- Because a linked list is a sequential data structure,
when you want to
insert a new element
into a linked list,
you must
first:
FIND the location of insertion before you can insert the element.
- The
easiest way
to insert a new element into
a linked list is
insert at the start
That is because head points to the first element of the list...
So you do NOT need to find the insert location :-)
- Before you can
insert a list element (variable),
you must
create a list variable
- Recall what I said about
creating variables:
Creating variables is reserve some unused memory for storage - Unlike the number of variables in an array
which is
static in size,
the
the number of variables in a linked list
is
dynamic,
New list elements can be created (new memory reserved) and then linked into an existing list
- The
new operator in
C++ is used to
allocate memory space for new variables
- Syntax of the
new operator
new TYPE;
- Semantics of the new
operator:
- The new operator
operates on a type.
- The new operator
will reserves
an amount of memory space (i.e., "create one variable")
to store a
variable of the type type
- The new operator returns the (first) address of the reserved memory
NOTE: Don't be surprised that an operator returns an address.
In fact, you have seen such an operator before:
&(variable) returns the address of variable
NOTE: since new TYPE returns an address of type TYPE, we must store the return value in a variable of the reference type:
TYPE *ptr;
- The new operator
operates on a type.
- Example:
class ListElem { int value; ListElem *next; }; ListElem *p; // p will receive the address p = new ListElem; p->value = 1234; p->next = ...;
- We will start the
insertion
starting from
an empty list.
- Recall that the
empty list is always represented
as follows:

- The empty list was setup
using the following statement:
ListElem head = NULL;
- Algorithm to inserting new element at the start of list:
Assume: head = start of linked list (or NULL for empty list)
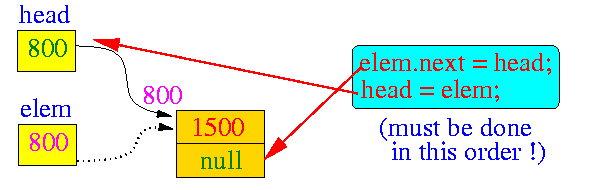
(1) Make a new list element: ListElem *elem; elem = new ListElem; (2) Fill the information portion of the list element: elem->value = 1500; (3) Link new element at start of list: elem.next = head; // Make new list element points // to the start of "old list" head = elem; // Make "head" points to // the **new** starting object
- The following diagrams show what the
insert algorithm
does
- This is the
initial situation
- the list is
empty

- The new
operation
creates a new list variable :
- The statement p->value = 1500 stores the value 1500 in the "value" field.
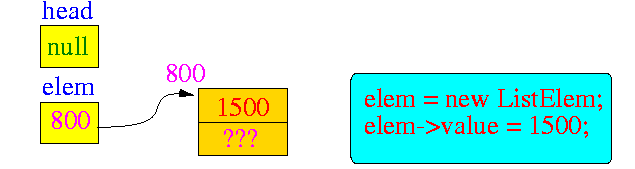
- Then the two linking statements
links the new list variable
before the first element
in the list:
- This is the
initial situation
- the list is
empty
- The following diagrams show what the
insert algorithm
does when it
insert another element
in the list:
- This is the
initial situation
- it is the list
after the first insertion
(redrawn a little):
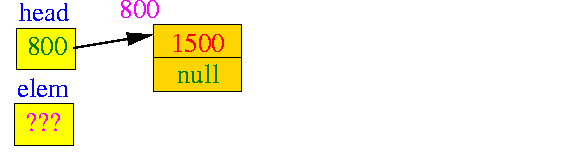
- The new
operation
creates another list variable :
- The new value is assigned by p->value = 1234
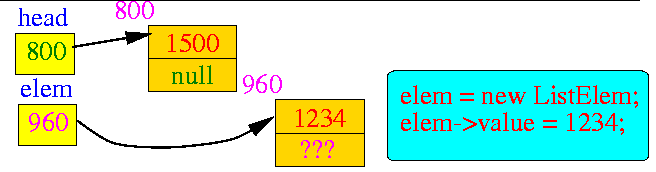
- Then the two linking statements
links the new list variable
before the first element
in the list:
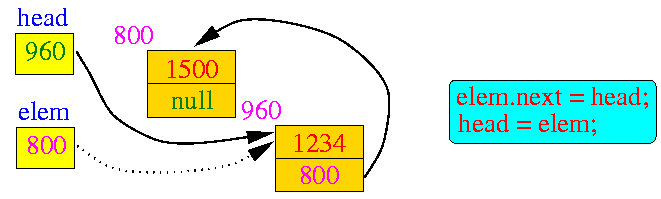
- This is the
initial situation
- it is the list
after the first insertion
(redrawn a little):
- If you
follow the links
starting at head ,
you will find:
- First list element = 1234
- Second list element = 1500
- End of list (NULL)
- The insert at head algorithm:
class ListElem { public: int value; // Integer ListElem *next; // Pointer used to make link }; int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { ListElem *head, *elem; // Empty list head = NULL; // Insert first element elem = new ListElem; elem->value = 1500; elem->next = head; head = elem; // Insert second element elem = new ListElem; elem->value = 1234; elem->next = head; head = elem; } - Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
- Recall that it is good software engineering practice
to
write a function
to
perform a well-defined task
Well, insert a new list element at head is a well-defined task
- Input parameters: What information
does the function need to do the job
- The start (head) of the list
- The new list element
NOTE: we assume that the value in the list element has already been initialized (that is NOT part of the insert algorithm !)
- Output parameters: What information
does the function return
- The start (head) the new list
NOTE: there are 2 ways to return the head value:
- Return the
new head
as the
function value
- Return the new head using a variable (that must be passed by-reference
- Algorithm:
class ListElem { public: int value; ListElem *next; }; ListElem * InsertAtHead(ListElem * head, ListElem * elem) { elem->next = head; // Make new list element points // to the start of "old list" return(elem); // Return the new head }
- How to use this function:
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { ListElem *head, *p; head = NULL; // Empty list p = new ListElem; p->value = 1500; head = InsertAtHead(head, p); // <--- record the new head in "head" }
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
- Algorithm:
class ListElem { public: int value; ListElem *next; }; // The "head" variable is BOTH input and output variable ! void InsertAtHead(ListElem * & head, ListElem * elem) { elem->next = head; // Make new list element points // to the start of "old list" head = elem; // Make link AND return NEW head value }NOTE: The head parameter MUST be passed by-reference
(Otherwise, the function CANNOT change the variable head in main's scope !!!)
- How to use this function:
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { ListElem *head, *p; head = NULL; // Empty list p = new ListElem; p->value = 1500; InsertAtHead(head, p); // <--- pass "head" by reference }
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here