|
In CS170, you have learned how to create arrays in Java:
public class demo {
public static void main( String[] args )
{
int[] A; // A is a reference variable !
A = new int[10]; // The new operator allocates
// memory for an array object
// and returns its base address
// The #bytes of memory needed
// = array size * sizeof(int)
}
}
|
Java has dynamic arrays
I want to make sure you understand how a dynamic array is implemented first.
I will illustrate what happens inside the computer system in this program:
int[] A; // A is a reference variable !
A = new int[10];
|
"int[] A" will allocate (reserve memory) a reference variable A:
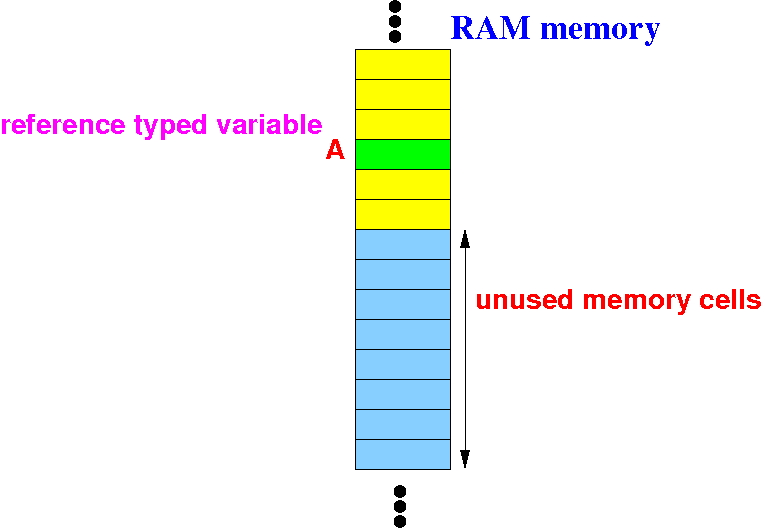
I will illustrate what happens inside the computer system in this program:
int[] A; // A is a reference variable !
A = new int[10];
|
"new int[10]" will allocate (reserve memory) for an int[10] array (= 40 bytes) and return its base address:
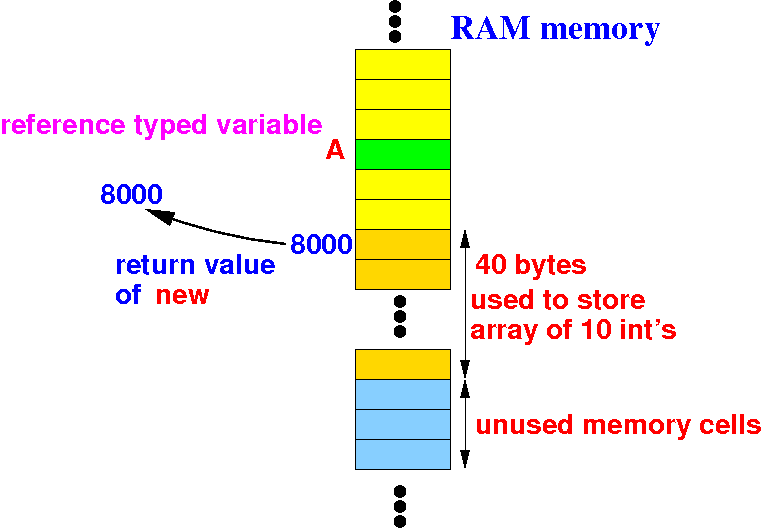
I will illustrate what happens inside the computer system in this program:
int[] A; // A is a reference variable !
