- Recall that:
int i; // An integer variable int a[10]; // An integer array int *p; // A reference variable to an int variable // p can contain an address of an int variable
- Consider these 2 kinds of
int variables:
int i; // An integer variable int a[10]; // An integer arrayIllustrated:
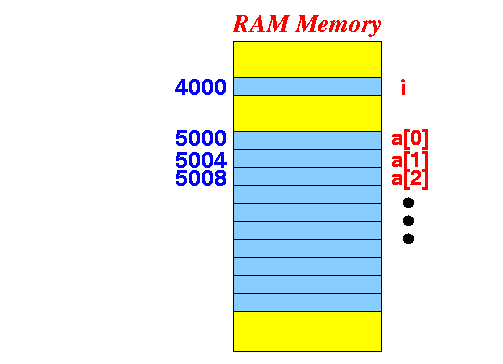
Notice that:
- i is an int typed variable
- a[0] is an int typed variable
- a[1] is an int typed variable
- And so on...
- Therefore, we can use an
int *p variable to access
any one of these
int typed variables:
int *p; p = &i; *p will access i p = &a[0]; *p will access a[0] p = &a[1]; *p will access a[1]
- Definition:
pointer addition
- The expression:
referenceVariable + integerevaluates (returns) to the address
referenceVariable + integer*sizeof( (*referenceVariable) )
Example:
- Initially, the variable p
points to the variable a[0]:
int a[10]; int *p; p = &a[0];
- Then the expression
p + 1 will
evaluates to:
p + 1 ===> &a[0] + 1*sizeof( (*p) ) // (*p) is an int ! <===> &a[0] + 1*4 <===> &a[0] + 4 - The expression
p + 2 will
evaluates to:
p + 2 ===> &a[0] + 1*sizeof( (*p) ) // (*p) is an int ! <===> &a[0] + 2*4 <===> &a[0] + 8
Example C progra:
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int a[10]; int *p; p = &a[0]; // p points to variable a[0] printf("p = %u, &a[%d] = %u\n", p, 0, &a[0] ); printf("p + 1 = %u, &a[%d] = %u\n", p+1, 1, &a[1] ); printf("p + 2 = %u, &a[%d] = %u\n", p+2, 2, &a[2] ); printf("p + 3 = %u, &a[%d] = %u\n", p+3, 3, &a[3] ); }Output of C program:
p = 4290769444, &a[0] = 4290769444 (increased by 4 !!!) p + 1 = 4290769448, &a[1] = 4290769448 p + 2 = 4290769452, &a[2] = 4290769452 p + 3 = 4290769456, &a[3] = 4290769456
- The expression:
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link(s) and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: gcc pointer-arithm1.c
- To run: ./a.out
- The following figure
shows the
result of the
p+1
and p+2 more
clearly:
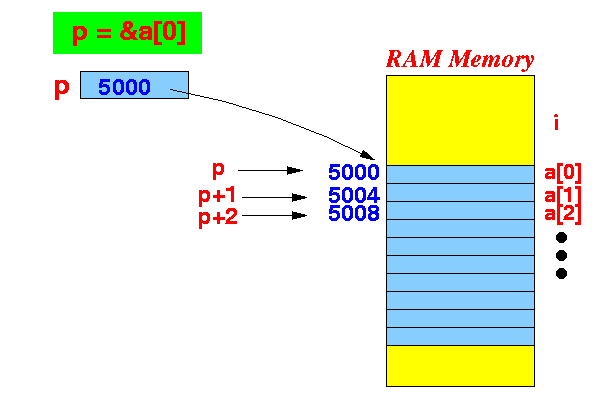
In other words:
If p points to a[0] then: p + 1 = &a[0] + 4 = the address of the array element a[1] !! p + 2 = &a[0] + 8 = the address of the array element a[2] !!
- In general:
- The expression:
p + xevaluates to:
- the address of the xth array element following the array element that is pointed to by p !!
