- Recall:
function with an array parameter
void print( int N, double x[ ] ) { int i; for ( i = 0; i < N; i++ ) printf("%lf\n", x[i] ); } int main( int argc, char *argv[ ] ) { double a[10]; print( a ) ; }
- Fact:
- The data type of
a in the example is:
(double *) // address of the double variable &a[0]
- The data type of
a in the example is:
- We can re-write the
definition of the function as follows:
void print( int N, double *x ) { int i; for ( i = 0; i < N; i++ ) printf("%lf\n", x[i] ); // x[i] <==> *(x + i) !!! } int main( int argc, char *argv[ ] ) { double a[10]; print( a ) ; }
- Fact:
- The above syntax equivalence
does not generalize
to more than one-level of [ ]
- In other words:
p[i][j] is invalid
- Multi-dimensional arrays:
- If you want dynamic multi-dimensional arrays in C, you have to maintain the array yourself !!!
- The above syntax equivalence
does not generalize
to more than one-level of [ ]
- Implementing a 2-dimensional
(dynamic) array:
- You must
map the
elements in a
two-dimensional array onto
a one-dimensional array.
Example:
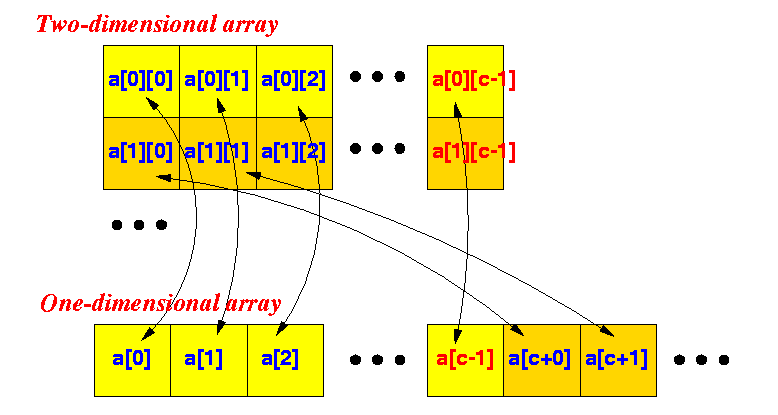
- The mapping is as follows:
mapped to a[i][j] ===> a[ i + j*columnSize ]
- You must
map the
elements in a
two-dimensional array onto
a one-dimensional array.
- Example: a
3x4 (dynamically allocated) array
#define NRows 3 #define NCols 4 int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int i, j; double* p; // We uses this reference variable to access // dynamically created array elements p = calloc(NRows*NCols, sizeof(double) ); // 3x4 = 12 elements for ( i = 0; i < NRows; i++ ) for ( j = 0; j < NCols; j++ ) p[i*NCols+j] = i+j; // put value i+j in array element p[i][j] for ( i = 0; i < NRows; i++ ) { for ( j = 0; j < NCols; j++ ) printf("p[%d][%d] = %lf ", i, j, p[i*NCols+j] ); putchar('\n'); } free(p); // Un-reserve the first array }Result:
p[0][0] = 0.000000 p[0][1] = 1.000000 p[0][2] = 2.000000 p[0][3] = 3.000000 p[1][0] = 1.000000 p[1][1] = 2.000000 p[1][2] = 3.000000 p[1][3] = 4.000000 p[2][0] = 2.000000 p[2][1] = 3.000000 p[2][2] = 4.000000 p[2][3] = 5.000000
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link(s) and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: gcc dyn-array3.c
- To run: ./a.out