Different kinds of
array variables used in
programming language
- Programming languages can
provide
2 kinds of
array variables:
-
Static
arrays
-
Dynamic
arrays
|
-
Static arrays
(e.g.: in
C programs)
- The
location of
static arrays
cannot
be changed
after the array has been
created/allocated
- The size (=
number of elements)
of the
array variable
cannot be changed
|
-
Dynamic arrays
(e.g.: in
Java programs)
- The
location of
dynamic arrays
can
be changed
after the array has been
created/allocated
- The size (=
number of elements)
associated with the
array variable
can be changed
|
|
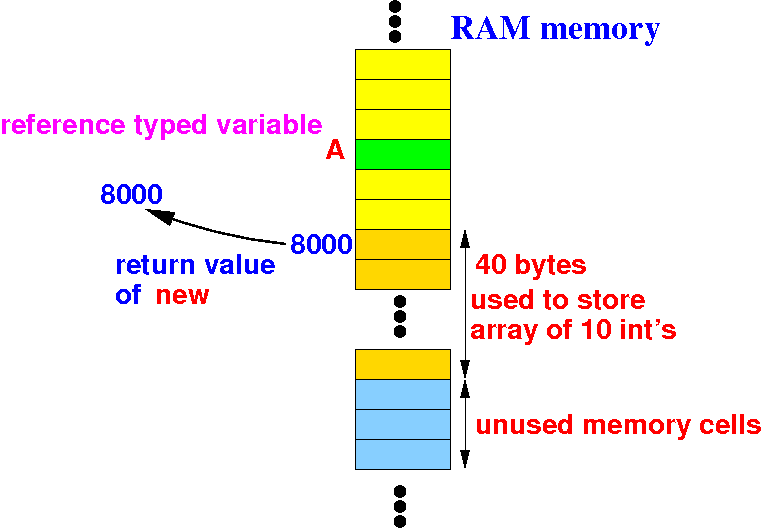
Review: Java's syntax to
define an array
- Java defines
an int array A
of 10 elements as
follows:
int[] A;
A = new int[10];
|
|
Review: Java's syntax to
define an array
Review: Java's syntax to
define an array
Review: Java's syntax to
define an array
Review: Java's syntax to
define an array
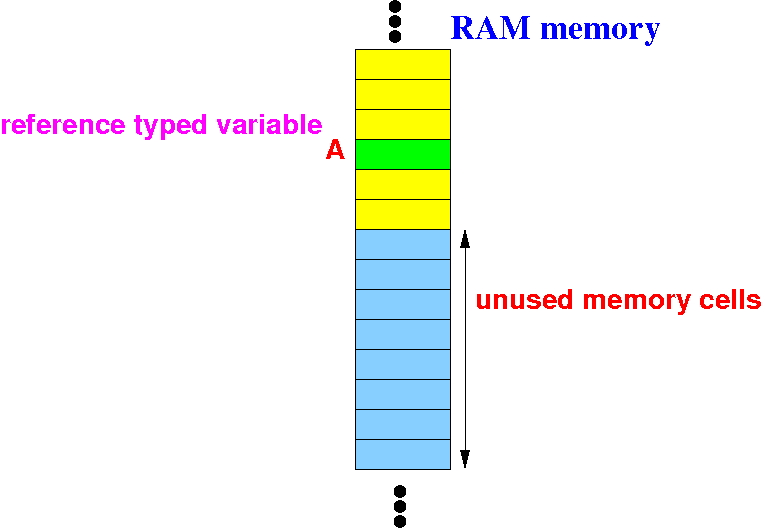
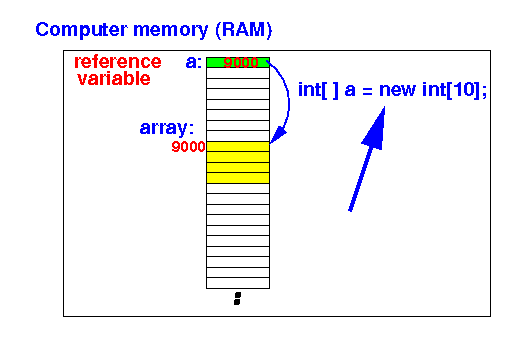
Why is
Java's array
dynamic ?