A = new int[10];
|
"A = " will assign the return value to the variable A:
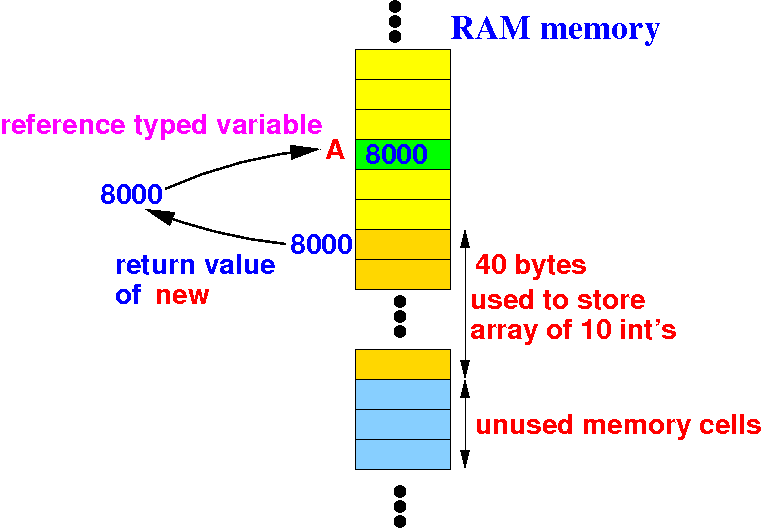
Summary of the effect of:
int[] A; // A is a reference variable !
A = new int[10];
|
The reference variable A will point to a newly created int[10] (array of 10 integers) object:
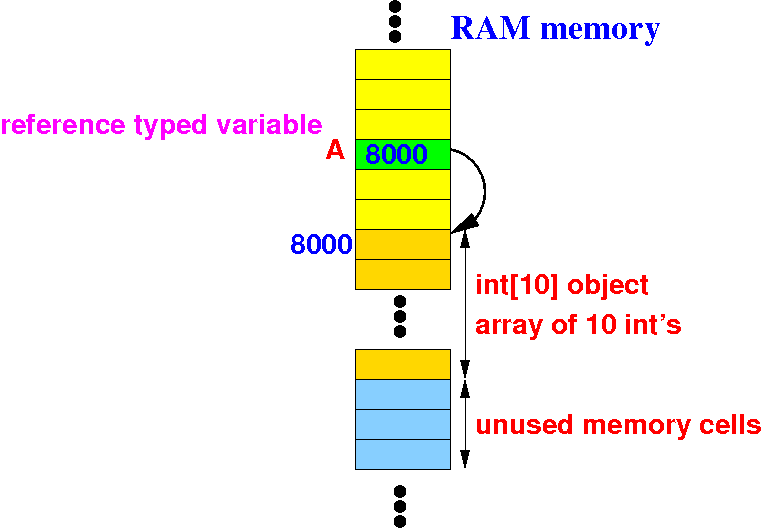
We can achieve the identical result (= create a dynamic array) in C with the following:
int main( int argc, char *argv[] )
{
int *A; // A is a reference variable !
A = malloc( 10*sizeof(int) );
// The malloc(10*sizeof(int) call
// allocates memory for an array
// and returns its base address
// The #bytes of memory needed
// = array size * sizeof(int)
}
}
|
I will illustrate what happens inside the computer system in this program:
int *A; // A is a reference variable !
A = malloc( 10*sizeof(int) );
|
"int *A" will allocate (reserve memory) a reference variable A:

I will illustrate what happens inside the computer system in this program:
int *A; // A is a reference variable !
A = malloc( 10*sizeof(int) );
|
"malloc(10*sizeof(int))" will allocate (reserve memory) for an int[10] array and return its base address:
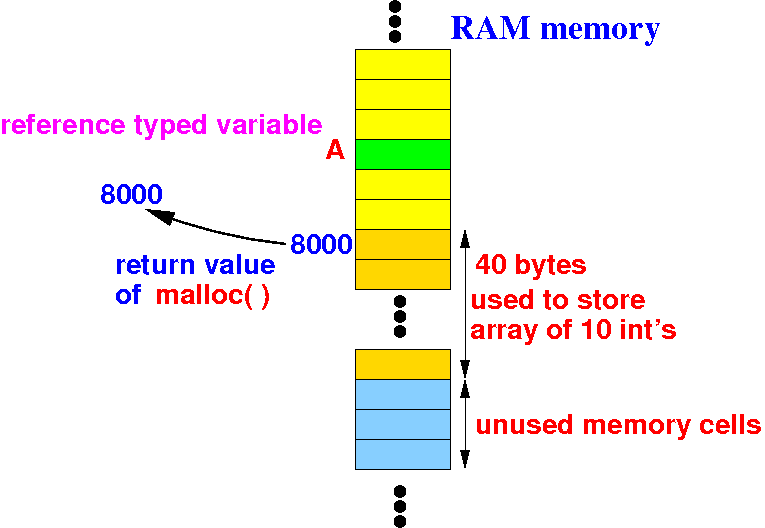
I will illustrate what happens inside the computer system in this program:
int *A; // A is a reference variable !
