The OpenMP
multi-threading API
- OpenMP:
- OpenMP (Open Multi-Processing)
is an
application programming interface (API)
that supports
multi-platform
shared-memory
multiprocessing programming
|
- How
OpenMP
works:
- OpenMP
is implemented
using multithreading
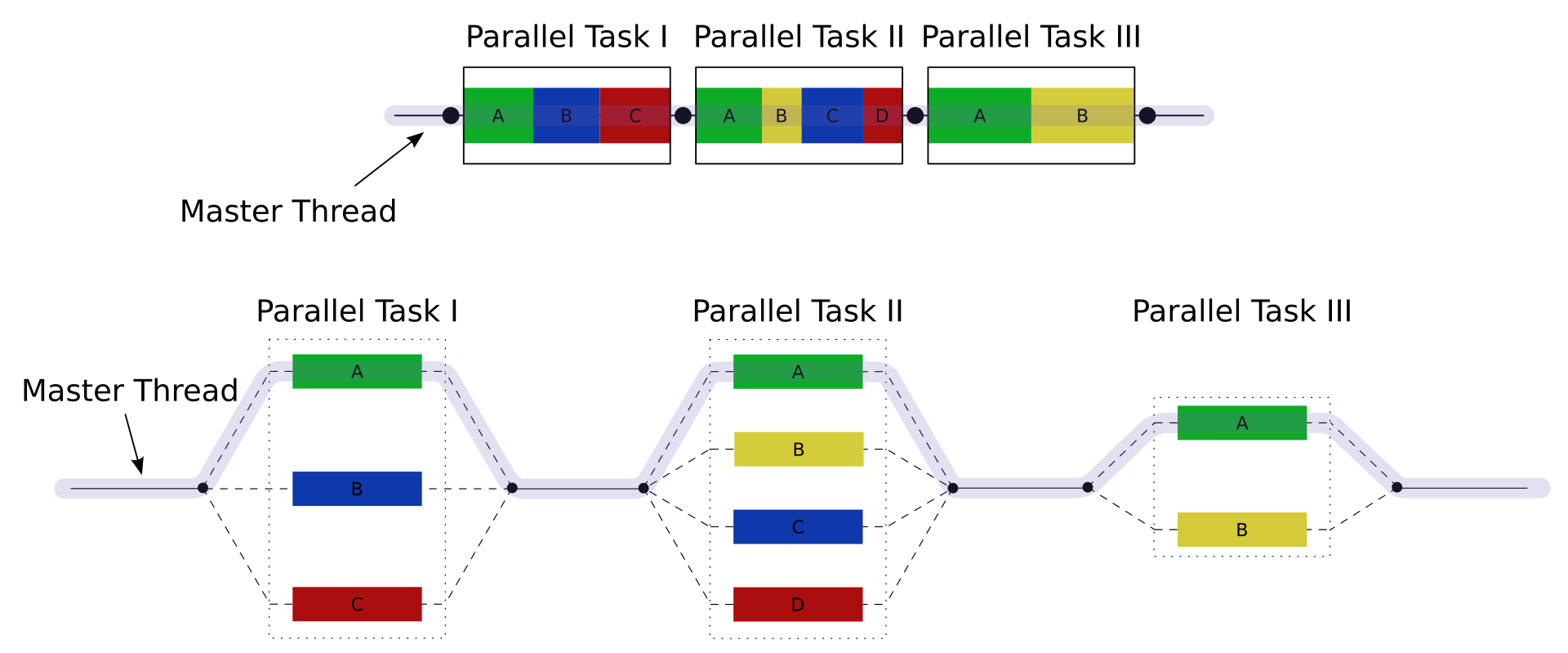
- A primary thread
creates
a specified number of
sub-threads that
execute in
parallel
|
|
The pragma compiler directive
- The #pragme
directive:
- Example:
#pragma GCC poison printf: disallow the use of printf
|
- The
Open Multi-Processing (OpenMP)
is a
directive-based
API for
developing
parallel programs on
shared-memory
SIMD processors
|
DEMO:
demo/OpenMP/pragma.c
Defining
parallel regions in a
C program
-
Parallel region:
-
Parallel region =
code in a
C program that is
executed by
multiple threads
|
- Syntax to
define a
parallel region
in OpenMP:
#pragma omp parallel [Options...]
{ ...
... Parallel region
...
... Program statements between the braces
... are executed in parallel by multiple threads
...
}
|
-
Controlling the
number of
threads in the
parallel region:
- Set the
environment variable
OMP_NUM_THREADS
(e.g.:
export
OMP_NUM_THREADS=4)
- Set
number of threads with
library function
omp_set_num_threads(n)
|
|
Your first
OpenMP program
- The Hello World
program in
OpenMP:
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
#pragma omp parallel
{
printf("Hello World!\n");
}
}
|
- Compiling an
OpenMP
C program:
-
Output: printed 4 times
(
by default:
# threads =
# CPU cores)
Hello World!
Hello World!
Hello World!
Hello World!
|
|
DEMO:
demo/OpenMP/hello1.c
Finding the ID of a
thread and
the number of
threads in the
parallel region
- Some useful
OpenMP
library functions:
omp_get_thread_num( ): returns the ID of a thread
omp_get_num_threads( ): returns the # threads in the parallel region
|
- Example:
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
#pragma omp parallel
{
int nthreads;
int myid;
myid = omp_get_thread_num(); // Get my ID in thread group
printf("Hello, I am thread %d...\n", myid);
if (myid == 0)
{
nthreads = omp_get_num_threads();
printf("Thread 0: Number of threads used = %d\n", nthreads);
}
}
}
|
|
DEMO:
demo/OpenMP/hello2.c
What is happening inside a
OpenMP program
- Graphical representation
of the execution of the
OpenMP
"Hello World"
program:
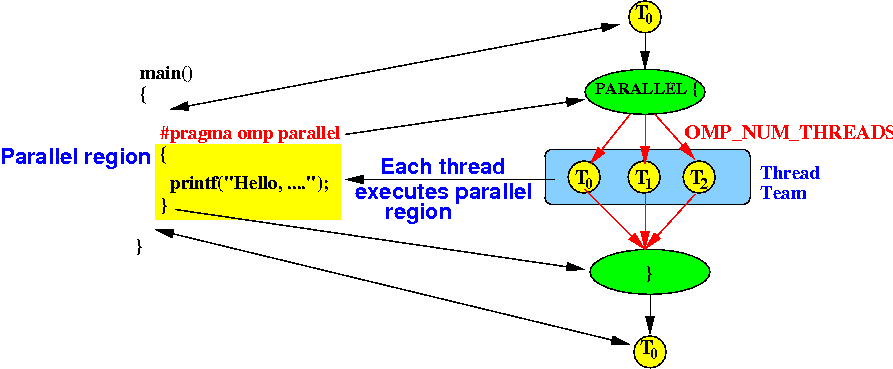
- Before
the compiler directive
#pragma omp parallel,
the program is
single-threaded
- The compiler directive
#pragma omp parallel,
tells the C compiler
to create a
thread team to
execute the
parallel region
- At the end
of the parallel region,
the threads are
implicitly
joined
|
|
❮
❯

