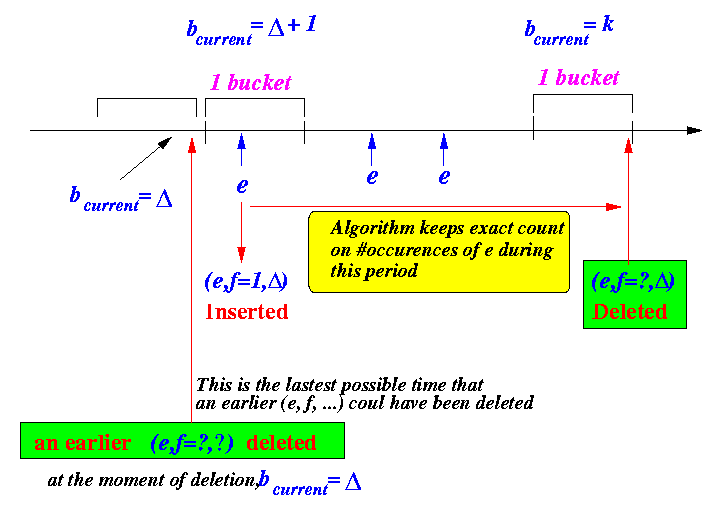
Previous buckets... Current bucket |<------------------------>|<---------------->| | | | | N=k*w | | | V V V +--------------------------+-**************---+-------------------------> bcurrent=Δ+1 ^ bcurrent = k ^ | | |<----------------------------->| | keeps the exact count for e | (e, f=1, Δ) | | (e, f=?, Δ) is deleted here
- The entry for item e
was inserted in some
"previous" bucket
(it can be the current bucket also).
- Let us assume that
the entry for item e
was inserted when
bcurrent = Δ+1.
Therefore, the entry (e, f=1, Δ) will be inserted at that time.
(See the figure above for reference)
Noteworthy fact:
- After inserting the
entry e,
the algorithm will keep an
exact count for
the elements e
onwards (until the entry
(e, f, Δ)
is deleted)
Note: this is similar to the Counting Sample algorithm
- After inserting the
entry e,
the algorithm will keep an
exact count for
the elements e
onwards (until the entry
(e, f, Δ)
is deleted)
- The following is a better figure
that summarizes the relationships that we have
discovered so far:
- Since the item e is
insert in when
bcurrent = Δ + 1,
this item does not appear
in the set D at that time.
There are 2 reasons why e ∉ D when bcurrent = Δ + 1:
- There were no occurrences of
e
prior to bucket
bcurrent = Δ + 1
- If there were occurrences of
e
prior to bucket
bcurrent = Δ + 1,
but the
(e, f, Δ)
was deleted...
Then the latest time that the entry (e, f, Δ) could have been deleted by the algorithm is at the end of bucket Δ (see figure above)
- There were no occurrences of
e
prior to bucket
bcurrent = Δ + 1
- Now: Δ < k.
Therefore, we can apply the induction hypothesis:
- We know that
the entry
(e, f, Δ)
was deleted when
bcurrent ≤ Δ
- According to the induction hypothesis, when an entry (e, f, Δ) is deleted when bcurrent ≤ Δ, the actual number of occurences of e (fe) at that moment is less than or equal to bcurrent = Δ.
Therefore:
Previous buckets... Current bucket -----|<------------------->|<---------------->| | | | | N=k*w | | | V V V -----+---------------------+-**************---+-------------------------> bcurrent=Δ+1 ^ bcurrent = k ^ ^ | | | |<--------------------------->| | | keeps exact count for e | | (e, f=1, Δ) | | | | (e, f, Δ) is deleted here | |<-------->|<--------------------------->| | zero e exactly f e's ^ fe ≤ Δ | | fe ≤ Δ + fBecause:
- The exact count of item
e
at the boundary of bucket
Δ is:
-
fe ≤ Δ
- And, the algorithm counts every occurence of e starting in bucket Δ + 1 until the deletion of (e, f, Δ)
We have that exact count of item e at the boundary of bucket k (the moment that e is deleted) is:
- fe ≤ Δ + f ....... (1)
Now the algorithm will delete the item e when:
- f + Δ ≤ bcurrent (= k) ....... (2)
From Equations (1) and (2), we conclude that:
- The entry
(e, f, Δ)
deleted
when bcurrent
= k always has:
-
fe ≤ f + Δ
≤
bcurrent = k
This is exactly what we needed to prove: Click here !!!