A = malloc( 10*sizeof(int) );
|
"A = " will assign the return value to the variable A:
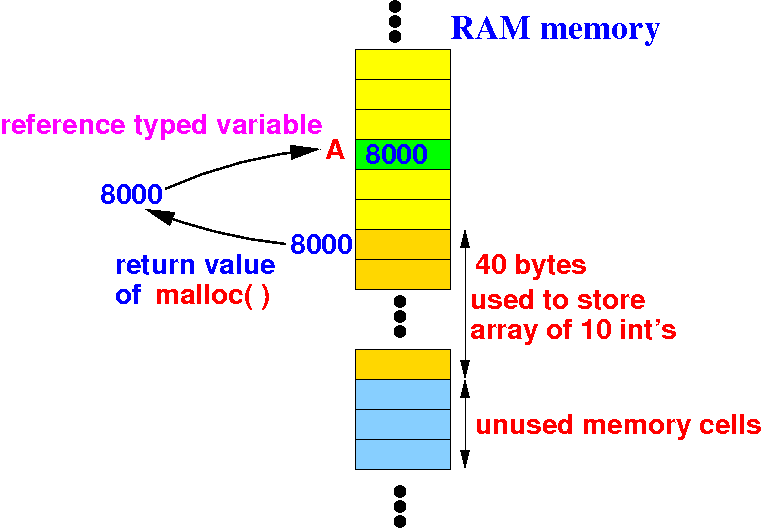
Summary of the effect of:
int *A; // A is a reference variable !
A = malloc( 10*sizeof(int) );
|
The reference variable A will point to a newly created int[10] (array of 10 integers) object:

In addition: we also need programming language support to access the elements in a dynamic array:
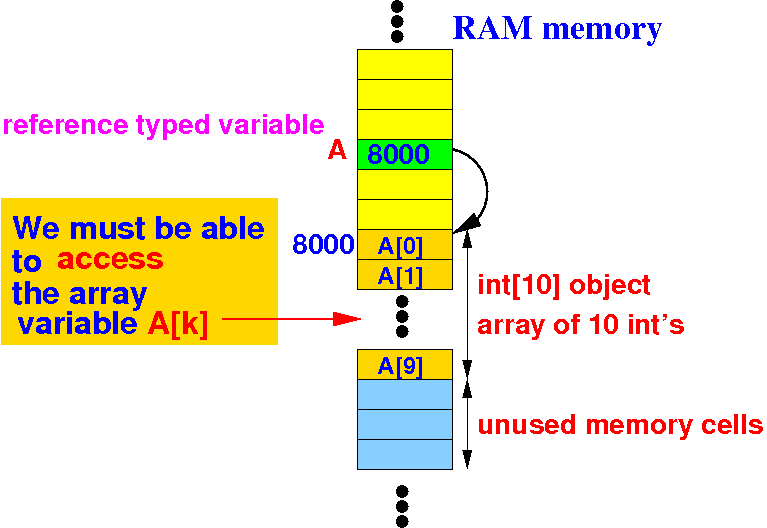
Notice that:
A ≡ &A[0] |
The C programming language support to access the elements in a dynamic array is pointer arithmetic:
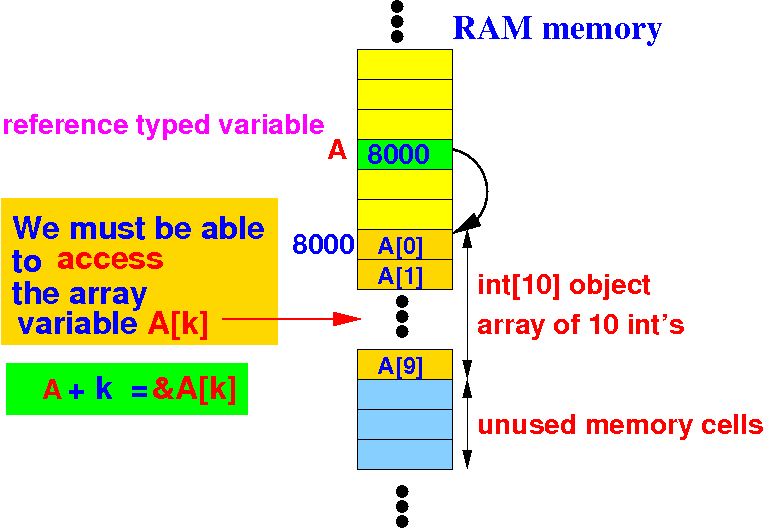
The address of the array element A[k] is equal to:
A + k ≡ &A[k] = address of array element A[k] |
Using pointer arithmetic, the kth-element of the dynamic array is accessed as:
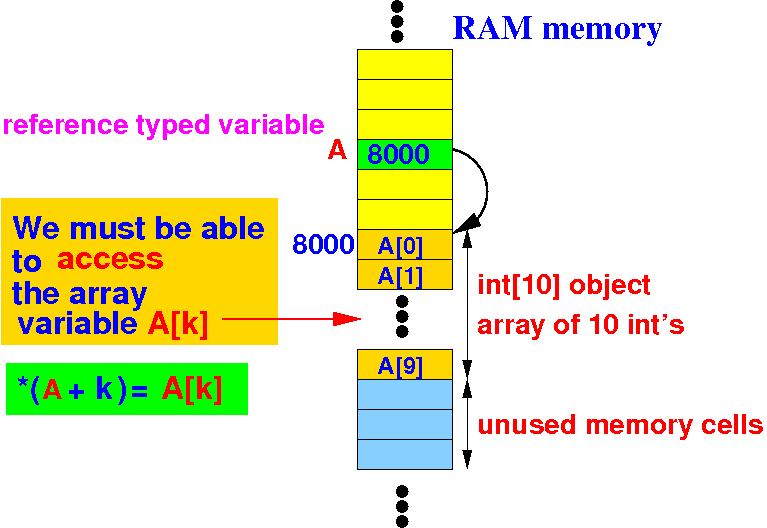
De-reference:
*(A + k) ≡ *&A[k] ≡ A[k]
|
