- Built-in types
provided by C/C++ allow the programmer to define
variables to store very simple values
- Most computer applications (even numerical programs)
will use an array of different kinds of values.
- Although the programmer can define multiple variables to
store the various values, managing
the different values stored in a large number of variables
can be more complicated that it ought to be....
- Every modern programming languages allow the programmer to define
structured variables
that enable the programmer to all the different kinds of value
in one place
- Some modern programming languages
(e.g., Java)
will even allow the programmer to define
functions
that will ONLY operate on
the prescribed type of variables
(object oriented programming languages)
- A few programming languages (e.g., C++, Algol68) go all the way and allow the programmer to define operators that will ONLY operate on the prescribed type of variables
- An array is probably the most simplest kind of structured
variables...
- An array consists of N variables of the same type
- Syntax to define an one-dimensional
array variable:
TYPE array_var_name[SIZE]; // Uninitialized TYPE array_var_name[SIZE] = {value1, value2, ...}; // Initialized TYPE array_var_name[] = {value1, value2, ...}; // Initialized with size of // array determined by number // of items in initialization - NOTE:
- Array indices in C/C++ always start at
0
So the indices of an array of size N are 0..N-1
- A common way to run down every element of an array in C/C++ is:
int i; for (i = 0; i < N; i = i + 1) { A[i]... }
- Array indices in C/C++ always start at
0
- Example Program:
(Demo effect of various array definitions) ---
click here

Multi-dimensional arrays (matrices)
- Multidimensional arrays can be described as arrays of arrays.
For example, a two dimensional array can be imagined as a Two dimensional table of a certain data type:
jimmy is an two dimensional array of 3x5 values of type int.
The way to declare this array is:
int jimmy [3][5];
- Each individual element in the array can be referenced
using a multi-dimensional bracket index notation
- Remember that array indices in C/C++ always start with 0 (ZERO)
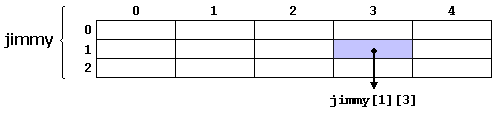
- For example, to reference the
second element vertically
and fourth horizontally is:
-
jimmy[1][3]:
- Higher dimensional arrays are defined in a similar manner;
- Example: a 3 dimensional array
int A[10][5][20];
- The main thing that you have to be aware of is that
array variables can take up a large amount
of computer memory
- Sometimes, due to memory restrictions, your program with
a very large array will compile, but will not run
(it will not run at all or it will not finish in a reasonable
amount of time).
- Programs with large arrays may run slower because a computer
technique known as virtual memory.
- The virtual memory increase the available main memory of the computer through the use of (much slower) disk memory space.
- The computer memory uses linear addresses
- A multi-dimensional array needs to be
linearized to be stored in memory
- There are 2 ways to linearize an array:
- row major:
store elements of the last index in consecutive
memory
A[0][0] A[0][1] A[0][2] A[0][3] A[0][4] A[1][0] A[1][1] A[1][2] A[1][3] A[1][4] A[2][0] A[2][1] A[2][2] A[2][3] A[2][4] stored as:
A[0][0] A[0][1] A[0][2] A[0][3] A[0][4] A[1][0] A[1][1] ... A[2][3] A[2][4] - column major:
store elements of the first index in consecutive
memory
A[0][0] A[0][1] A[0][2] A[0][3] A[0][4] A[1][0] A[1][1] A[1][2] A[1][3] A[1][4] A[2][0] A[2][1] A[2][2] A[2][3] A[2][4] stored as:
A[0][0] A[1][0] A[2][0] A[0][1] A[1][1] A[2][1] A[0][2] ... A[1][4] A[2][4]
- row major:
store elements of the last index in consecutive
memory
- Arrays in C, C++ and Java are stored
in row major manner
- Arrays in Fortran are stored
in column major manner
- This detail will be very important when you mix functions that are written in different programming languages!!!
- Multidimensional arrays are nothing more than an
mapping, since we can obtain
the
same results
with a one-dimensional array
by manipulating its indices.
- For example: defining a multi-dimensional array
int jimmy[3][5];
is equivalenet to: int jimmy[3*5];
jimmy[i][j]
is equivalenet to: jimmy[i*5+j]
- Example Program:
(Demo how to linearize arrays in C++) ---
click here

- In C++, is not possible to pass
by value
a complete block of memory as a parameter to a function,
- The main reason that C++ prehibits the programmer to
pass an entire array by value is
efficiency:
it takes a long time to copy over so many values, and it takes
a lot of memory to store so many array values (at the called
function)
- Array in C++ must be passed
by REFERENCE
It may sound strange that you can pass an entire array by reference...
But due to the fact that arrays are stored in row major manner, if we know:
- The location of the FIRST element of the array
- The dimension of the array
Then we can find the location of any element of that array.
- The location of the FIRST element of the array
- Example:
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { void Print(float [][4]); // How to declare function // with ARRAY parameter // NOTE: parameter and the // first dimension is NOT // required // You MAY write: // void Print(float X[3][4]); float A[3][4]; int i, j, k; k = 1; for (i = 0; i < 3; i = i + 1) for (j = 0; j < 4; j = j + 1) { A[i][j] = k; k = k + 1; } Print(A); // How to pass ARRAY parameter } void Print(float H[3][4]) // How to define function // with array parameter // NOTE: first dimension is IGNORED // by the compiler... { int i, j, k; for (i = 0; i < 3; i = i + 1) { for (j = 0; j < 4; j = j + 1) cout << H[i][j] << "\t"; cout << "\n"; } } - NOTE:
- The shape of the array is actually determined by the
last N-1 indices...
- The first dimension of the array tells us
how many slices of that shape there are in the array
- Example 1: a 3x4 array consists of 3 "slices" of 4
elements (in a row)
- Example 2: a 3x4x5 array consists of 3
"slices" of 4x5 elements (in a plane), and so on...
- The C++ compiler really does not care how many slides
the array consists of; it only care about the shape of each slice...
- Hence: the first dimension is NOT REQUIRED in the function declaration !!
- The shape of the array is actually determined by the
last N-1 indices...
- Example Program:
(Demo passing array as parameter) ---
click here
