Increaseing memory size and width
- It is not necessary
to construct
very large
memory circuits
- There are 2 techniques that can be
used to expand the
"size" of
a memory circuit:
- One technique can
increase the
width
(=
# bits in a row of memory)
of
memory circuits
- One technique can
increase the
size
(=
# rows in a memory
circuit) of
memory circuits
|
- You also can combine the
2 techniques to
increase
both the
width and the
size of
any memory circuit
|
Increasing the width of a
memory circuit
Previously, we
constructed a
memory that has
4 bits in
each row
(i.e.: width=4 bits):
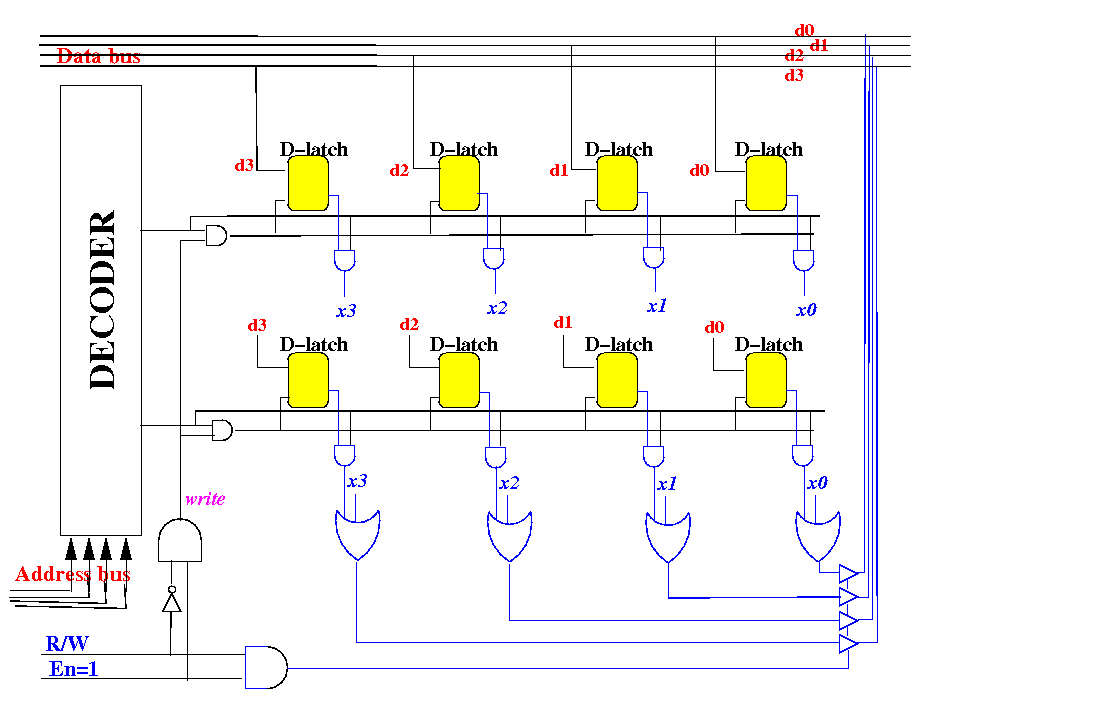
(Actually, I used 4 bits