- The expression:
- The − operator
on reference variables has a
similar effect as the
+ operator:
- Suppose, the variable p
points to the variable a[5]:
int a[10]; int *p; p = &a[5];
- Then the expression
p - 1 will
evaluates to:
p - 1 ===> &a[5] - 1*sizeof( (*p) ) // (*p) is an int ! <===> &a[5] - 1*4 <===> &a[5] - 4 - The expression
p - 2 will
evaluates to:
p - 2 ===> &a[5] - 1*sizeof( (*p) ) // (*p) is an int ! <===> &a[5] - 2*4 <===> &a[5] - 8
In other words:
If p points to a[5] then: p - 1 = &a[5] - 4 = the address of the array element a[4] !! p - 2 = &a[5] - 8 = the address of the array element a[3] !!
- Suppose, the variable p
points to the variable a[5]:
- In general:
- The expression:
p - xevaluates to:
- the address of the xth array element prior to the array element that is pointed to by p !!
- The expression:
- Using pointer arithmetic
to access array elements
- Because the expression:
p + xevaluates to:
- the address of the xth array element following the array element that is pointed to by p !!
- Therefore:
the expression:
*( p + x )evaluates to:
- the variable that is the xth array element following the array element that is pointed to by p !!
Example:

Explanation:
- If p = &a[0], then:
*p is an alias for a[0] *(p+0) is also an alias for a[0] *(p+1) is also an alias for a[1] *(p+2) is also an alias for a[2]
- Because the expression:
- Example C program:
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int a[10] = { 11, 22, 33, 44, 55, 66, 77, 88, 99, 777 }; int *p; p = &a[0]; // p points to variable a[0] printf("*p = %d, a[%d] = %d\n", *p, 0, a[0] ); printf("*(p + 1) = %d, a[%d] = %d\n", *(p+1), 1, a[1] ); printf("*(p + 2) = %d, a[%d] = %d\n", *(p+2), 2, a[2] ); printf("*(p + 3) = %d, a[%d] = %d\n", *(p+3), 3, a[3] ); }Output:
*p = 11, a[0] = 11 *(p + 1) = 22, a[1] = 22 *(p + 2) = 33, a[2] = 33 *(p + 3) = 44, a[3] = 44
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link(s) and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: gcc pointer-arithm2.c
- To run: ./a.out
- Review:
post increment/decrement operators
p++ means: 1. p = p + 1 2. returns the OLD value (before the increment) in p p-- means: 1. p = p - 1 2. returns the OLD value (before the increment) in p
- Applying the
post increment/decrement operators on
reference veriables:
if p is a reference typed variable, then: p++ means: 1. p = p + 1 and will store p + 1*sizeof( (*p) ) into p 2. returns the OLD value (before the increment) in p p-- means: 1. p = p - 1 and will store p - 1*sizeof( (*p) ) into p 2. returns the OLD value (before the increment) in p
- Example:
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int a[10]; int *p; p = &a[0]; // p points to variable a[0] printf("staring p = %u\n", p); p++; printf("after p++: p = %u\n", p ); p++; printf("after p++: p = %u\n", p ); p++; printf("after p++: p = %u\n", p ); }Output:
staring p = 4290769444 // p++ increases p by 4 = sizeof(int) !!! after p++: p = 4290769448 after p++: p = 4290769452 after p++: p = 4290769456
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link(s) and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: gcc pointer-arithm3.c
- To run: ./a.out
- Meaning of the expression
*(p++):
means *(p++) <===> *( p++ ) // apply p++ first p++ : 1. p = p+1 2. returns the OLD value of p !!! <===> *( use the OLD value of p ) <===> the variable pointed to by the OLD value of p !!!In plain English:
- Use the (array) element
that is currently pointed to
by p
- Increment p to point to the next (array) element
- Use the (array) element
that is currently pointed to
by p
- Example:
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int a[10] = { 11, 22, 33, 44, 55, 66, 77, 88, 99, 777 }; int i; int *p; printf("Array a[]: "); for ( i = 0; i < 10; i++ ) printf("%d ", a[i] ); putchar('\n'); p = &a[0]; // p points to variable a[0] printf("*(p++) = %d\n", *(p++) ); printf("*(p++) = %d\n", *(p++) ); printf("*(p++) = %d\n", *(p++) ); printf("*(p++) = %d\n", *(p++) ); }Output:
Array a[]: 11 22 33 44 55 66 77 88 99 777 *(p++) = 11 *(p++) = 22 *(p++) = 33 *(p++) = 44
Explanation:
- Initially, p points
to a[0]
- Then the expression:
*(p++)will return a[0] because p++ uses the old value (= &a[0]) of p.
