Physical organization of a computer
|
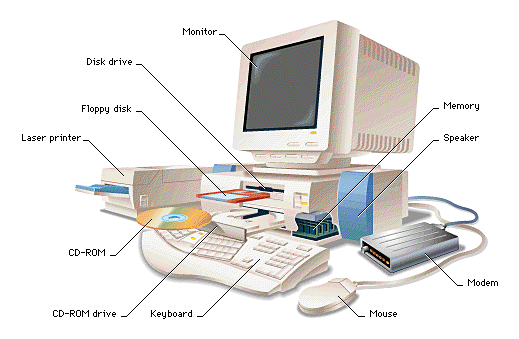
Physical organization of a computer
|
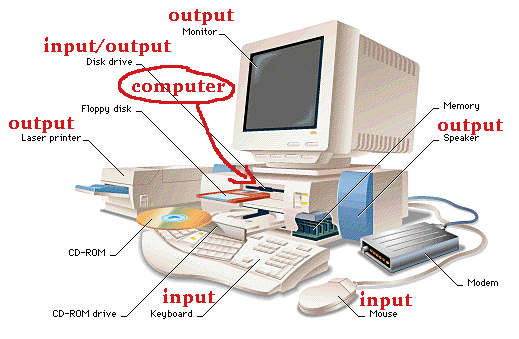
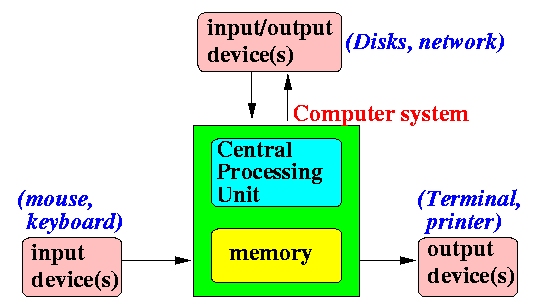
Logical (functional)
organization of a computer
|
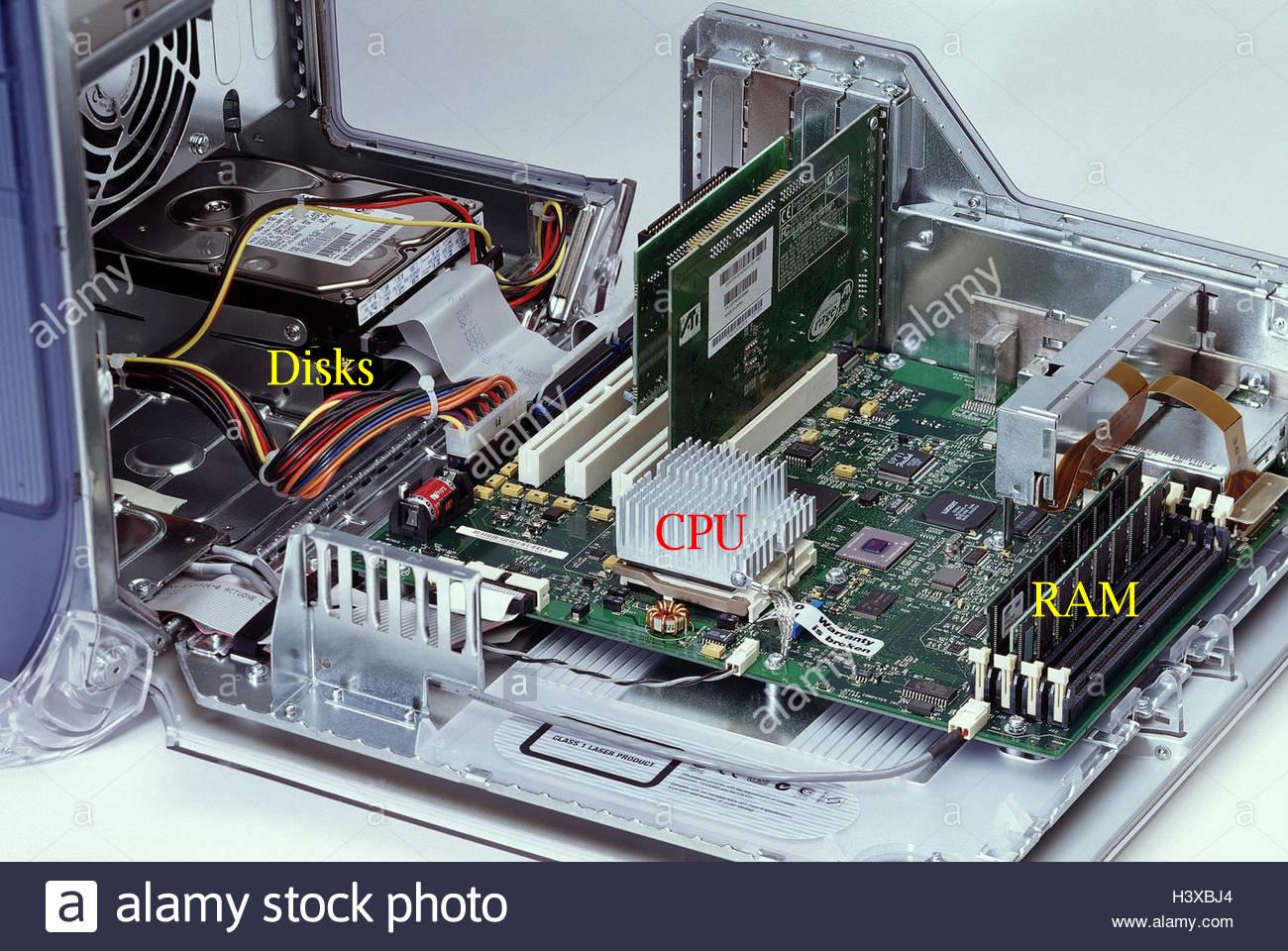