to keep the design simple)
Increasing the width of a
memory circuit
Suppose, we
constructed a
memory that
only has
1 bit in
each row
(i.e.: width=1 bit):
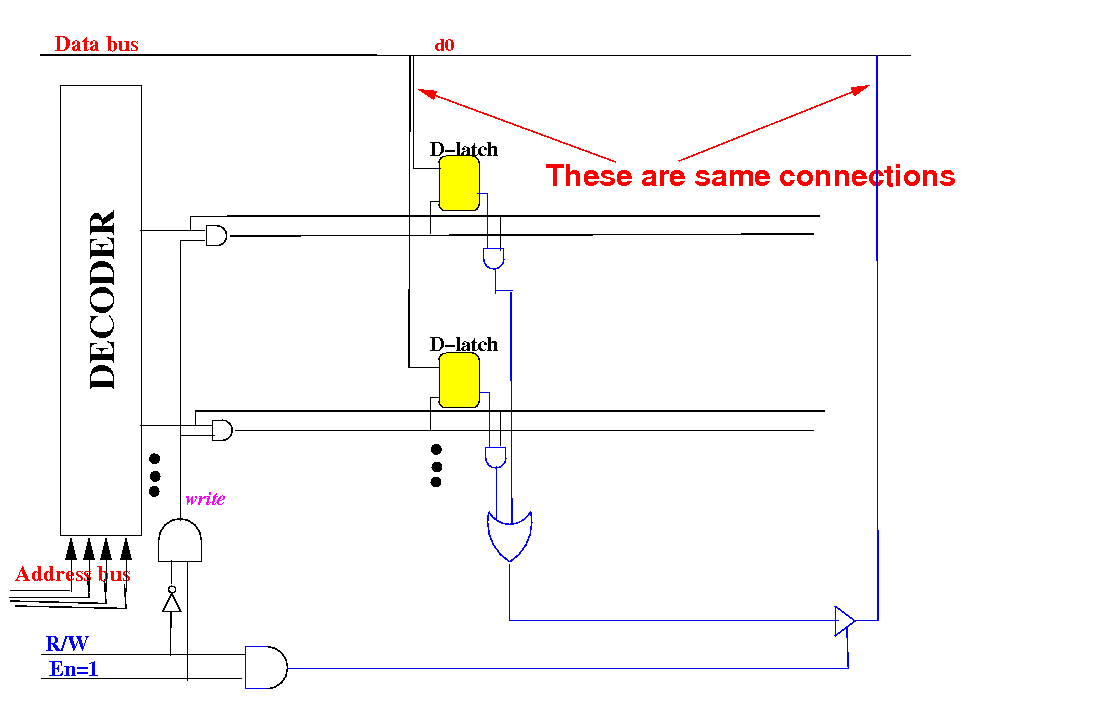
The input and
output of the
D-latch are
both connected to
the data bus wire -
redraw it
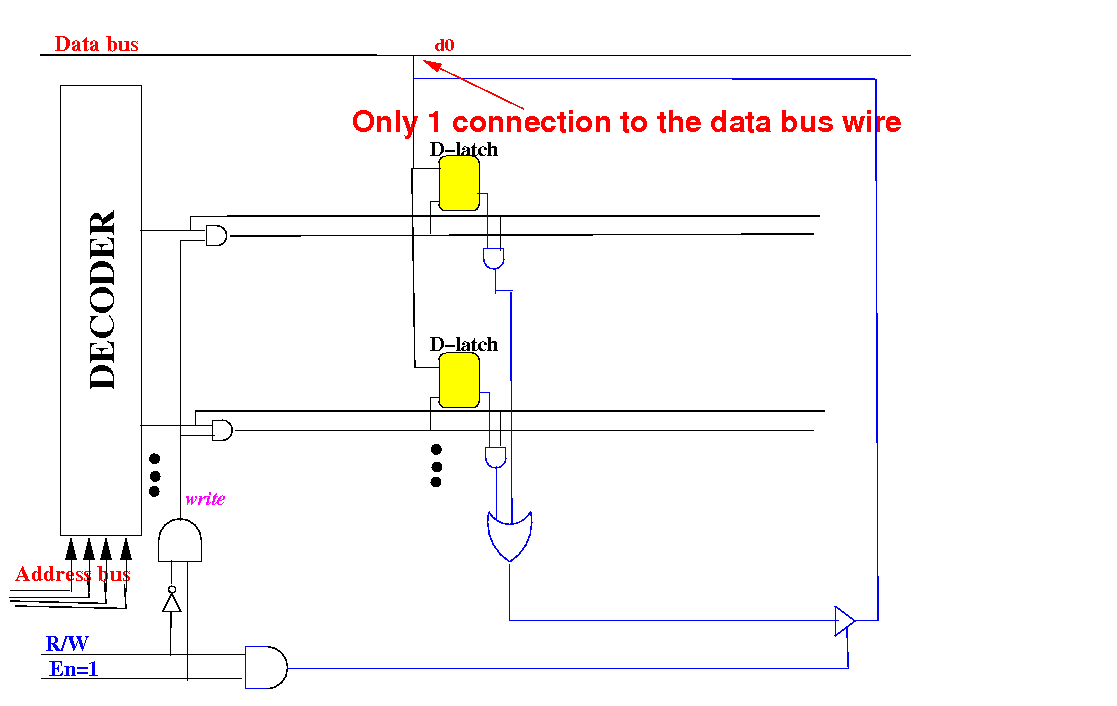
Increasing the width of a
memory circuit
There is actually
only 1 connection to
the data bus wire:
Increasing the width of a
memory circuit
We can represent this as
follows - it has
N address lines and
1 data line:
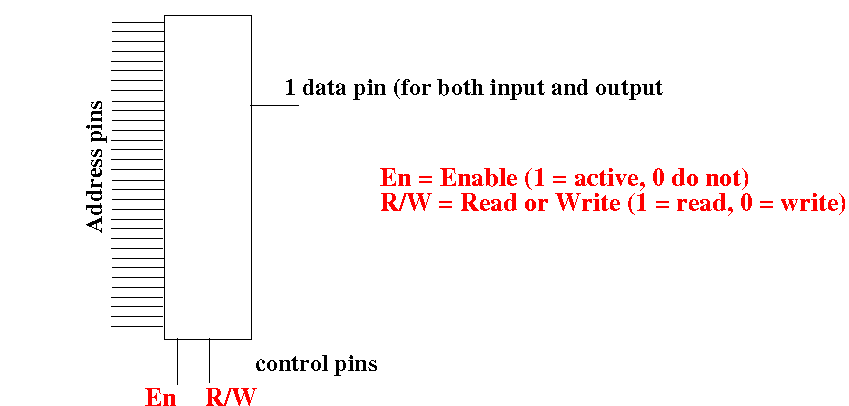
This memory circuit has
2N rows and
1 bit in
each row.