Using the short hand operator [ ], the kth-element of the dynamic array is accessed as:
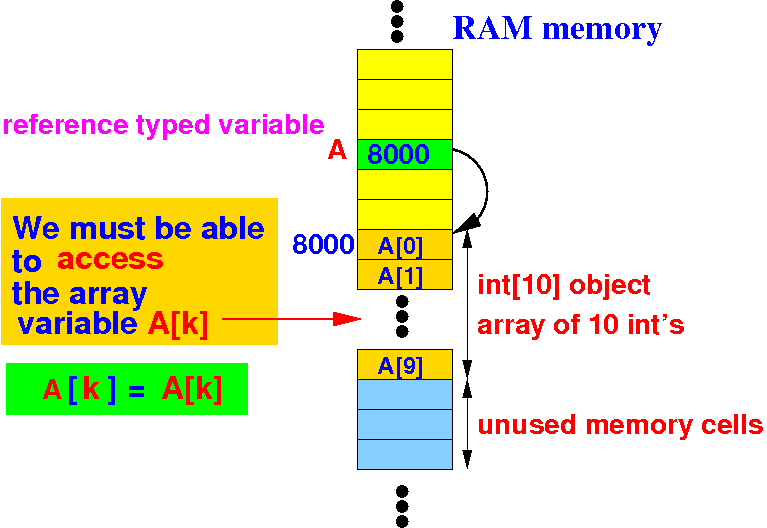
Use short hand operator [ ]:
A[ k ] ≡ *&A[k] ≡ A[k]
|
I.e.: C uses a similar syntax to access elements in a dynamic array
Difference: static array uses ConstantRef[k] and dynamic array uses RefVariable[k]
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
int i;
double* p; // We uses this reference variable to access
// dynamically created array elements
p = malloc(10 * sizeof(double) ); // Make double array of 10 elements
for ( i = 0; i < 10; i++ )
p[i] = i; // put value i in array element i
for ( i = 0; i < 10; i++ )
printf("p[%d] = %lf\n", i, p[i] );
free(p); // Un-reserve the memory for array
// We can change the size of the dynamic array
p = malloc(20 * sizeof(double) ); // Make double array of 20 elements
}
|
DEMO: demo/C/set2/dyn-array1.c