- The specification of a
parameter variable
in a function definition
is actually a
variable declaration,
but without
using the
extern keyword
- Example:
double cube( double x ) { return( x * x * x ); }The parameter specification
double x
is actually a declaration.
It's somewhat like the construct:
extern double x
- We can tell that
a parameter specification is in fact a
declaration
by using an array
as parameter
- Recall that in a
declaration of an array variable,
the SIZE (dimension) can
be omitted
Example:
Array definition: int a[10]; // SIZE is required // in array definition Array declaration: extern int a[]; or: extern int a[10];
- Consider the following function that
sum the elements in an
array of 10 elements:
int sum( int a[10] ) { int s = 0; for ( i = 0; i < 10; i++ ) s = s + a[i]; }
int main() { int x[10]; int s; fill x with value; s = sum(x); }
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
- The program will work
without the
SIZE information in the array:
int sum( int a[] ) // No size info !!! { int s = 0; for ( i = 0; i < 10; i++ ) s = s + a[i]; }
int main() { int x[10]; int s; fill x with value; s = sum(x); }This is only allowed when the array variable (a) is declared !!!
- Now consider the parameters of the
C++'s main
function:
int main ( int argc, char * argv[] ) { ... } - The parameter specification
declares the following types
of parameters:
- argc:
int
Read the specification as:
extern int argc
- argv:
one-dimensional array of char *
Read the specification as:
extern char * argv[]
- argc:
int
- The array of char *
is used to point to a
sequence of strings:
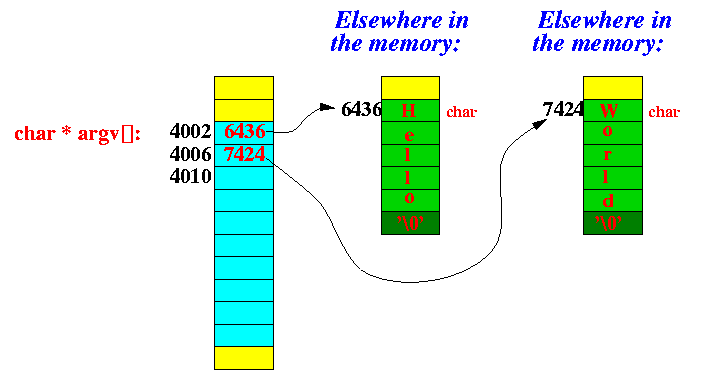
In the figure above, we see that:
argv[0] points to the string "Hello" argv[1] points to the string "World"
- It is quite easy to use argv[]
because Java's
main() function,
also uses an
String array as parameter.
- The only difference is that
Java's array has an
internal length
information, while
the length of argv[]
in C++ is given in the
first parameter of
main()
- Here is an example program that
prints all
the strings in
the array argv[]:
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int i; for ( i = 0; i < argc; i++ ) cout << "argv[" << i << "] = " << argv[i] << endl; }
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
- It is common to
provide integers or
double as
arguments to a program
-
In Java, you convert the
string command line arguments
using:
int Integer.parseInt( String s ); double Double.parseDouble( String s );Notice that these are class (static) methods.
-
In C++, you convert the
string command line arguments
using:
int atoi( char *s ); // ASCII to Integer double atof( char * s ); // ASCII to floatExample:
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int i; double sum = 0; for ( i = 1; i < argc; i++ ) sum = sum + atof( argv[i] ); cout << "sum = " << sum << endl; }
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here