- The syntax to define
an one-dimensional array in C++
is:
TYPE arrayName[ constantSize ];
Example:
int a[100]; // array of 100 integers double b[10]; // array of 10 doubles
Compare the difference with Java:
int[] a = new int[100]; // array of 100 integers double[] b = new double[10]; // array of 10 doubles
- The internal storage
of arrays in C++
is also different from Java
- An array in C++ is
stored directly:
int a[10]; Storage structure in C++: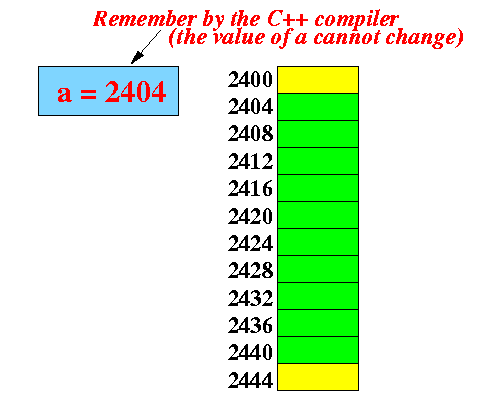
- When an array is defined,
the C++ compiler will
allocate space to store the
array and then
record the following
information in the array:
- The name of the array
(a)
- The type of the array
(int)
- The address of the first element of the array (2404 in the example)
Furthermore:
- The address of the first element
of the array
cannot be changed
(This address is recorded by the C++ compiler and it is fixed after the array is defined)
- In other words: arrays in C++ are static (location is fixed after its creation)
- The name of the array
(a)
- Compare the difference with
Java:
An array in Java is stored indirectly:
int[] a; // defines variable a a = new int [10]; // record location of array in a Storage structure in Java: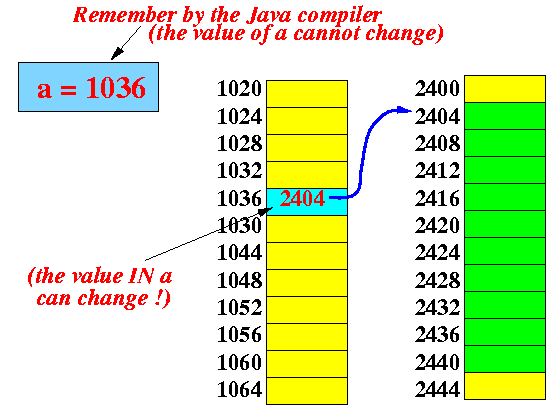
- The syntax to access
individual array elements in
C++ is the same as Java
Example:
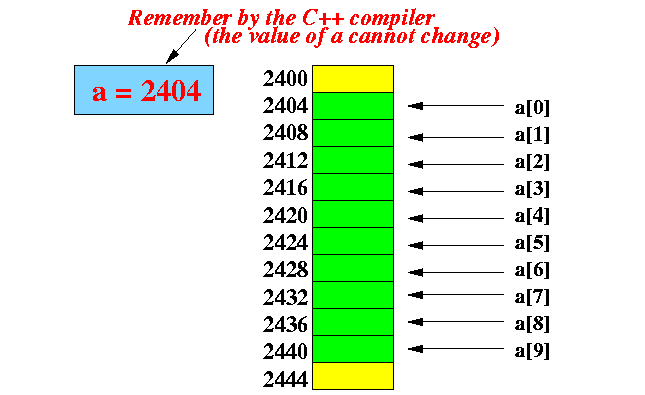
Example: Find smallest element in an array
int a[10]; int min, i; min = a[0]; for ( i = 0; i < 10; i++ ) { if ( a[i] < min ) min = a[i]; } cout << "min = " << min << endl;
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
- Important difference in array between C++ and Java:
- C++ does not
perform
run time array bound checks
(While Java does perform run time array bound checks)
- C++ does not
perform
run time array bound checks
- C++ is designed for speed
When you access an array element a[i], the index i may be out of bound
Java inserts code in the program to perform runtime array bound checks and an out of bound array index will cause a run time error
- run time array bound checks will slow down a program !!!
C++ does not perform runtime array bound checks !!!
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- a C++ Prog file with index out of bound error: click here
- a Java Prog file with index out of bound error: click here
- Again, you must be more responsible when programming with C++