- Dynamic arrays use
a
reference variable to
point to
the
actual
array:
|
Dynamic arrays are
not the norm in
high level programming languages
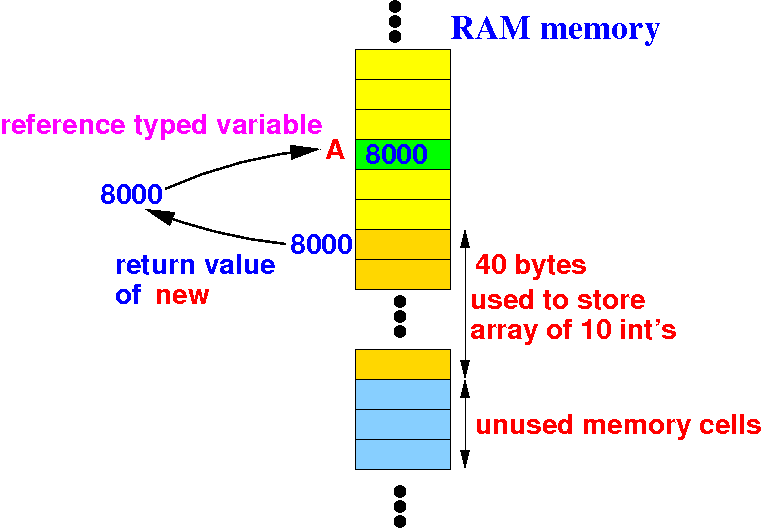
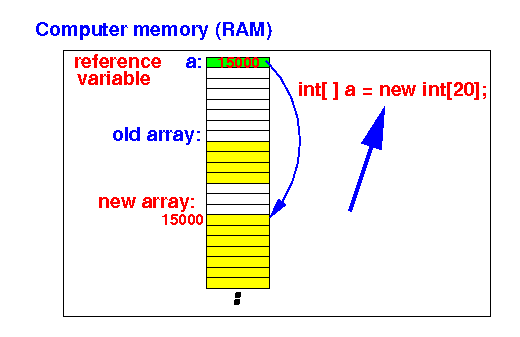
Why is
Java's array
dynamic ?
- The
location and
size of the
array can be
changed by
updating
the reference variable:
|
Dynamic arrays are
not the norm in
high level programming languages
Why is
C's array
static ?
- A static array uses
a
identifier
(= symbolic
constant) to
define
location of
an array:
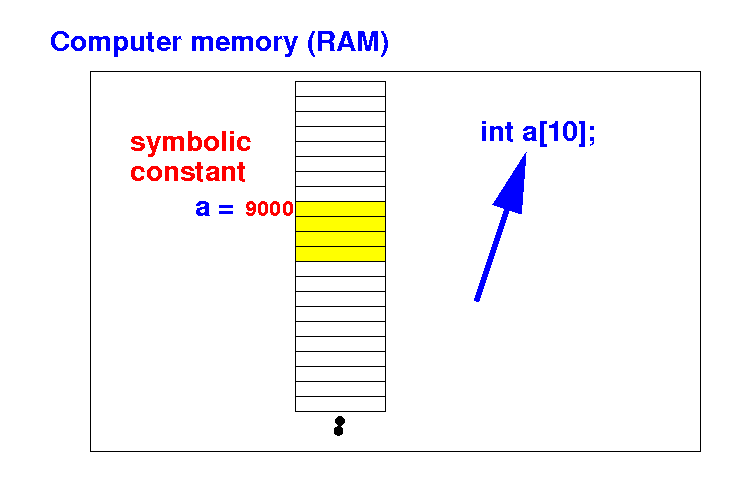
- A
symbolic
constant
cannot be change
after the
array has been
defined
|
Why is
C's array
static ?