Is such memory circuit
useful ???
Increasing the width of a
memory circuit
Problem: use
8 of these
2N×1
memory circuits
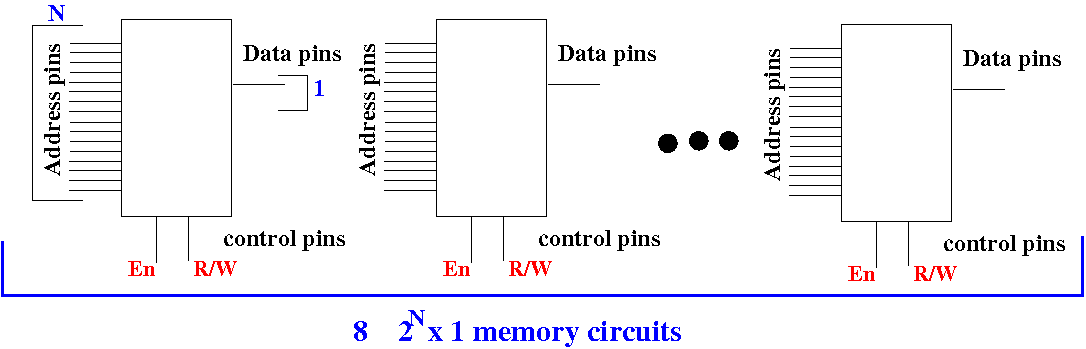
construct a
2N×8
memory circuits:
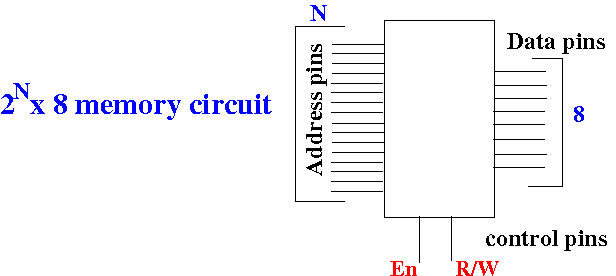
A 2N×8
memory circuit has
2N rows and
8 bits in
each row.
Increasing the width of a
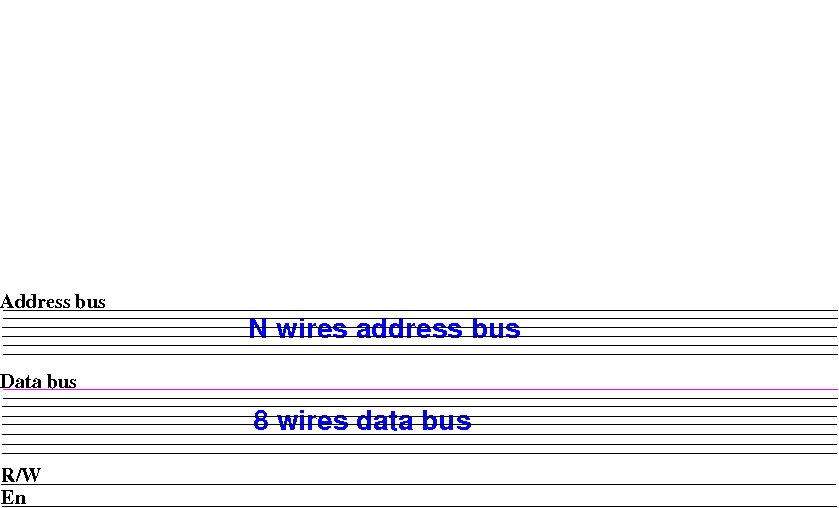
memory circuit
We start with drawing out
all the
input and output signals:
Increasing the width of a
memory circuit
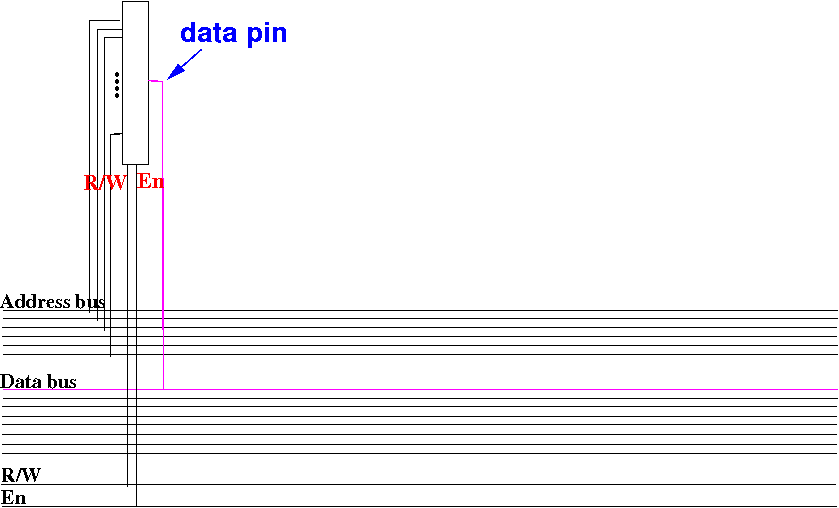
