How
is an array
stored in
memory
This material is
mostly for
review -- so I'll go over them
quickly
The array elements of an
array are
stored
contiguously
in memory
without
gaps:

Because:
- When the first
array element
meets the
alignment requirement,
all
subsequent
element will
also
meet it
|
How to
store a byte typed array
A byte (typed) array
uses 1 byte to store
each of its array element
How a
byte typed array is
stored
in memory:

Remember:
There are no gaps between
array elements !
How to
store
a short typed array
A short (typed) array
uses 2 bytes to store
each of its array element
How a
short typed array is
stored
in memory:

Remember:
There are no gaps between
array elements !
How to
store
a int typed array
A int (typed) array
uses 4 bytes to store
each of its array element
How an
int typed array is
stored
in memory:

Remember:
There are no gaps between
array elements !
Array used in
CS255 ARM assembler programming
- Recall that
there are 2 types of
arrays:
|
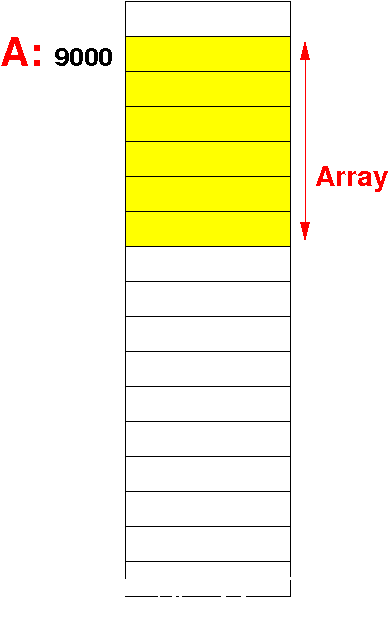
Static
array
(C)
|
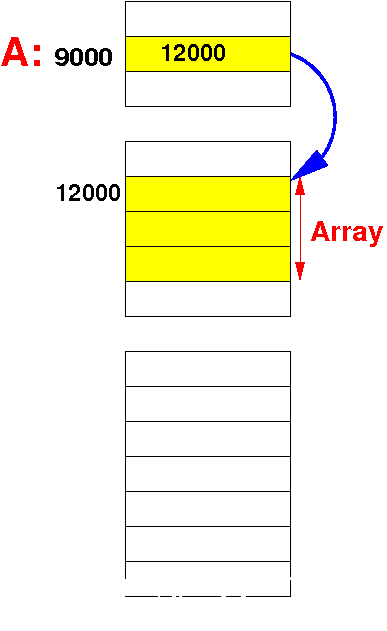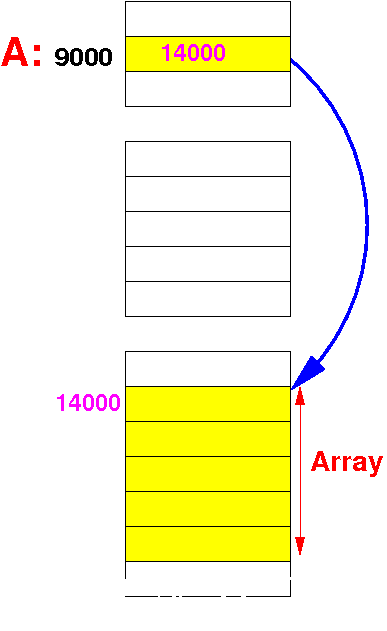
Dynamic
array
(Java)
|
|
|
|
The array variable (A)
is a
(symbolic) constant for the
location (= address) of
the array
|
The array variable (A)
is a
reference variable that
contains the
base address of the array
|
|
Array used in
CS255 ARM assembler programming
- We will use
static arrays
in ARM assembler programming
(just like
C):
-
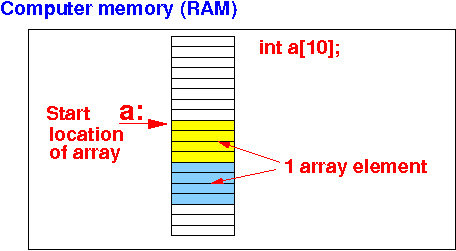
Base address:
-
Base address of
an array = the
start location of the
array
|
- The base address of
the (static) array will
be
marked
by a label
(= symbolic
constant)
that
cannot
be change
(= "static")
|
❮
❯