- We know that
the entry
(e, f, Δ)
was deleted when
bcurrent ≤ Δ
Induction hypothesis: assume the statement is true for all i < k
We need to prove that:
Proof:
- If an entry
(e, f, Δ)
is deleted when
bcurrent = i,
the actual count of the number of occurences of
e
is less than or equal to
i,
for all i ≤ k-1
- When an entry
(e, f, Δ)
is deleted
in the delete phase of the algorithm
when
bcurrent = k,
then:
Lemma 4.3 will tell us something what kinds of elements are included in the data structure D
- Lemma 4.3
- If the item e
is not included
in D, then
(i.e., (e, f, Δ) ∉ D),
then:
- fe ≤ ε × N
i.e., the true frequency count of e is less than or equal to ε × N
Proof:
- Case 1: (trivial case)
- If e
does not appear
in the input stream, then
trivially,
the entry (e, f, Δ)
was never entered
into D and hence,
(e, f, Δ) ∉ D
We have then:
-
fe = 0
and trivially:
-
fe (= 0) ≤
ε × N
is true... lucky :-)
- If e
does not appear
in the input stream, then
trivially,
the entry (e, f, Δ)
was never entered
into D and hence,
(e, f, Δ) ∉ D
- Case 2:
-
If e was in the
input stream, and the entry
(e, f, Δ)
is not in the output set
D, then:
- (e, f, Δ) was deleted in some bucket.
- The following diagram show the
timing of the events
since the time that
(e, f, Δ)
was last deleted
from D:
- Let's look at the
last deletion
of the item e from D.
Notation:
- Assume that
the item e was
deleted in the
bucket denoted by:
bcurrent
- Currently, the current bucket is denoted by b*current
The item e did not appeared in the input since its last deletion !
- Assume that
the item e was
deleted in the
bucket denoted by:
bcurrent
- According to Lemma 4.2
( click here),
because
(e, f, Δ)
is deleted in
bucket
bcurrent:
- The actual count at that moment fe ≤ bcurrent ............ (1)
- And according to Lemma 4.1
( click here),
- bcurrent = ε × N at any bucket boundary ............ (2)
- Since
the entry
(e, f, Δ)
was deleted at a bucket boundary,
therefore, at that time
(when (e, f, Δ)
was deleted):
- fe ≤ bcurrent = ε × N
- Summary:
no item e in input ---------+----------------------------+--------- ^ ^ | | | | Last deletion Algorithm ends of e with e ∉ D | Here: fe ≤ εN - And since after its deletion,
no item e
has arrived, we have:
- fe ≤ ε × N
will still be true at the end of the algorithm

- Let's look at the
last deletion
of the item e from D.
-
If e was in the
input stream, and the entry
(e, f, Δ)
is not in the output set
D, then:
- If the item e
is not included
in D, then
(i.e., (e, f, Δ) ∉ D),
then:
- Therefore, if
(e, f, Δ) ∉ D,
then, the actual frequence
of item
e:
fe
≤ ε × N
That's what we needed to prove...
- Lemma 4.2
- If (e, f, Δ) ∉ D, when the algorithm terminates then, the actual frequence of item e: fe ≤ ε × N
- We can re-phrase it this way
(apply rules of negation):
- If the actual frequence of item e: fe > ε × N then, (e, f, Δ) ∈ D, when the algorithm terminates
- Therefore, the output set
D contains
all the frequent elements
- Next: how accurate is the frequency count computed by the algorithm ?
The following lemma tells us how accurate the approximate frequency f is.
