Representing unsigned (integer) values inside the computer
- Computers
use the
binary number system
to represent (= store)
unsigned (integer = whole) numbers.
- The binary number system
is similar to the
decimal number system that
you have
learned in
high school
|
The binary number system (repeat + summary)
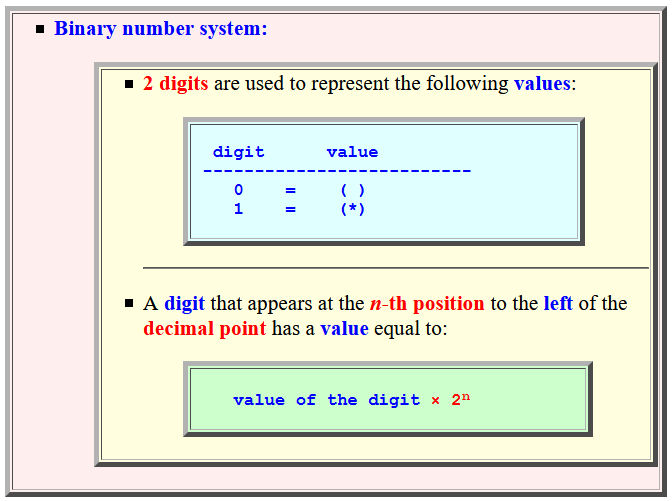
The binary number system:
Storing integer (whole) values inside a computer program
Storing
integer (whole) values:
- Computer memory was
a scarce resource
(used to be very expensive !)
- Traditionally,
programming language provided
integer representations of
different lengths
for different needs
-
Shorter representations to
minimize
storage requirements
-
Longer representations to
maximize
accuracy requirements
|
Storing integer (whole) values inside a computer program
Program data types to
represent (store)
integer (whole) values:
- byte:
uses 1 byte of memory
- short:
uses 2 bytes of memory
- int:
uses 4 bytes of memory
- long:
uses 8 bytes of memory
|
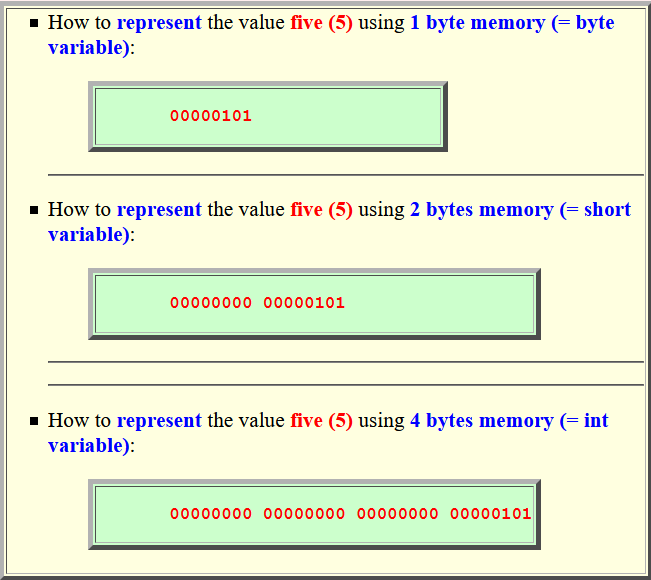
Storing integer (whole) values inside a computer program
How to store (= represent)
the value 5 in
different data types:
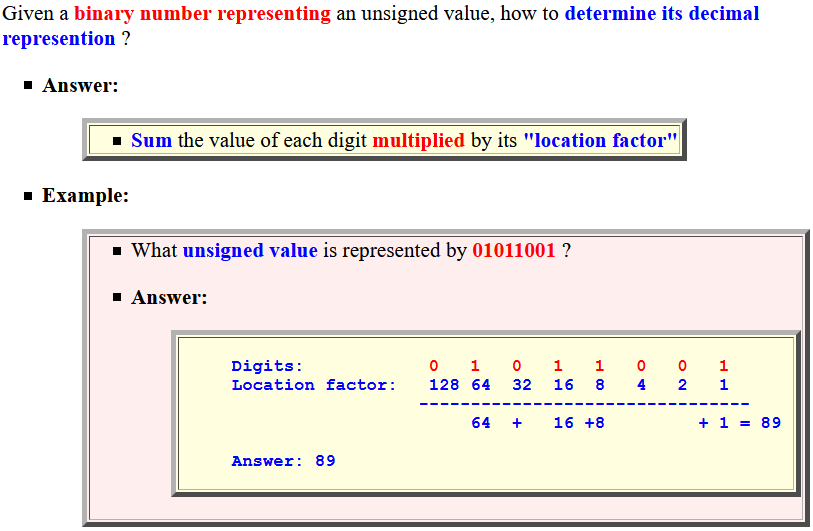
Interpreting binary numbers

Converting from binary ⇒ decimal
representation
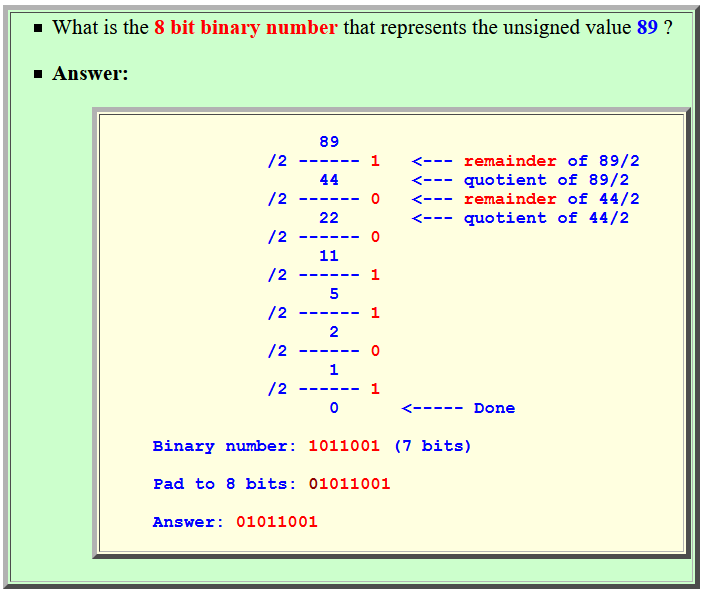
Converting from decimal ⇒ binary
representation

Example:
•
Find the 8 bits binary representation
for the
decimal representation
89
(I'll work it out in class)
Converting from decimal ⇒ binary
representation
Solution:
Quiz 1 - Applying what you have learned

Quiz 1 - Applying what you have learned

Answer:
9 decimal ⇒ 1001 binary
Stored in 1 byte: 00001001
Therefore, x contains: 00001001
|
Quiz 2 - Applying what you have learned

Quiz 2 - Applying what you have learned

Answer:
9 decimal ⇒ 1001 binary
Stored in 4 bytes: 00000000 00000000 00000000 0001001
Therefore, x contains: 00000000000000000000000000001001
|
A "binary number" joke...

❮
❯










