- What is Aloha:
- The very first midium access protocol developed at the University of Hawaii around 1970.
- Their problem:
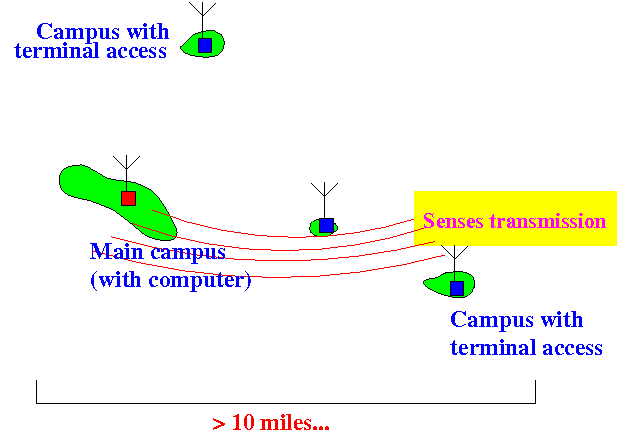
- The U. of Hawaii had campuses on different islands
- Computers were located on the main campus
(computers were very exensive in those days):
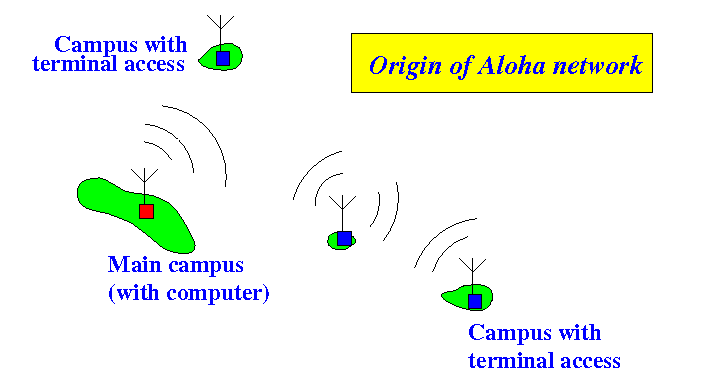
- The wireless network allows terminals located at other campuses (on other islands) to gain access to the computers on the main campus.
- The U. of Hawaii had campuses on different islands
- Fact about radio transmissions
- Simultaneous transmissions will cause
both messages
to be received
in error:
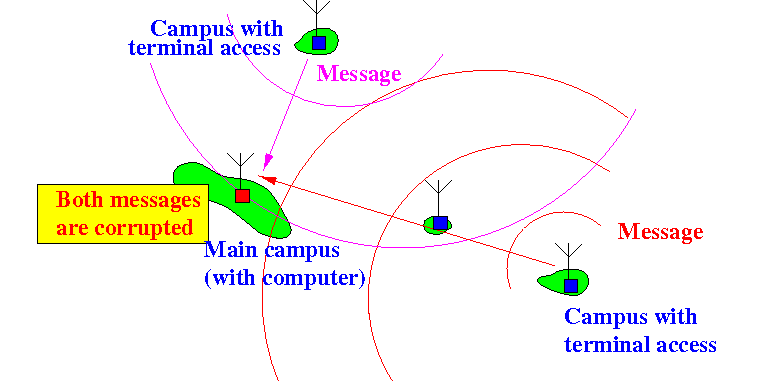
- Simultaneous transmissions will cause
both messages
to be received
in error:
- The challenge:
- Allow users at statlite campusses to communicate with the main campus
Protocol: the need for "order"
- To ensure that messages are received correctly,
the nodes in the network
must follow a
well-defined
precedure.
The University of Hawaii designed the world's first (wireless network - shared medium) medium access protocol.
For obvious reasons, they called their protocol the "Aloha" protocol...