- Example: you
cannot
update
an array "variable" in
C
(but is allowed in
Java):
| C's array identifier is a constant |
Java's array identifier is a variable |
int main()
{
double a[10];
double b[10];
a = b; // Illegal to update
// a CONSTANT
// (analogy: 9 = 4;)
}
|
public static void main(String[] args)
{
double[] a = new double[10];
double[] b = new double[10];
a = b; // You can update
// an variable
// Analogy: a = 4;
}
|
|
DEMO:
/home/cs255001/demo/C/set1/staticArray.c +
dynArray.java
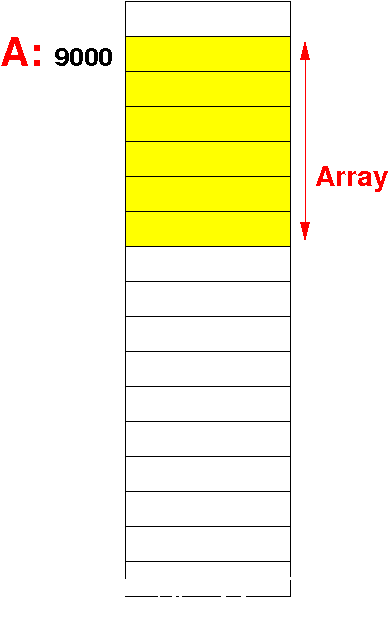
Summary:
how are static and
dynamic arrays
implemented
|
Static
array
(C)
|
Dynamic
array
(Java)
|
|
|
|
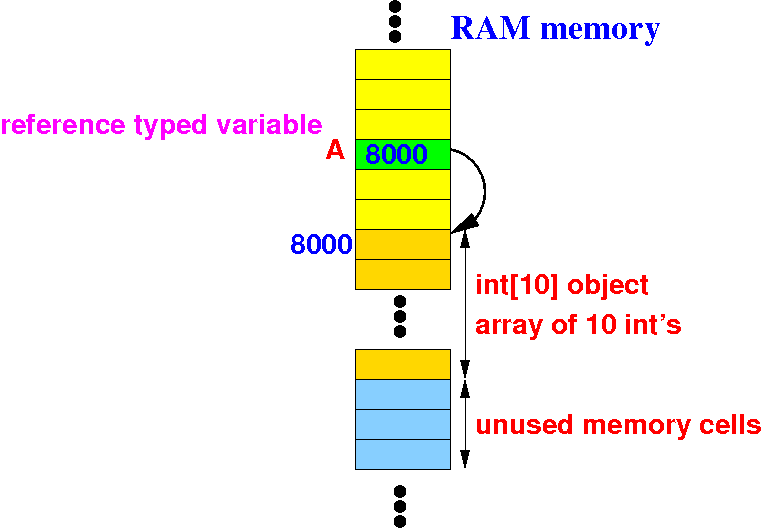
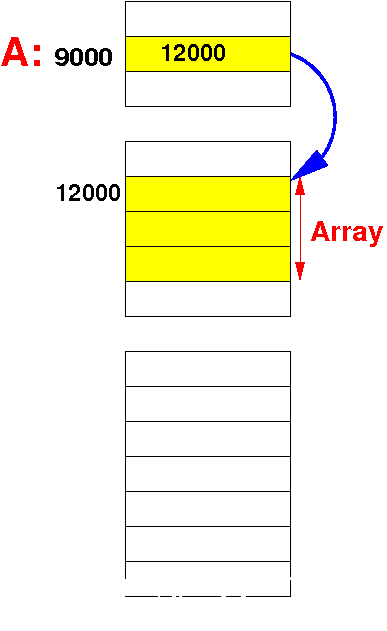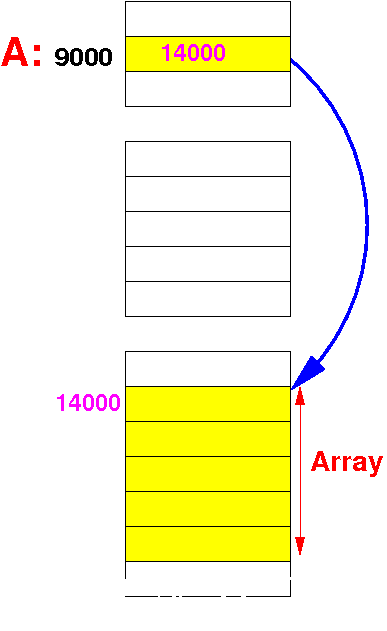
The array variable (A)
is a
(symbolic) constant for the
location (= address) of
the array and
cannot change
(therefore, the array is
static)
|
The array variable (A)
is a
reference variable that
contains the
base address of the array and
can be
updated
with a new location
|
Pros and cons of
static vs
dynamic arrays
- Dynamic arrays:
(Java !)
- Advantage:
flexible, you can
increase the
size if
needed
- Disadvantage:
slower
(need one extra memory access
per array operation)
|
- Static arrays:
(C)
- Advantage:
faster
- Disadvantage: not flexible
(cannot change
array size)
|
|
❮
❯