CUDA program:
kernel
Kernel =
the program (function)
that is executed by
the GPU
Example:
__global__ void hello( )
{
printf("Hello World\n");
// CUDA C code
// uses printf( ) in CUDA C library
}
|
A
kernel
(= a GPU function/program) is
executed by a
grid
(of
threads)
Note:
- Different threads
will use
different operands
|
Threads
(terminology)
Thread =
single execution unit that
run
CUDA code ("kernel")
on the GPU
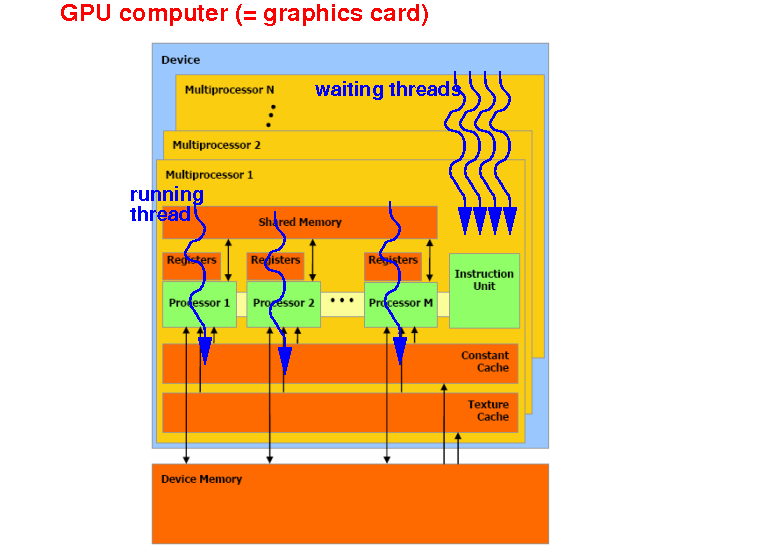
Each thread is
executed by
1 CUDA core (= processor)
Multiple threads can be
assigned to the
same
CUDA core
(A CUDA core will
switch execution
between different threads !)
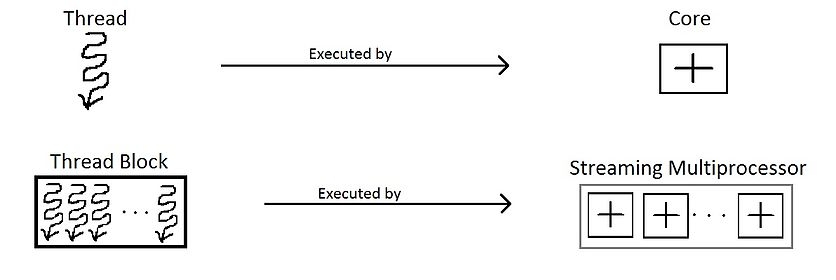
Thread organization:
thread block
-
Multiple
threads are
organized (= grouped) into a
"thread block"
-
Threads in the
same
thread block
are run on
the
same
stream multiprocessor (SM)
- Multiple
thread blocks can be
assigned to
one multiprocessor
|
- Organization:
- A (thread) block has
3 dimensions:
x ≤ 1024
y ≤ 1024 and x * y * z ≤ 1024 (i.e.: max 1024 threads in a block)
z ≤ 64
|
|
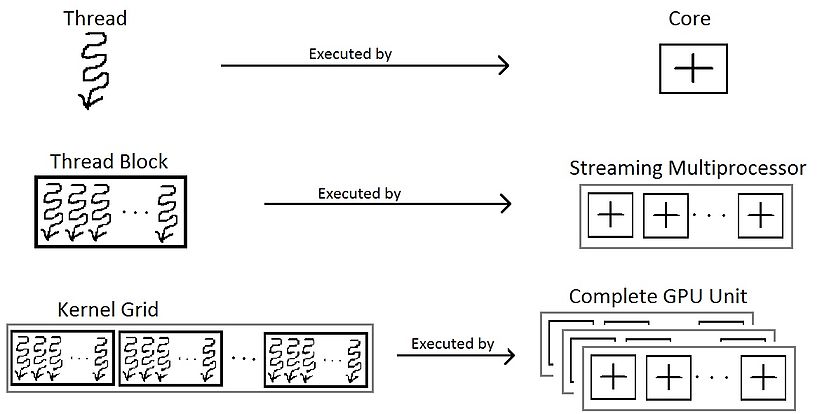
Thread organization:
grid
-
Multiple
thread
blocks are
organized (= grouped) into a
"grid"
-
Threads in the
same
grid
are run on
the
same
GPU
|
- Organization:
- A grid also has
3 dimensions:
x ≤ 231-1
y ≤ 65535
z ≤ 65535
|
|
CUDA program execution:
"launching"
the kernel on a grid
- Grid =
all the threads that
execute the
same
CUDA
kernel function
- A
grid is
create by
the host program when it
"launches" (= calls)
a kernel function
-
Kernel launching
syntax:
KernelFunction <<<NBlocks, NThreads>>> (params);
Run KernelFunction on GPU using a grid that consists of:
NBlocks thread blocks with
NThreads threads in each thread block
|
|
❮
❯