- The Aloha protocol
- If a node has a
message to transmit,
transmit it immediately
- After transmission,
wait a
time out period
(for the ACK)
- If ACK is received within
time out, done
Otherwise: (probably collision due to simultaneous transmissions)
- wait a random interval (to avoid
- Retransmit the message
- If a node has a
message to transmit,
transmit it immediately
- Note:
- The most likely
cause that a transmission
was corrupted is:
collision (simultaneous transmission)
- The random delay in included
into the protocol to
reduce the likelihood
of a repeated
collision
Hopefully, different nodes will pick different random delays and avoid a collision in the next attempt.
- The most likely
cause that a transmission
was corrupted is:
collision (simultaneous transmission)
- $64,000 question:
- Why does a node
not sense the channel
for transmissions before
it transmits ???
Would this help reduce the likelihood of collision ?
- Why does a node
not sense the channel
for transmissions before
it transmits ???
- No:
- Facts:
- the messages were
short
(we had text terminals
in those days, not graphical terminals)
and
- the distance between the islands were large.
- the messages were
short
(we had text terminals
in those days, not graphical terminals)
and
- Facts:
- The futility of sensing the transmission channel:
- First: understand that the
collision of the waves
must take place at the
receiver
to realise a collision:
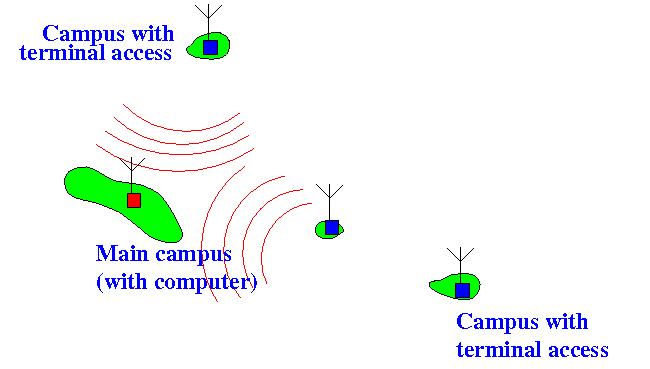
- A node starts tranmitting, but the
transmission will
not be detected
by a remote node:
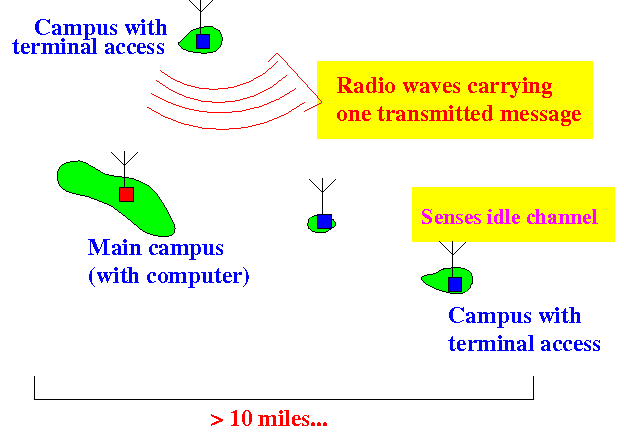
- When the transmission can be
sense, the transmission has
pass the receiver (main campus)
and
would not
cause a collision
if the romote campus
would start a transmission:
- First: understand that the
collision of the waves
must take place at the
receiver
to realise a collision:
- Slotted Aloha:
- To minimize the
likelihood that 2 transmissions will
collide,
a simple addition to
the Aloha protocol is
synchronized transmissions
- All senders' transmissions in slotted schemes are synchronized
- To minimize the
likelihood that 2 transmissions will
collide,
a simple addition to
the Aloha protocol is
synchronized transmissions
- Slotten transmission algorithm:
- Time is divided into
slots
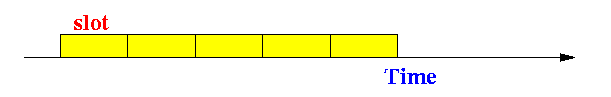
- A transmission
can only begin
at the start of
a slot
- Transmissions last at most one slot
- Time unit used = length of a slot
- Time is divided into
slots