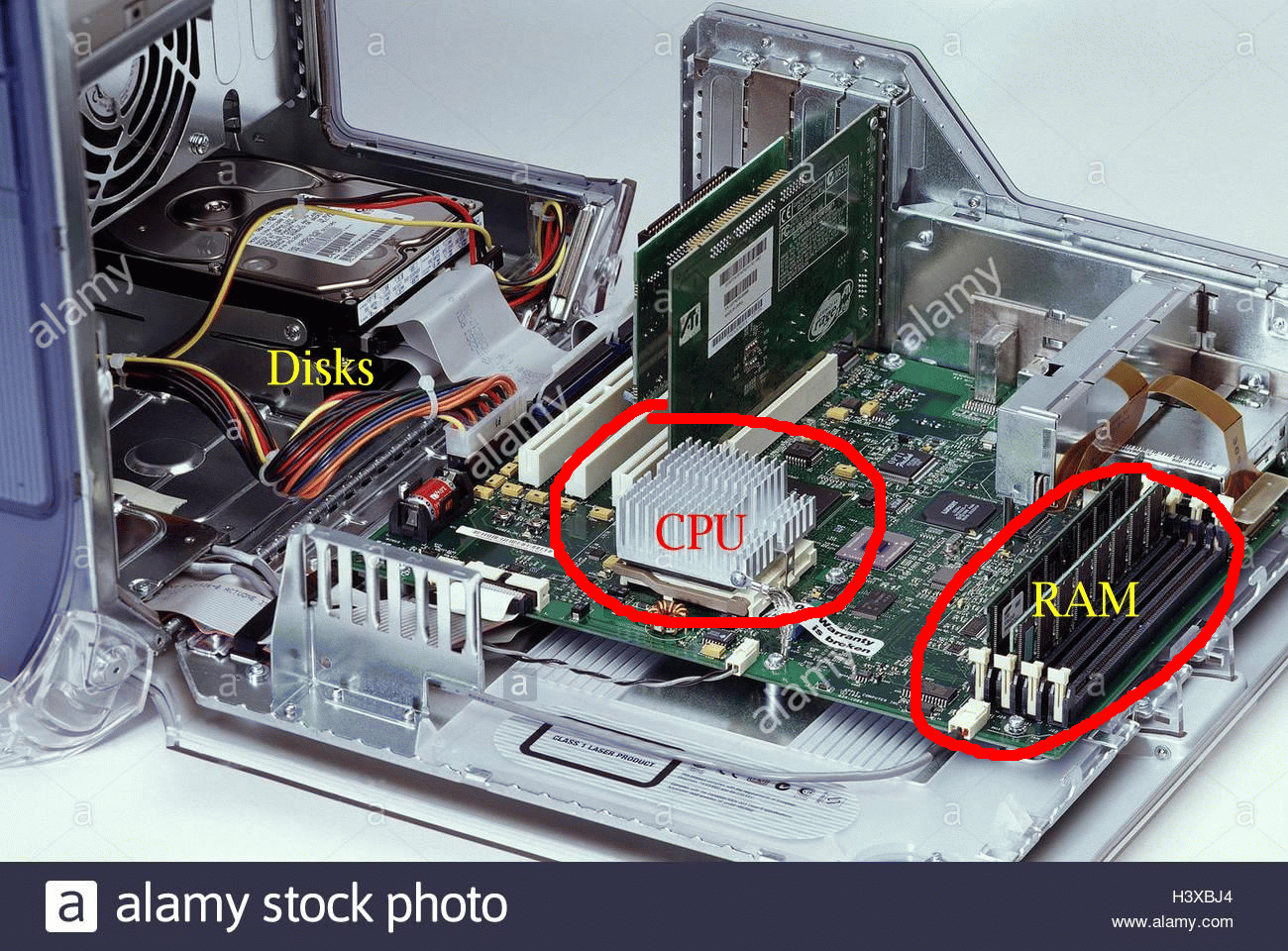
What a computer looks like from
inside
|
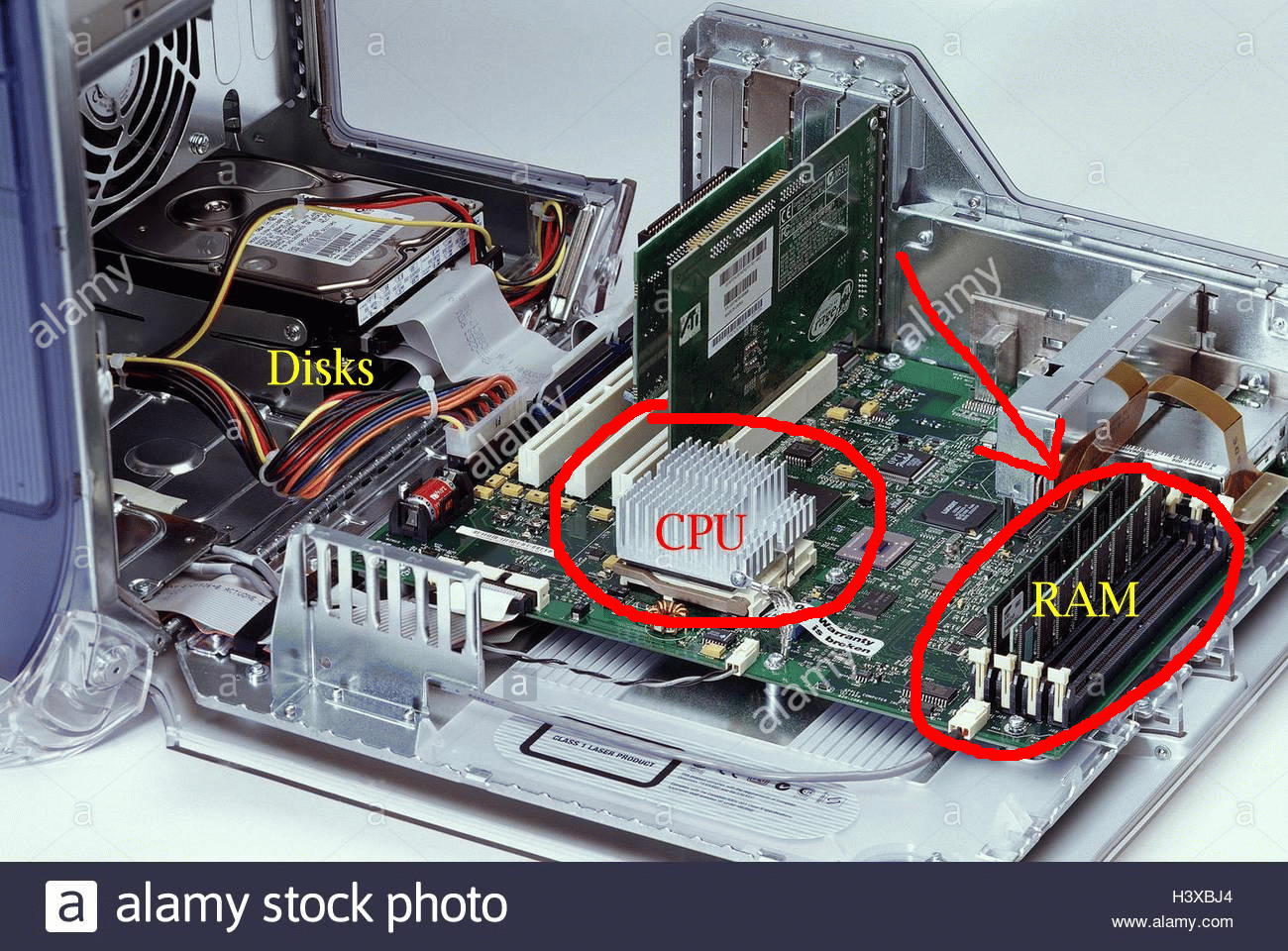
What a computer looks like from
inside
|
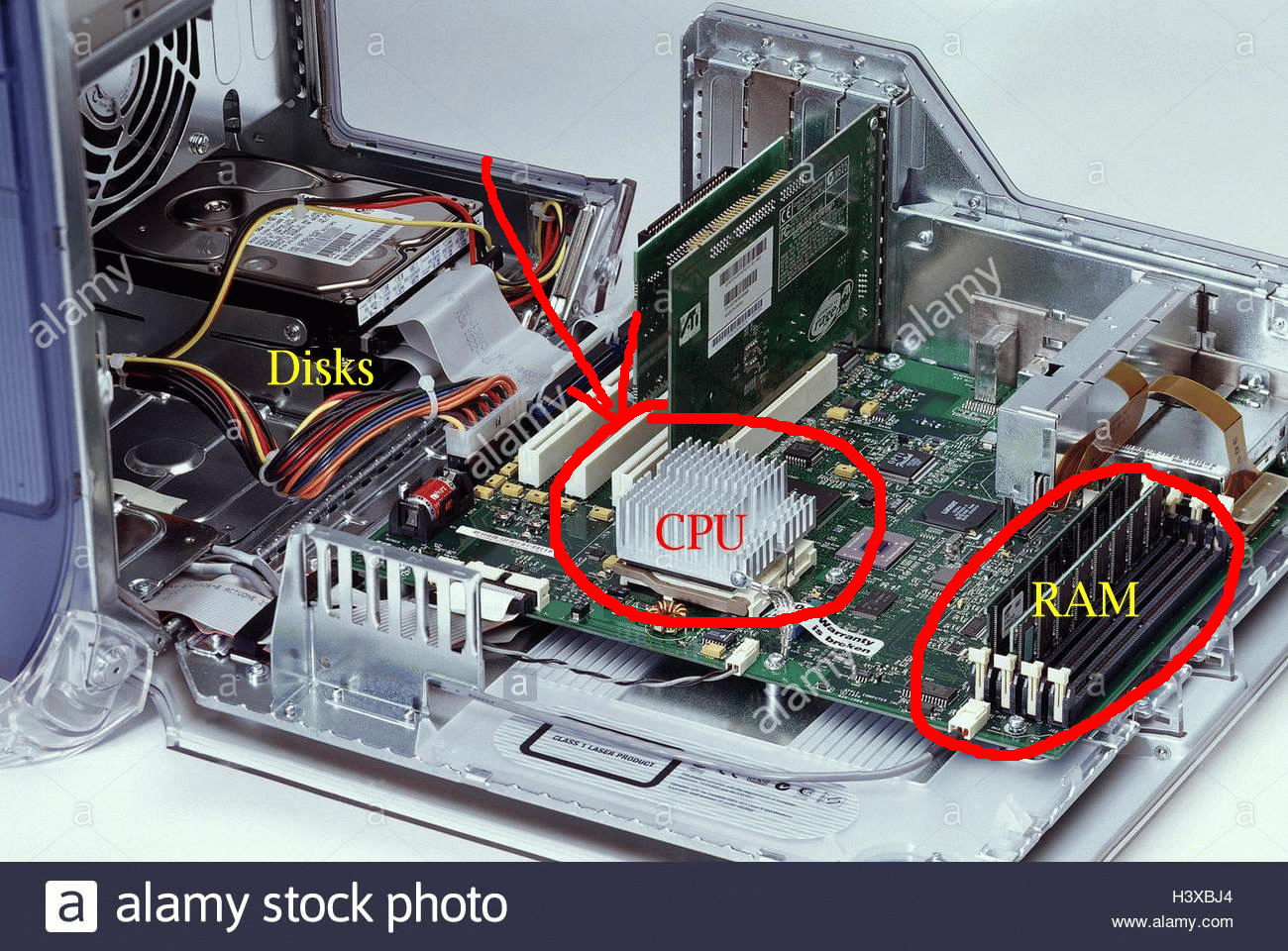
What a computer looks like from
inside
|
What a computer looks like from
inside
|
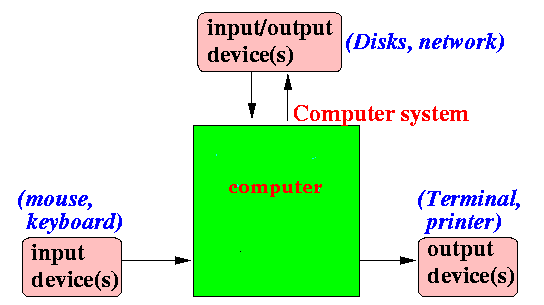
Updated
logical (functional)
organization of a computer
|
Components of a computer
A computer consists of 4 types of components:
|
We take a closer look at the computer (main) memory component next
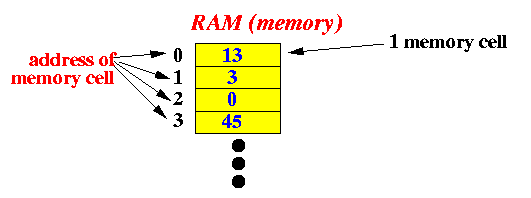
Computer memory
(a.k.a.: Random Access Memory or RAM)
|
Analogy to help you
understand a computer memory
|
Operations
that a computer can perform on the main memory
|
Analogy to help you understand the
write and
read operations to a computer memory
|
Question: how can a computer store things (like text) other than numbers ?? --- To be revealed