At the start of the course, we have studied the computer memory:
|
We will now study the other component of the computer system: the Central Processing Unit
Recall:
|
In order to perform these functions, the CPU contains circuitry (= discussed in CS355) that enable the CPU to perform its function
In CS255, we will only study the logical structure of the CPU (i.e.: discuss the CPU abstractly)
Logically, the CPU consists of these functional components:
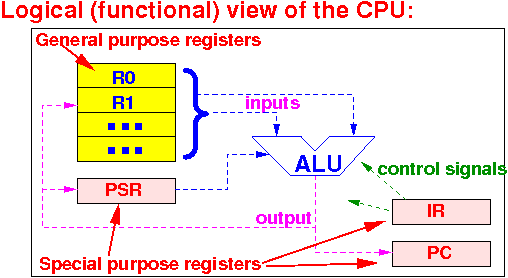
(1) A number of
general purpose registers
(2) A number of
special purpose registers (IR, PC, PSR)
(3) An
Arithmetic and logic unit
(4)
Wires that
interconnect the
various components
What are registers:
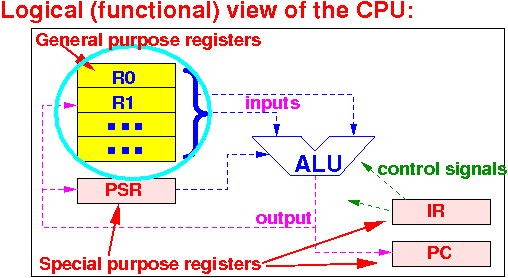
A register is a memory device on the CPU that can store a binary number (typically 32/64 bits long)
What are general purpose registers:
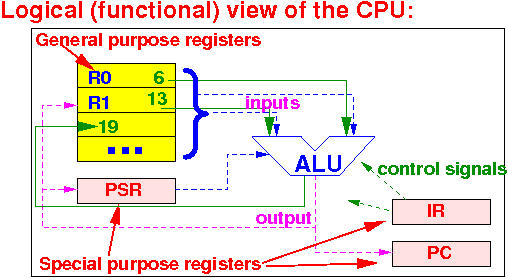
General purpuse registers are used to store:
|
Comment: I used decimal numbers in the figure - they are actually binary numbers
And you know how to convert a decimal number into a binary number...
What is the Arithmetic and Logic Unit (ALU):
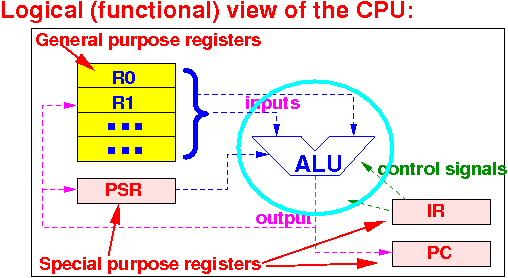
The ALU contains digital circuitry that can perform:
|
DEMO:
/home/cs255001/demo/355/add-circuit
DEMO:
/home/cs255001/demo/355/multiply-circuit
How does the Arithmetic and Logic Unit know what operation that it needs to perform ???
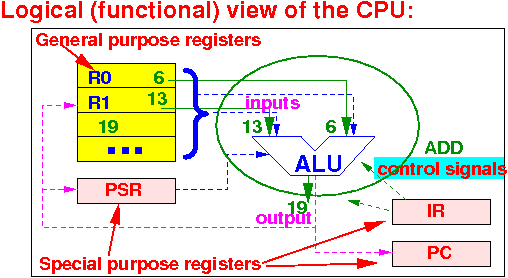
The operation performed by the ALU is determined by:
|
In
CS355, we will build a
simple ALU circuit
using a digital simulator
DEMO:
/home/cs255001/demo/355/ALU-circuit
What are special purpose registers:
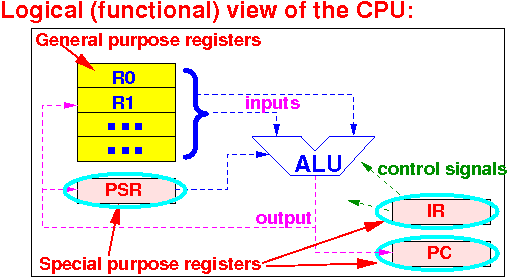
Special purpuse registers are:
|
I.e.: the (binary) number in a special purpose register has a pre-assigned meaning !
What is the Program Counter (PC) special purpose register used for:
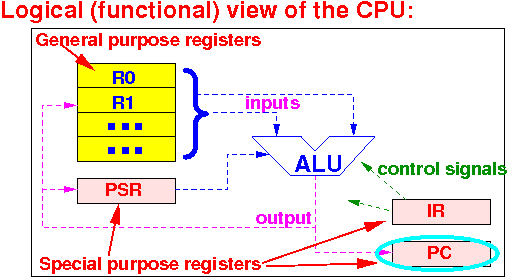
The program counter (PC) contains:
|
Recall that all instructions are stored in the memory !!