We use 1 (one)
2N×1 memory circuit to
store the
data transfered over
1 data bus wire:
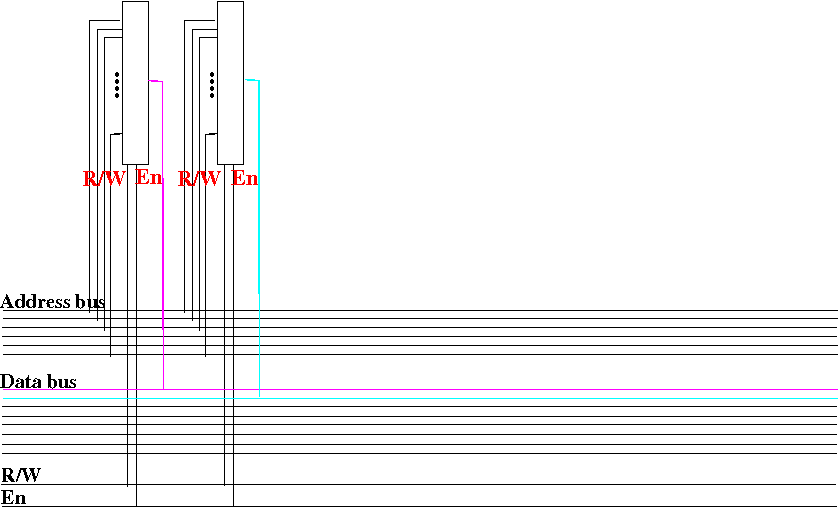
Increasing the width of a
memory circuit
We use another
2N×1 memory circuit to
store the
data transfered over
another 1 data bus wire:
Increasing the width of a
memory circuit
And so on:
connect the output of
each 2N×1 memory circuit
to a different data bus wire:
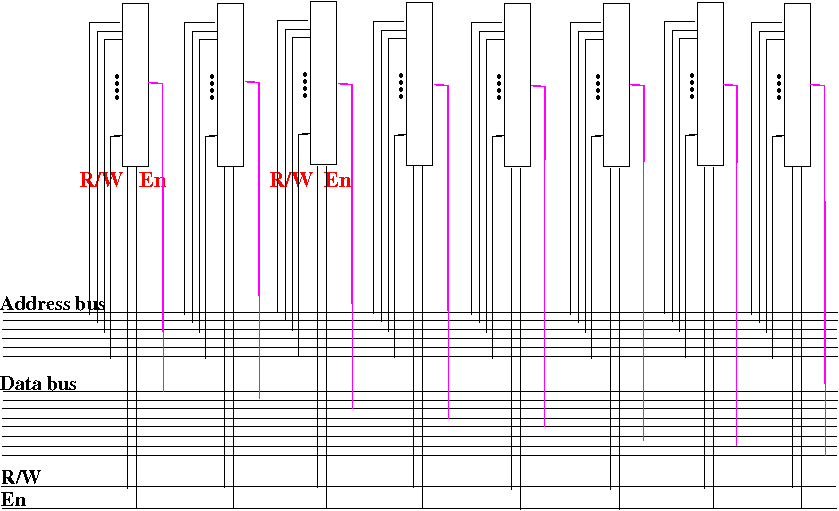
The resulting circuit is
a
2N×8 memory circuit
!
