The smallest unit of Computer Memory:
bit
- Computers use
memory devices built with
electronics
- The smallest
memory device used
by the computer works like
a switch:

- The smallest
memory device
can be in one of
2 states:
- off state
(which we call state 0)
- on state
(which we call state 1)
-- (0 and 1 are called
binary digits)
|
- The smallest
memory device is called
a bit
(=
binary digit)
|
Building computer memory that can
store larger numbers
- A bit can
be in one of
2 states:
0 or 1
Therefore,
a bit can
store (= remember)
one of 2 values:
0 or 1
- A row of
n bits can be in
one of
2n states
Each switch can be
in 2 states.
The total # combinations =
2 × 2 × ... × 2 =
2n
|
Example: building a
larger computer memory using
3 switches
- Example:
a row of
3 swicthes can be in
one of 23 = 8 states:
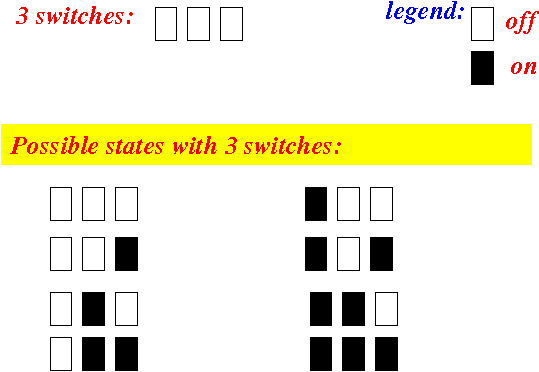
- We can
assign
a number to
each state (i.e.: a code) !!!
|
Assigning a number to each
state comprised of
3 switches
- Example:
how to assign
a number to
each state of
3 switches:
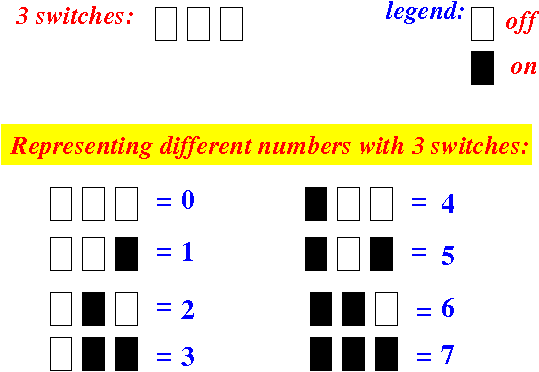
- This code is called: the
binary number
system
in Mathematics
|
The binary number system
- The decimal value that is
encoded (represented) by a
binary number is computed
as follows:
(each di is a
binary digit (0 or 1))
|
Binary number
|
Corresponding decimal value
|
|
dn-1
dn-2 ... d1 d0
|
dn-1×2n-1
+ dn-2×2n-2
+ ...
+ d1×21
+ d0×20
|
Examples:
|
Binary number
|
Corresponding decimal value
|
|
0
|
0×20 = 0
|
|
1
|
1×20 = 1
|
|
10
|
1×21 + 0
×20 = 2
|
|
1010
|
1×23
+ 0×22
+ 1×21
+ 0×20
= 8 + 2 = 10
|
|
Quiz: what is written on this T-shirt ?
- What is the
message on this
T-shirt ?

- Answer: ???
|
Quiz: what is written on this T-shirt ?
- What is the
message on this
T-shirt ?

- Answer:
There are 2
(binary number 10) types of people
in the world: ....
|
What does the binary number system
has to do with computer memory ?
- Recall that
computer memory consists of
memory cells:
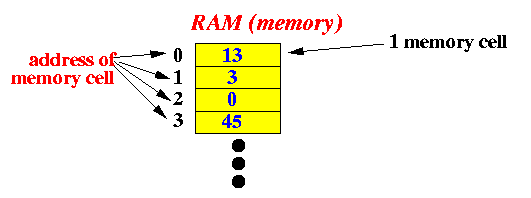
- Each memory cell is
identified by
a unique
address (= a number)
- Each memory cell
stores
a
number
|
What does the binary number system
has to do with computer memory ?
- The computer
uses the
binary number system
to represent
the numbers:
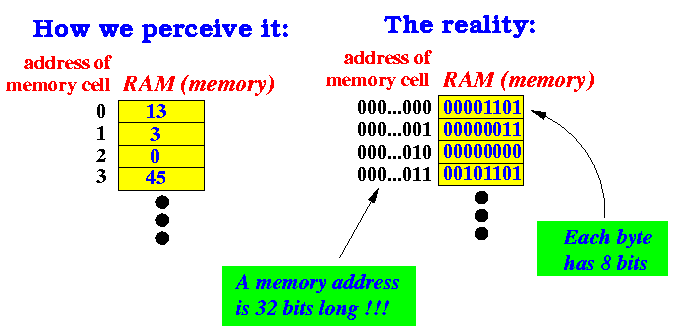
- Each memory cell is
identified by
a unique
address
as a binary number
- Each memory cell
stores
a
number
as a binary number
|
Structure of the
computer memory
- In theory, we
can make computer memory with
any number of
bits
- For historical reasons,
computer manufacturers have
decided on
memory cells that contains
8 bits:
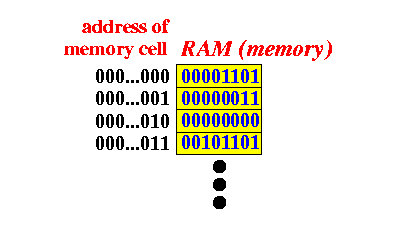
- We call a memory cell of 8 bits:
one byte of memory
|
Computer memory jargon
- A bit =
a
binary digit
--
which is
the unit (= building block) of
the computer memory
- A byte =
8 bits
--
which is
the
unit of
addressable/identfiable
computer memory
(you
cannot use less than
1 byte in
any computer operations)
- KByte =
kilo byte =
1024 (= 210) bytes
(approximately 103 bytes)
- MByte =
mega byte =
1048576 (= 220) bytes
(approximately 106 bytes)
- GByte =
giga byte =
1073741824 (= 230) bytes
(approximately 109 bytes)
*****
Today's
computers has about
8-16 GBytes of
RAM
- TByte =
tera byte =
1099511627776 (= 240) bytes
(approximately 1012 bytes)
*****
Today's
hard disks can hold about
2-10 TBytes of
data
|
❮
❯







