|
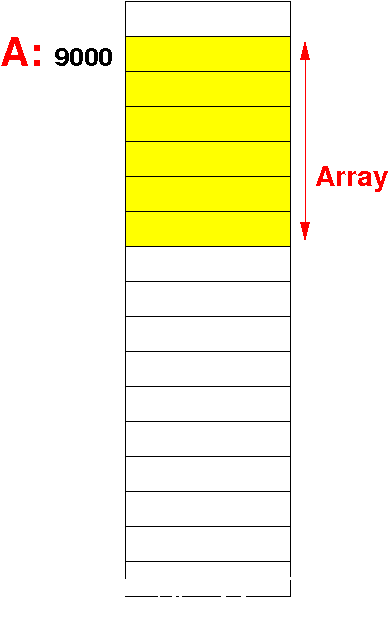
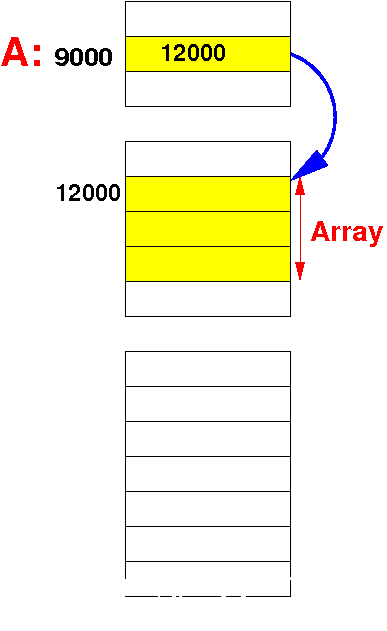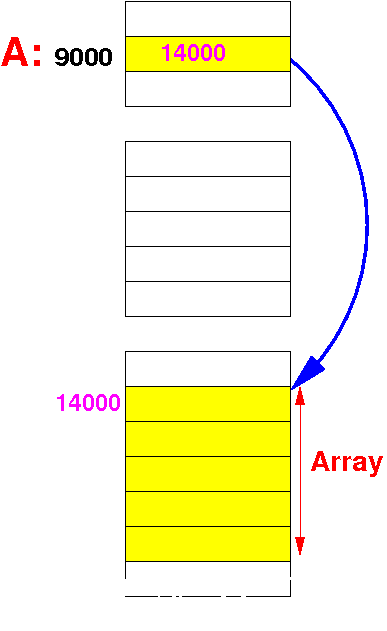
| Static array (C) | Dynamic array (Java) |
|---|---|
|
|
| The base address of a static array is a constant number (i.e.: a label) | The base address of a dynamic array is stored in a variable |
|
Example:
#include <stdio.h>
int main( int argc, char *argv[] )
{
int A[10], i;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++ )
A[i] = i*i; // Assign a value to A[i]
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++ )
printf("%d\n", A[i]); // Using the value in A[i]
}
|
|
Example:
#include <stdio.h>
int main( int argc, char *argv[] )
{
int A[10], i;
for (i = 0; i < 10; i++ )
A[i] = i*i; // Assign a value to A[i]
for (i = 0; i < 20 ; i++ ) // index out of bound !!
printf("%d\n", A[i]); // Using the value in A[i]
}
|
How to specific an array parameter in a function:
#include <stdio.h> int sumArray( int A[], int n /*array length*/ ) { int i, s; s = 0; for (i = 0; i < n; i++) s += A[i]; return(s); } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int B[10] = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9}; // B[5 - 9] are init to 0 int r; r = sumArray(B, 10); // Pass array B as parameter printf("r = %d\n", r); } |
Note: we must pass the array length as an additional parameter to a function in C (because the array data type in C does not contain the array length !!)
Program that shows that array variables are "passed-by-reference":
#include <stdio.h> void clearArrayElem( int A[], int i) { A[i] = 0; // Update one array elem... } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int B[10] = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9, 11, 13, 15, 17, 19}; int k; for ( k = 0; k < 10; k++ ) printf("%d ", B[k]); printf("\n\n"); clearArrayElem(B, 5); // B[5] changed to 0 ! for ( k = 0; k < 10; k++ ) printf("%d ", B[k]); printf("\n\n"); } |
Actually, C passes the address of the array B by-value....