How is the program counter (PC) used:
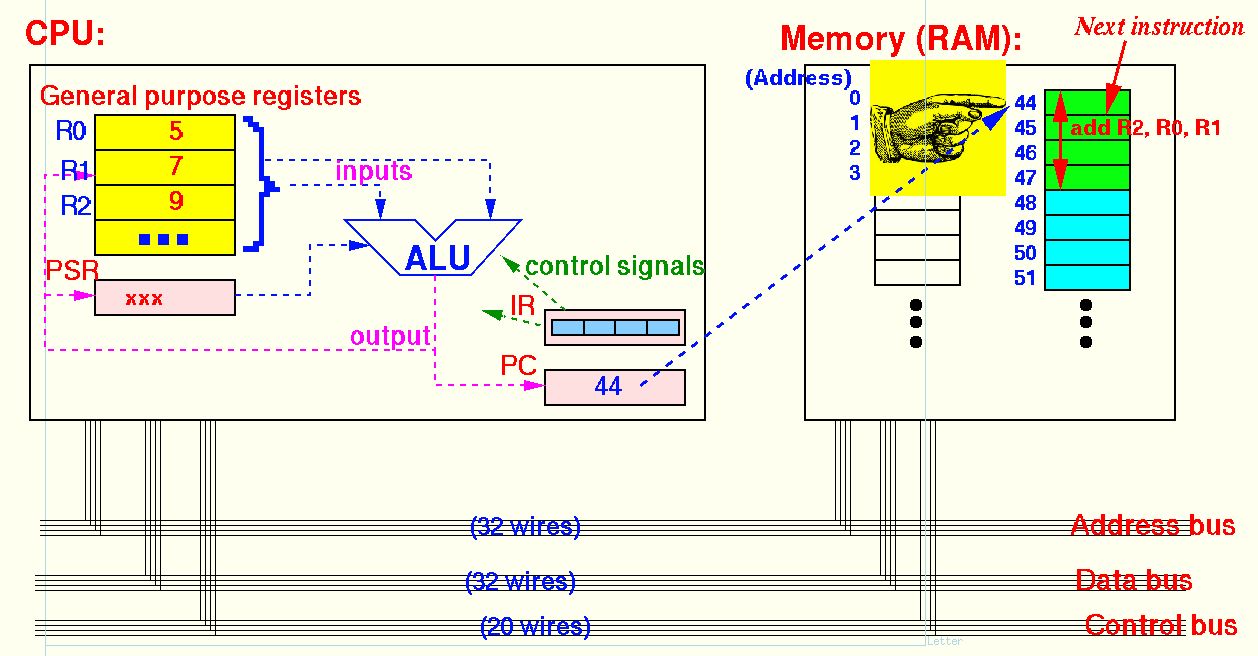
The program pointer (PC) is pointing at the memory location where the CPU can obtain the next (computer) instruction !!!
What is the Instruction Register (IR) special purpose register used for:
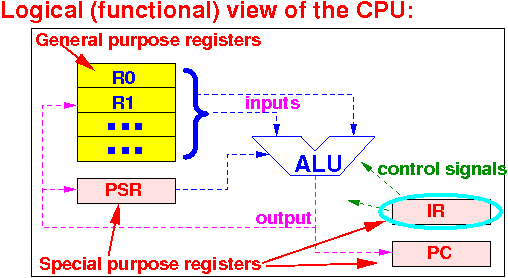
The Instruction Register (IR) contains:
|
Note: the IR is "empty" when the CPU has finished executing an instruction and has not yet fetched the next one
How is the Instruction Register (IR) used:
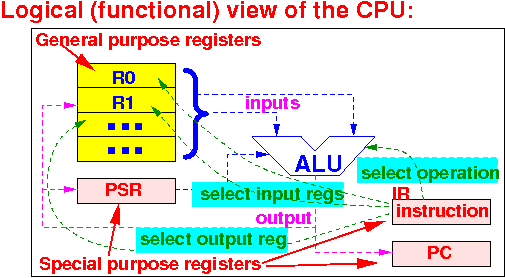
The Binary number in the Instruction register is used to:
|
For more datails: take CS355...
What is the Processor Status Register (PSR) special purpose register:
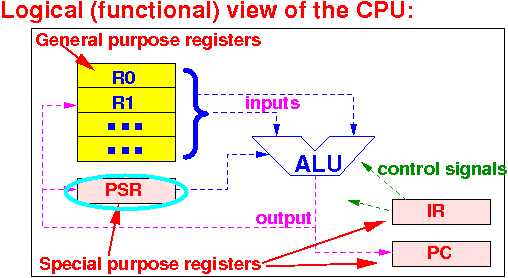
The Processor Status Register (PSR) contains:
|
Some of these status code bits contains the status information on the outcome of a machine instruction
How is the Processor Status Register (PSR) used:
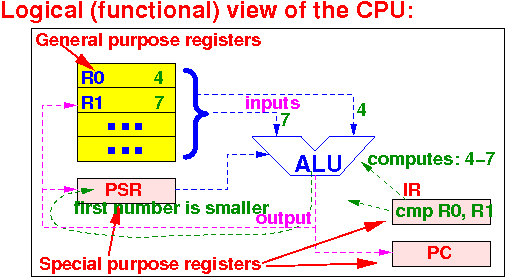
Some instructions will update the Processor Status Register (PSR)
E.g.: if the instruction compares 4 against 7, the status bits in the PSR will indicate that 4 < 7.
How is the Processor Status Register (PSR) used:
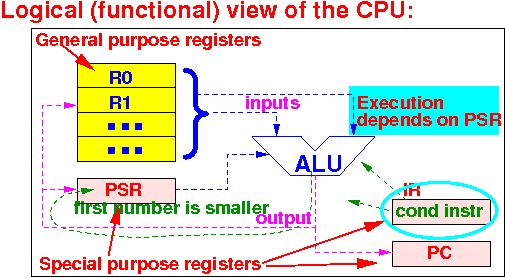
The next instruction executed will usually be a conditional instruction !!
The execution of a conditional instruction will depend on the current settings of the status bits in the PSR
We will study these conditional instructions soon in the Assembler Programming part of CS255