Increasing the width of a
memory circuit -
example application
- Memory chip manufacturers can
easily make
1,2,4 G×1 bit
memory chips
- They would use
32 of such
1,2,4 G×1 bit to make
4,8,16 Gbyte DDR memory circuits :
|
Increasing the size of a
memory circuit
Suppose you have
4 (four)
2N×8 bits
memory circuits:
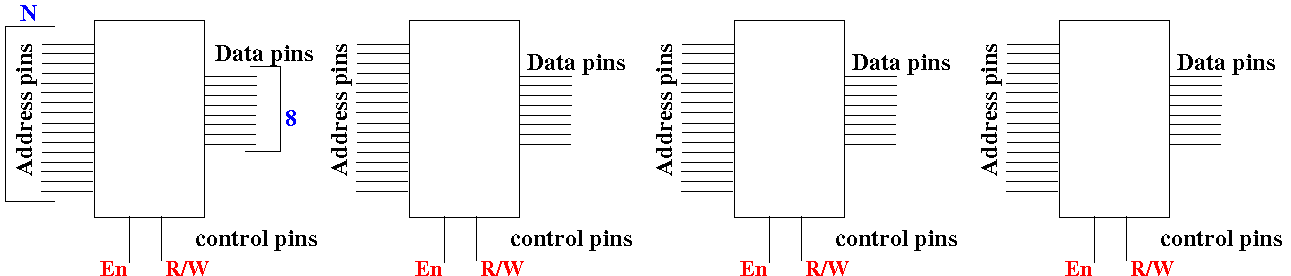
Construct a
(large size)
2N+2×8 bits
memory circuits:
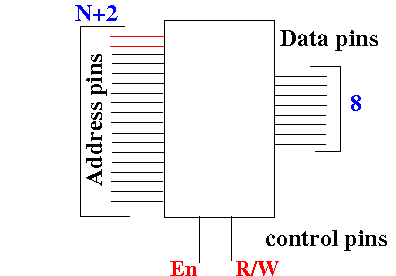
Increasing the
size of a memory circuit
For
simplicity
(of the presentation),
I will use a
concrete example with
10 address pins (wires):
- Suppose we have
4 (four)
210×8 bits
memory circuits:
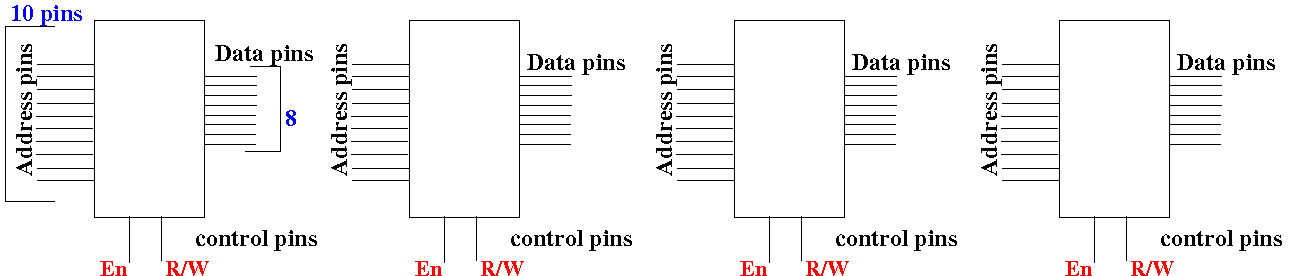
- Construct a
(large size)
212×8 bits
memory circuits:
|
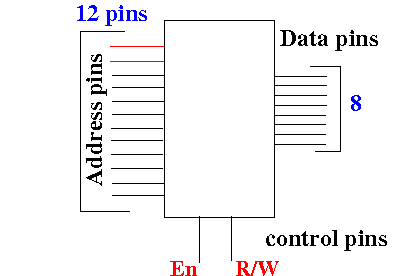
Increasing the size of a
memory circuit
-
background info
- The 212×8 bits
memory circuit has
12 address pins
- The 12 bits
binary numbers are
listed below
in 4 groups:
000000000000 010000000000 100000000000 110000000000
000000000001 010000000001 100000000001 110000000001
000000000010 010000000010 100000000010 110000000010
000000000011 010000000011 100000000011 110000000011
...
...