Situation where we need to declare a function:
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int B[10] = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9};
int r;
r = sumArray(B, 10); // Use function before it was defined
printf("r = %d\n", r);
}
int sumArray( int A[], int n /*array length*/ )
{
int i, s;
s = 0;
for (i = 0; i < n; i++)
s += A[i];
return(s);
}
|
How to declare a function with array as parameter (the easiest way):
#include <stdio.h> int sumArray( int A[], int n); // Declaration int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int B[10] = {1, 3, 5, 7, 9}; int r; r = sumArray(B, 10); //Compiler now has the data type info printf("r = %d\n", r); } int sumArray( int A[], int n /*array length*/ ) { int i, s; s = 0; for (i = 0; i < n; i++) s += A[i]; return(s); } |
|
|
Example:
#include <stdio.h>
int main( int argc, char *argv[] )
{
int A[4][3], i, j;
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++ )
for (j = 0; j < 3; j++ )
A[i][j] = i*j; // Assign a value to A[i][j]
for (i = 0; i < 4; i++ )
{ for (j = 0; j < 3; j++ )
printf("%d ", A[i][j]);
printf("\n");
}
}
|
How to specific a 2-dimensional array parameter in a function:
int sumArray( int A[][3], int m, int n) { // Explained in next slide int i, j, s; s = 0; for (i = 0; i < m; i++) for (j = 0; j < n; j++) s += A[i][j]; return(s); } int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int B[4][3] = {{1,3,5}, {1,1,1}, {2,1,2}, {3,2,4}}; int r; r = sumArray(B, 4, 3); // Pass 2 dim array B as param printf("r = %d\n", r); } |
Note: we must pass the array dimensions (4,3) as additional parameters to functions in C !
C stores a 2-dimensional array row-wise in memory:
int A[4][3]: Memory: +---------+---------+---------+ +---------+ | A[0][0] | A[0][1] | A[0][2] | A: | A[0][0] | (4 bytes) +---------+---------+---------+ +---------+ | A[1][0] | A[1][1] | A[1][2] | | A[0][1] | (4 bytes) +---------+---------+---------+ +---------+ | A[2][0] | A[2][1] | A[2][2] | | A[0][2] | (4 bytes) +---------+---------+---------+ +---------+ | A[3][0] | A[3][1] | A[3][2] | | A[1][0] | (4 bytes) +---------+---------+---------+ +---------+ | A[1][1] | (4 bytes) +---------+ | A[1][2] | (4 bytes) +---------+ ... Offset of A[1][0] = (3×1 + 0) × 4 = 3 × 4 Offset of A[1][2] = (3×1 + 2) × 4 = 5 × 4 |
The # columns is necessary to compute the offset of A[i][j] = (#cols × i + j) × sizeof(oneArrayElem)
Situation where we need to declare a function:
#include <stdio.h>
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int B[4][3] = {{1,3,5}, {1,1,1}, {2,1,2}, {3,2,4}};
int r;
r = sumArray(B, 4, 3); // Used function before def
printf("r = %d\n", r);
}
int sumArray( int A[][3], int m, int n)
{
int i, j, s;
s = 0;
for (i = 0; i < m; i++)
for (j = 0; j < n; j++)
s += A[i][j];
return(s);
}
|
How to declare a function with 2-dimensional array as parameter (the easiest way):
#include <stdio.h> int sumArray( int A[][3], int m, int n); // Declaration int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int B[4][3] = {{1,3,5}, {1,1,1}, {2,1,2}, {3,2,4}}; int r; r = sumArray(B, 4, 3); // Used function after declare printf("r = %d\n", r); } int sumArray( int A[][3], int m, int n) { int i, j, s; s = 0; for (i = 0; i < m; i++) for (j = 0; j < n; j++) s += A[i][j]; return(s); } |