The EGTAPI tool requires the assembler program to provide 5 location markers (= labels) to location the necessary information:
|
The main: label is already part of an assembler program
We must add the other 4 labels to an assembler program to make it run with EGTAPI.
.global main .global Stop, CodeEnd, DataStart, DataEnd .text main: // marks the start point of the program push {lr} // Save the return address on the stack push {fp} // Save the return address on the stack // Explained later in CS255 movw r0, #:lower16:HelloStr movt r0, #:upper16:HelloStr bl printf pop {fp} // Pop the frame pointer pop {pc} // Pop the return address // Explained later in CS255 Stop: // marks the stop point of the program CodeEnd: // mark the end of the code (= instructions) nop .data DataStart: // marks the start of the data HelloStr: // Label marking this location in memory .asciz "Hello World\n" // ASCII codes for the string DataEnd: // marks the end of the data .end |
DEMO: /home/cs255/cs255/hello/hello-egtapi.s on cs255host1
LabMachine>> /home/cs255001/bin/egtapi 1. Login in as: cs255001 or use your own NetID) 2. Select host "cs255host1" at the end of machine list 3. Login: cs255, pw: abc123 4. File Browser, go to "hello" directory 5. Select hello-egtapi.arm and click COMPILE |
Note: do not use cs255host1 to run your ARM assembler projects
For CS255 Assembler projects: use some lab machine (e.g.: lab1a)
Content of the memory:
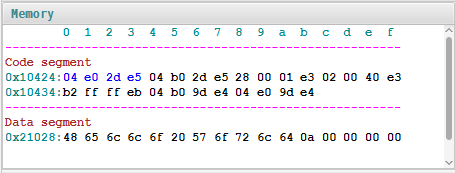
|
This is how the "Hello" program is stored in memory:
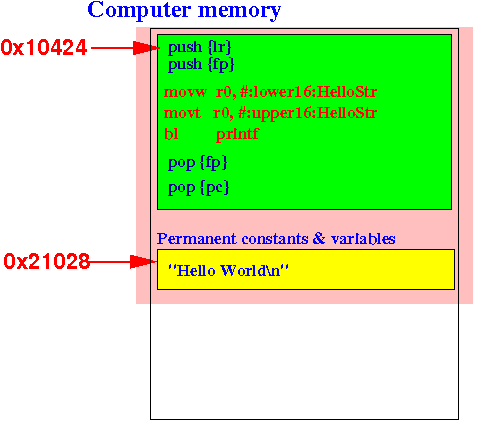
Can you see the string "Hello World\n" in the Data segment:

Can you see the string "Hello World\n" in the Data segment:

48 hex = ASCII code for 'H' 65 hex = ASCII code for 'e' 6c hex = ASCII code for 'l' 6c hex = ASCII code for 'l' 6f hex = ASCII code for 'o' 20 hex = ASCII code for ' ' (space) 57 hex = ASCII code for 'W' 6f hex = ASCII code for 'o' 72 hex = ASCII code for 'r' 6c hex = ASCII code for 'l' 64 hex = ASCII code for 'd' 0a hex = ASCII code for '\n' (newline) |