001111111111 011111111111 101111111111 111111111111
|
- Each one of a
12 bits
binary number can be used
to select a
(8 bits) memory cell in a
212×8
memory circuit
|
Increasing the size of a
memory circuit
-
background info
How to
construct a
212×8
memory circuit using
4 (four)
210×8
memory circuit:
- We use the
first
2 bits of the
(12 bits) address to
select (activate)
one of the
4 (four)
210×8
memory circuits
000000000000 010000000000 100000000000 110000000000
000000000001 010000000001 100000000001 110000000001
000000000010 010000000010 100000000010 110000000010
000000000011 010000000011 100000000011 110000000011
...
...
001111111111 011111111111 101111111111 111111111111
| | | |
V V V V
Activate #1 Activate #2 Activate #3 Activate #4
|
|
Increasing the size of a
memory circuit
-
background info
How to
construct a
212×8
memory circuit using
4 (four)
210×8
memory circuit:
- We use the
last
10 bits of the
(12 bits) address to
select
row of memory cells inside
the
actiavte
210×8
memory circuit
000000000000 010000000000 100000000000 110000000000
000000000001 010000000001 100000000001 110000000001
000000000010 010000000010 100000000010 110000000010
000000000011 010000000011 100000000011 110000000011
...
...
001111111111 011111111111 101111111111 111111111111
| | | |
V V V V
Select row (of memory cells) when activated
|
|
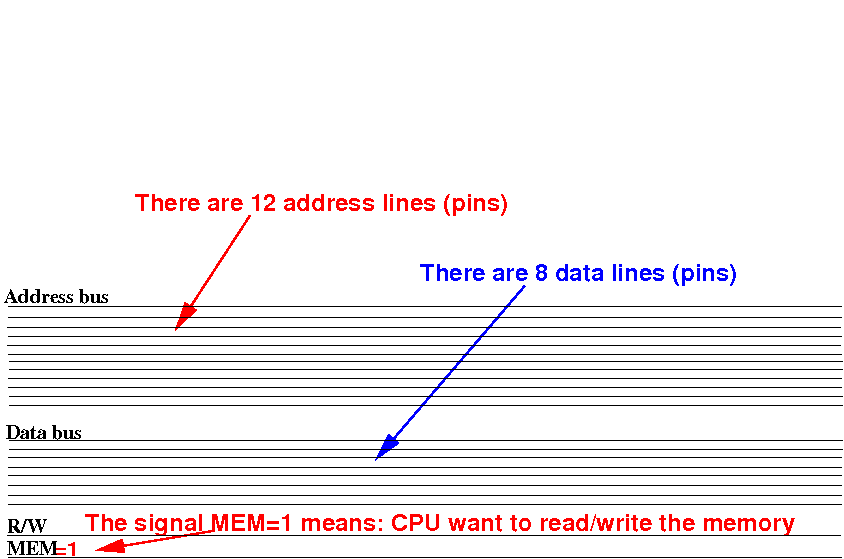
Increasing the
size
of a memory circuit
We start with the input and the
output signals:
Increasing the
size
of a memory circuit
Use a decoder to
translate the
first 2 bits of the
address into a
selection signal:
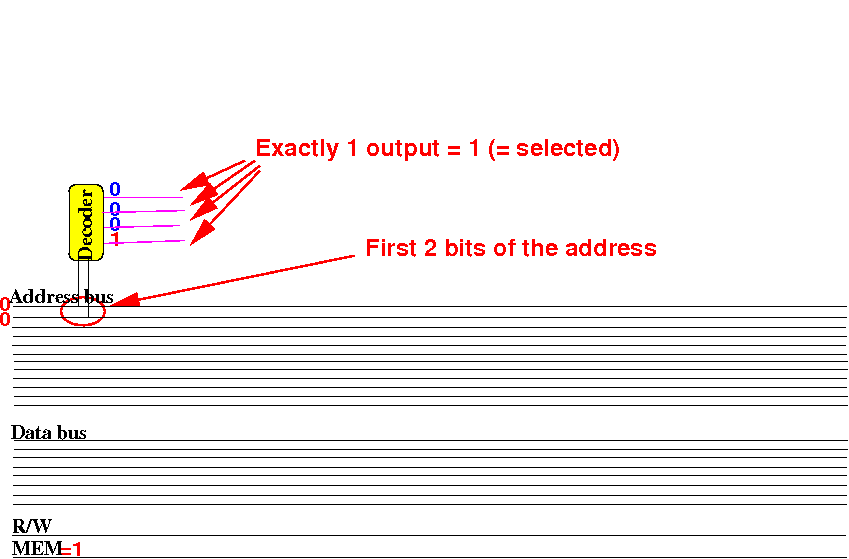
