- Parameter variables
are variables defined in the parameter list of a function:
Example: float RectangleRule(float f(float), float a, float b, int N) { ... } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { ... } - Purpose of Parameter Variables:
- To receive (important) values from
outside the
method
- More technically:
Parameters is a mechanism to pass a value out of a scope into another scope !!!
Schematically:
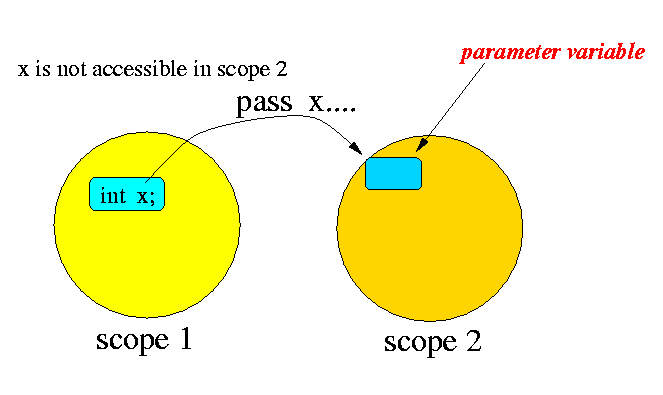
A concrete example:
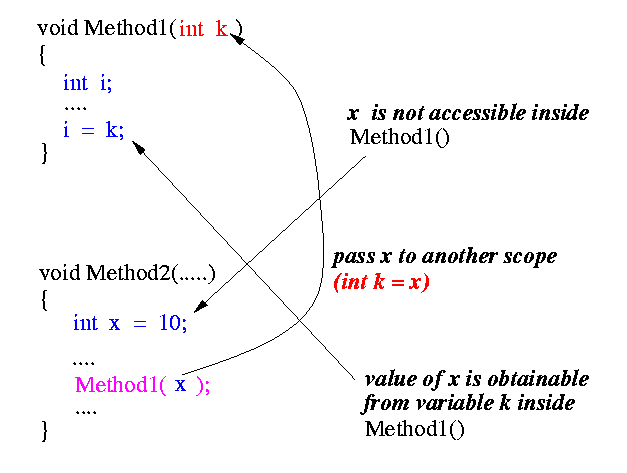
- To receive (important) values from
outside the
method
- Formal and actual parameters are matched according
to their position in the function definition and
function invocation.
- "Function invocation" = function call, or the use of the function.
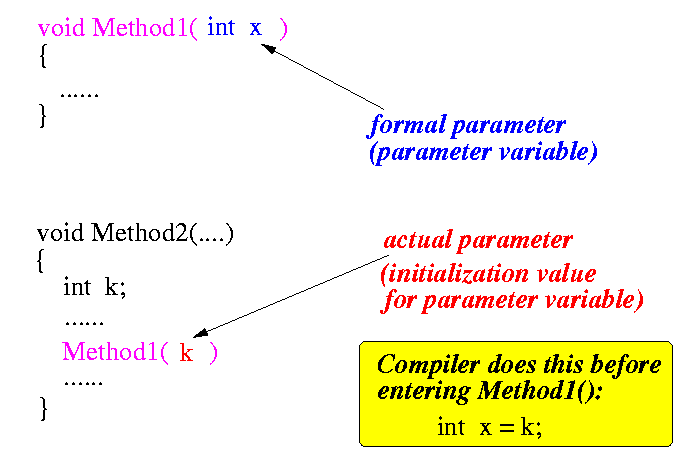
|
- Lifetime of a parameter variable:
- Start at the beginning of the method
- Ends at the end of the method
- Scope of a parameter variable:
- Start at the beginning of the method
- Ends at the end of the method
- In C, C++: except in an inner scope that has a variable with the same name (shadowing)
- In Java:: Java does NOT allow you to shadow parameter variables. So its scope and lifetime are the same in Java
- CONCLUSION:
Parameter variables behaves the same way as local variables defined at the beginning of a method
- The only difference between
parameter variables
and local variables
that the moment of creation:
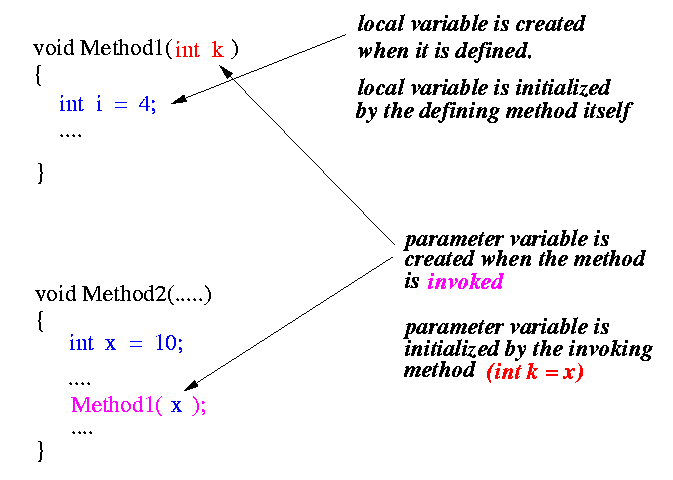
- Parameter varaibles are actually
created at the moment of
function invocation.
After creating the parameter variables, the function invocation immediately initialize the parameter variables with the values of the "actual parameters" in the invocation.
- Local variables are created after the moment of function invocation....
- Parameter varaibles are actually
created at the moment of
function invocation.
- NOTE:
Although the parameter variable k in the example was created and initialized when Method2() invokes Method1(), the function Method1() CANNOT access the variable k because (no opportunity):
- The program execution leaves Method1() and
continues in Method2(): so Method1()
has NO opportunity to access k after
it invokes Method2()
- The variable k is destroyed at the end of Method2(), before returning back to Method1(): so Method1() again has NO opportunity to access k when the invocation of Method2() finishes
- The program execution leaves Method1() and
continues in Method2(): so Method1()
has NO opportunity to access k after
it invokes Method2()