- Objects in reality has
many different properties
Each property of the object is represented by one value (stored in a variable)
- Structured variables is
collection of variables
These variables collectively represent complete information on the entity
- Example:
A student has a name, address, phone number and major
Conceptually: "Student = (name, address, phone_number, major)"
Student John, Mary; // Define 2 students John.address // John's address Mary.address // John's address
- NOTE:
- This is the same concept of object in Java
- A structure or
structured types are defined in
C (and C++) as follows:
struct StructureName { type1 element1; type2 element2; type3 element3; ... };Example:
struct myStruct { int i; float f; };
- After defining the structure, you can define
variables of this
structure as follows:
struct myStruct x, A[3];
- NOTE:
- The struct construct
is a remmant of
C that is still supported by C++
(C++ is a superset of C)
- The use of struct
in C++ -
however -
has been superseded
by the class
- I only mention struct
for completeness sake.
We will only use class for the rest of the discussion
- The struct construct
is a remmant of
C that is still supported by C++
- A
more powerful structure construct
available in C++ is:
class
- Syntax to
define
a class structure
in C++ (NOT available in C):
class ClassName { [private:] [public:] [protected:] type1 var1; type2 var2; type3 var3; ... };Example:
class myClass { public: int a; // public float b; // public private: int a; // private float b; // private protected: int a; // protected float b; // protected } ; // ***** NOTE: ends in a semi-colon !!!
- NOTE:
- C++ takes a
"toggle"-approach
to denote
access specifiers
The keywords public, private and protected toggles the start of a section of variables
- In contrast, Java uses an
explicit enumeration approach.
Every variable must be explicitly denoted as public, private or protected
The Java approach is more verbose but will also result in less confusion (less error-prone)
- C++ takes a
"toggle"-approach
to denote
access specifiers
- The access specifiers
private,
public and
protected
have the
same meaning in
C++ and Java
- Meaning of the
access specifiers:
- public:
- Member variables with public access can be used in any part of the program
- private:
- Member variables with private access can only be used in a function (method) defined in the same class
- protected:
- Member variables with protected access can only be used in a function (method) defined in the same class or in a function (method) defined in a derived (child) class
- public:
- After defining the class structure, you can define
variables of this
class as follows:
ClassName variableName;
Example:
myClass x; // x is a myClass variable myClass a[10]; // array of 10 variables
- Recall that a
class variables in Java
contains an
address of a class object
The object itself (representation of the real entity) is created using the new operator
- In C++, the
definition:
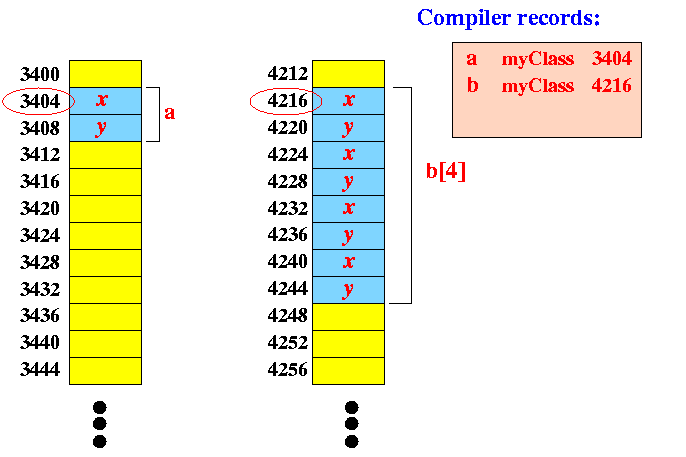
class myClass { int x; float y; }; myClass a; myClass b[4];will create the following:
- Notable difference between
C++ and Java
- A C++ class variable
contains all the member variables
in the class
- In other words: the object is stored in the C++ class variable ( not just an address as in Java )
- A C++ class variable
contains all the member variables
in the class
- The syntax to access
class variables in C++
is similar
to the one in Java
Because there are differences in how the data is stored, I will discuss the meaning of the various expression in some detail.
- Consider the following
class definition:
class myClass { public: int x; float y; };with the following variable definitions:
myClass a; myClass b[4];
- Suppose the variables are stored as follows:

- Individual member variables is
accessed in the same way as
Java:
a.x = 12; b[1].y = 34;
will result in:

- The reference operator &
can also be applied to
a class variable
Examples: (using the above figure)
&(a.x) returns 3404 &(a.y) returns 3408 &a returns 3404 &(b[0].x) returns 4216 &(b[0].y) returns 4220 &(b[2].x) returns 4232 &(b[0]) returns 4216 &b returns 4216
- We can also define
reference (pointer) variables
to a class type
Example:
myClass *p; // p contains an address of myClass variable
- We can store
the address of a
class variable
in a
reference variable to the class type
Example:
myClass a; myClass *p; p = &a; // p points to variable a
- The data structure created by the above
constructs (2 definitions and 1 assignment)
is given
graphically by:
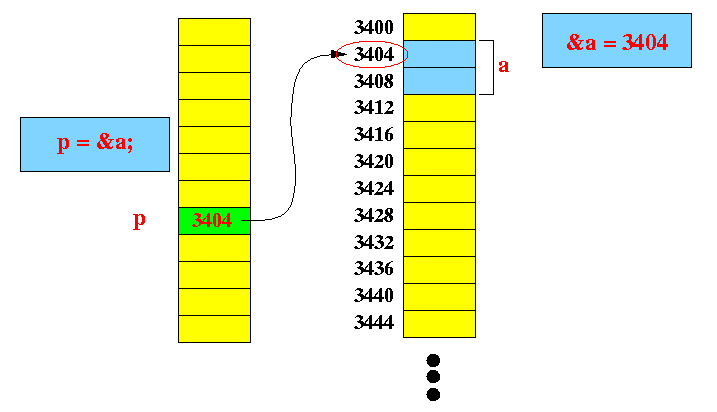
(It looks similar to an object variable pointing to ab object in Java.
It is indeed the same situation, except the "object" a was not created by a new operation - rather, it was allocated through a variable definition)
- The de-reference operator *
can also be applied to a
reference variable to a class type
Example:
myClass a; myClass *p; p = &a; // p points to variable a
The expression: *p is equivalent to a (when p points to a) Examples: (*p).x = 12; <==> a.x = 12; (*p).y = 34; <==> a.y = 34;
- The expression:
(*p).x
is a very commonly used expression in C++
(You will see it in linked lists)
- Because it is so
commonly used,
C++ has a short-hand for this
expression that look kinda "sexy":
p -> x <==> (*p).x
You must write -> without any spaces between these 2 characters !
Example program:
class myClass // How to define a "class" type { // This is NOT a variable definition public: int x; // It serves to tell C++ what "myClass" looks like float y; };
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { myClass a; // How to define class variables myClass b[4]; // How to define arrays of class variables myClass *p; // p can point to a myClass variable a.x = 1234; // How to use a struct variable a.y = 3.14; p = &b[2]; // p points to b[2] (*p).x = 12; // b[2].x = 12 p->y = 34; // b[2].y = 34 cout << "a = " << a.x << " " << a.y << endl; cout << "b[2] = " << b[2].x << " " << b[2].y << endl; }
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
- When a class variable is
defined elsewhere
(in another program file), and it is used
in the present file, then
the variable must be
declared.
- The syntax to
declare a
class variable is unchanged
(from that of declaring built-in types):
extern className varName; - Example:
myClass x; // Definition of the class variable x
extern myClass x; // Declaration