Increasing the
size
of a memory circuit
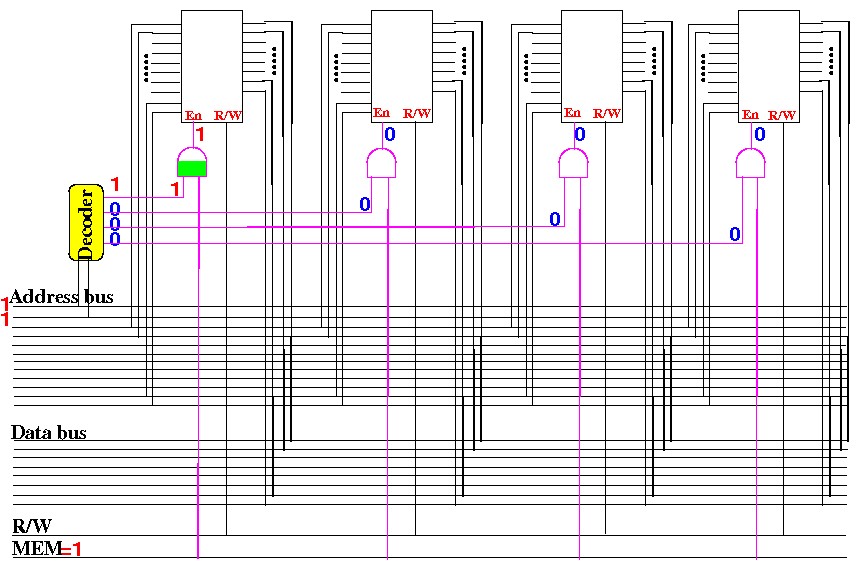
Activate
one of the 4 (four)
210×8 memory circuit
when
first 2 addr bits = 00:
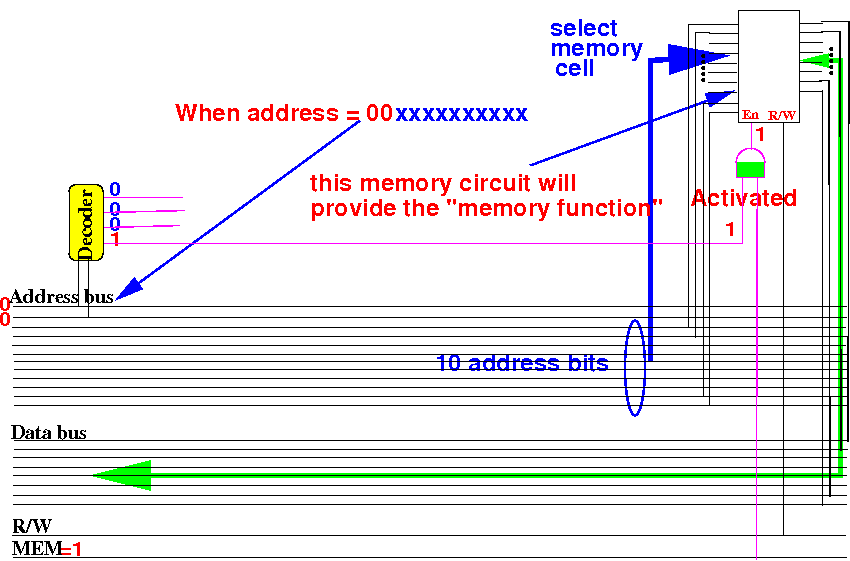
Increasing the
size
of a memory circuit
Activate
another of the 4 (four)
210×8 memory circuit
when
first 2 addr bits = 01:
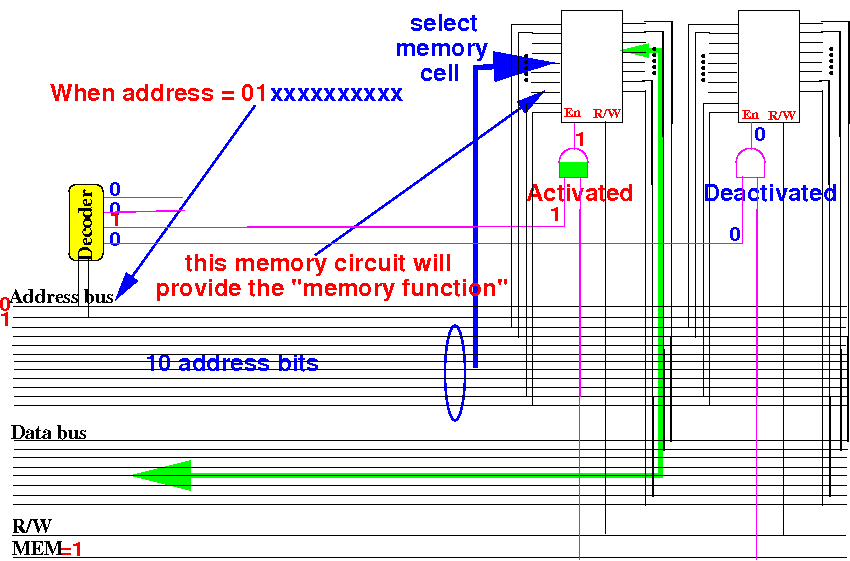
Increasing the
size
of a memory circuit
Activate
another of the 4 (four)
210×8 memory circuit
when
first 2 addr bits = 10:
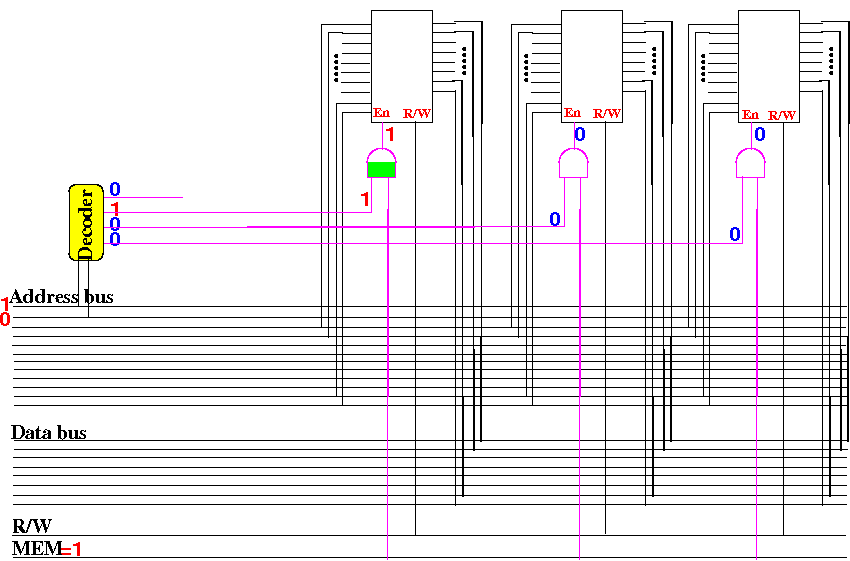
Increasing the
size
of a memory circuit
Activate
another of the 4 (four)
210×8 memory circuit
when
first 2 addr bits = 11:
Increasing the
size
of a memory circuit
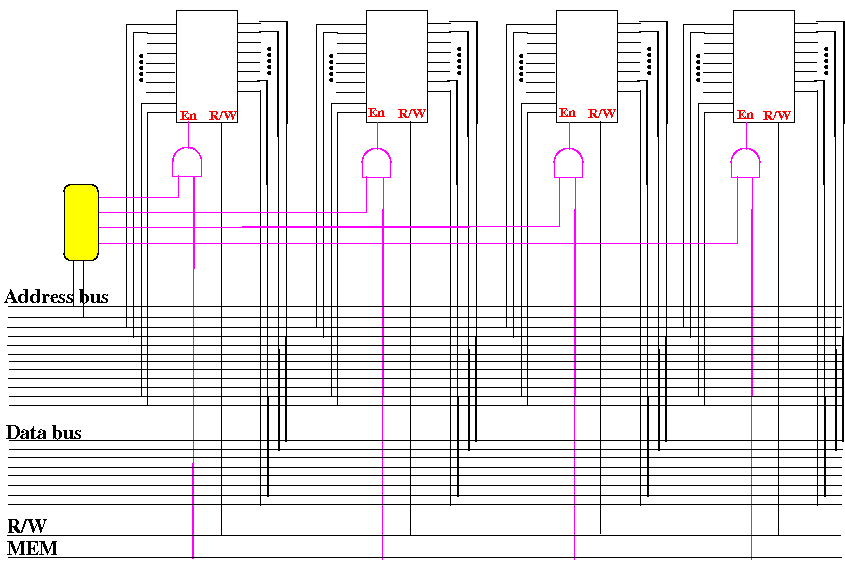
This is how to
increase the
size (= more rows) of
a memory circuit:
❮
❯





















