
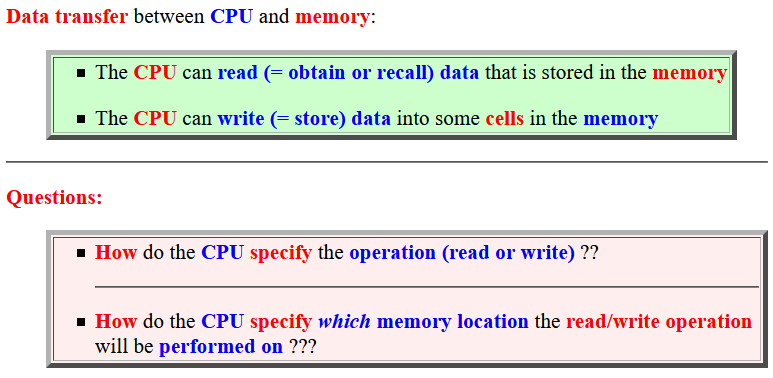



The address bus:

I.e.: the address bus is used to specify which memory location to read/write

The data bus:

I.e.: the data bus is used to convey the (binary) number to read/write

The control bus:

E.g.: the read/write command is to convey through a wire in the control bus
Interconnection schema:
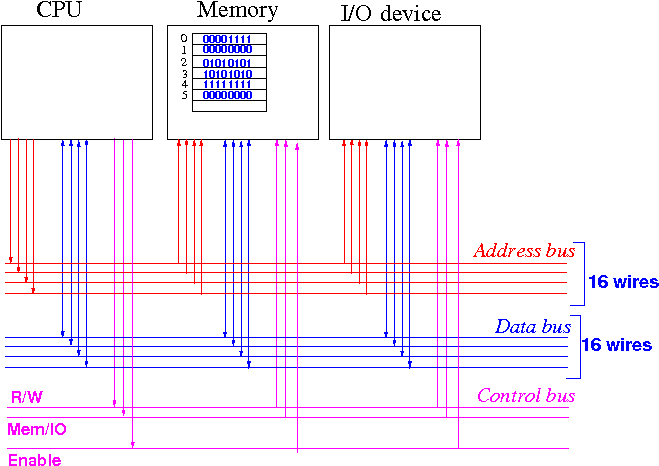
Enable:
1 = CPU performs transfer operation,
0 = CPU not active
R/W:
1 = Read operation,
0 = Write operation
Mem/IO:
1 = target is memory,
0 = target is IO device
Initial state: lines without signal are "don't care", i.e.: irrelevant

Enable = 0 will disable (= "turn off") all devices in the computer system
Suppose the CPU wants to read the data stored at memory address 4
CPU sends out "Read memory location 4" command:

R/W, Mem/IO, Enable are set to
read operation to memory
Address bus contains
4 (in binary)
Memory responds to the "Read memory location 4" command:

Data bus contains the value stored at location 4 in memory
CPU captures the data and terminates the transfer operation:

Enable = 0 will make all devices inactive
Initial state:

Enable = 0 will disable all devices in the computer system
Suppose the CPU wants to write the data 10101010 11111111 into memory location 4
CPU sends out "Write memory location 4" command and data 10101010 11111111 :

R/W, Mem/IO, Enable are set to
write operation to memory
Address bus contains
4 (in binary)
Data bus contains
10101010 11111111
Memory responds to the "Write memory location 4" command:
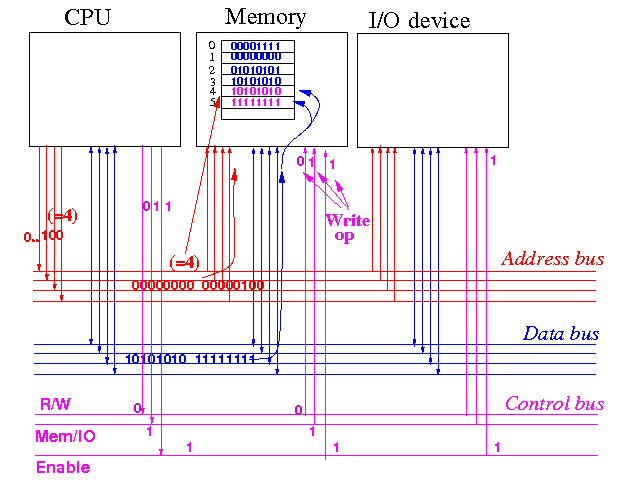
Memory will store the data on the data bus at the specified address
CPU terminates the transfer operation:

Enable = 0 will make all devices inactive