After this expression is evaluated, the variable p will point to a[1] !
- Then in the second iteration,
the expression:
*(p++)will return a[1] !!
After this expression is evaluated, the variable p will point to a[2] !
- And in the 3rd iteration,
the expression:
*(p++)will return a[2] !!
After this expression is evaluated, the variable p will point to a[2] !
- And so on....
- Initially, p points
to a[0]
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link(s) and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: gcc pointer-arithm4.c
- To run: ./a.out
- Here is a traditional program to
copy an array:
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int a[10] = { 11, 22, 33, 44, 55, 66, 77, 88, 99, 777 }; int b[10]; int i; for ( i = 0; i < 10; i++ ) b[i] = a[i]; printf("Array a[]: "); for ( i = 0; i < 10; i++ ) printf("%d ", a[i] ); putchar('\n'); printf("Array b[]: "); for ( i = 0; i < 10; i++ ) printf("%d ", b[i] ); putchar('\n'); }
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link(s) and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: gcc array-copy1.c
- To run: ./a.out
- Here is how you can use
pointer arithmetic to
perform the array copy operation:
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int a[10] = { 11, 22, 33, 44, 55, 66, 77, 88, 99, 777 }; int b[10]; int i; int *p, *q; // Defines 2 reference variables // Incorrect: int *p, q; - q will be an int p = &a[0]; q = &b[0]; for ( i = 0; i < 10; i++ ) *(q++) = *(p++); printf("Array a[]: "); for ( i = 0; i < 10; i++ ) printf("%d ", a[i] ); putchar('\n'); printf("Array b[]: "); for ( i = 0; i < 10; i++ ) printf("%d ", b[i] ); putchar('\n'); }
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link(s) and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: gcc array-copy2.c
- To run: ./a.out
- C fact:
- C programs often use
pointer arithmetic to
process elements in an array
Example:
p = &a[0]; // or p = a; for ( i = 0; i < 10; i++ ) *(p++) = .....;
instead of: for ( i = 0; i < 10; i++ ) a[i] = .....;
- C programs often use
pointer arithmetic to
process elements in an array
- Reason:
- Efficiency:
- The number of memory accesses
needed to obtain the value
using a[i] is:
1 memory read to get the value of i 1 memory read to get the value of a[i] ------------------------------------------- 2 memory read operations total
- When the pointer variable p
is stored in a register
(inside the CPU),
the number of memory accesses
needed to obtain the value
using *(p++) is:
1 memory read to get the value of *p 0 memory read to update p++ (in register) -------------------------------------------------------- 1 memory read operations total
- The number of memory accesses
needed to obtain the value
using a[i] is:
- Efficiency:
- Fact:
- The post increment operator
++
has a higher precedence
than the
de-reference operator
*
See: click here
- The post increment operator
++
has a higher precedence
than the
de-reference operator
*
- Therefore: *p++
is evaluated as follows:
*p++ ===> *p++ // * and ++ has same priority // ==> Use associativity rule // ==> Perform operations from right-to-left ! // ==> Perform ++ first !!! ===> *(p++)
- Conclusion:
- We could have written the
array copy program like
like:
int main(int argc, char *argv[]) { int a[10] = { 11, 22, 33, 44, 55, 66, 77, 88, 99, 777 }; int b[10]; int i; int *p, *q; // Defines 2 reference variables // Incorrect: int *p, q; - q will be an int p = &a[0]; q = &b[0]; for ( i = 0; i < 10; i++ ) *q++ = *p++; printf("Array a[]: "); for ( i = 0; i < 10; i++ ) printf("%d ", a[i] ); putchar('\n'); printf("Array b[]: "); for ( i = 0; i < 10; i++ ) printf("%d ", b[i] ); putchar('\n'); }
- We could have written the
array copy program like
like:
- Very frequently used expression in C:
DataType * p; *p++*p++ means:
- Use the
variable (array element) that is
currently pointed to
by p
- Incremenet p to point to the next (array) element
- Use the
variable (array element) that is
currently pointed to
by p