- Lemma 4.4
-
If (e, f, Δ) ∈ D,
then:
- f ≤ fe ≤ f + &epsilon × N
I.e., the actual count fe is a value between f (from the algorithm output) and f + εN
Proof:
-
Part 1:
f ≤
fe
- Since the value
f
(variable in the algorithm)
count the item
e in the input
after the entry
(e, f, Δ)
has been inserted in D,
and
the entry (e, f, Δ)
may have been deleted before,
it is obvious that:
-
f ≤ fe
(NOTE: Because the reported count f can be less than fe, the algorithm is called Lossy Counting)
- To show that:
fe ≤ f + &epsilon × N
,
consider the following
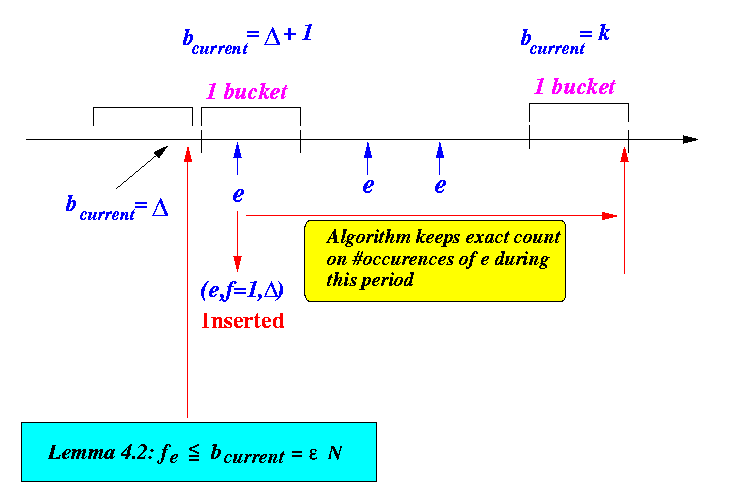
timing diagram.
- Assume that item e was
last inserted in the
bucket
bcurrent =
Δ + 1
- Because e ∈ D, the item e is not removed from D since this (last) insertion
- Assume that item e was
last inserted in the
bucket
bcurrent =
Δ + 1
- Note:
- From the moment that (e, f, Δ) is inserted in D, the algorithm keeps an exact count on the number of occurences of e
- Therefore:
- The only occurrences of e that the algorithm fails to count are those that appeared prior to the bucket Δ + 1.
- The maximum
number of occurrences of
e that
were not counted
can be computed as follows:
- The maximum number of
missing count (worst case scenario) happens when
the entry
(e, f, Δ)
was deleted in
the bucket
just prior to the
bucket Δ+1
(in which
(e, f=1, Δ)
was entered into D)
- In this worst case scenario,
--- according to
Lemma 4.2 ---
at the moment of deletion,
the actual frequence of
the item e
is at most:
- fe ≤ bcurrent .... Lemma 4.2
- With Lemma 4.1, we get:
- fe ≤
bcurrent =
&epsilon × N*
....
Lemma 4.1
(N* is the number to items processed at the end of bucket Δ)
- Therefore:
fe ≤
bcurrent =
&epsilon × N*
≤
&epsilon × N
(N is the total number to items processed)
- fe ≤
bcurrent =
&epsilon × N*
....
Lemma 4.1
- The maximum number of
missing count (worst case scenario) happens when
the entry
(e, f, Δ)
was deleted in
the bucket
just prior to the
bucket Δ+1
(in which
(e, f=1, Δ)
was entered into D)
- So actual count
fe of the
number of items e
is at most &epsilon × N
more than
the reported value
f:
- fe ≤ f + &epsilon × N
Part 2: fe ≤ f + &epsilon × N
-
If (e, f, Δ) ∈ D,
then:
- Their algorithm can be easily adapted to find
frequent item SETS
- The format of each entry in D is changed to:
-
(s, f, Δ)
where s is a set of items.
- Here is the modified algorithm:
D = empty; // Empty list... bcurrent = 1; N = 0; // Number of items processed while (NOT EOF) do { x = next item SET in stream; N = N + 1; // One more item SET processed // Tally step... if ( x ∈ D ) { for each (si, fi, Δi) ∈ D) do { if ( si ⊂ x ) fi++; // Found, increase its count } } else { insert (x, 1, bcurrent-1) into D; // New element has frequency count 1 // and maximum error Δ = bcurrent- 1 } // Space Reduction step... if ( N == 0 mod w ) { // Bucket boundary reached, cleanup the infrequent items !! for each (si, fi, Δi,) ∈ D do { if ( fi + &Deltai ≤ bcurrent ) delete (si, fi, &Deltai) from D; } bcurrent++; // Next bucket... } } Output all entries with fi ≥ (s - ε) × N
- See paper, Table 2: ( click here )