- Important: properties of the (2,4)-tree
- Size property:
- Each internal node has at most 4 children nodes
- Depth (height) property:
- Let E be
the set of internal nodes
which only have
external children nodes
- All external node of the nodes of E have the same height (depth)
- Let E be
the set of internal nodes
which only have
external children nodes
- Size property:
- Inserting an new entry:
- A new entry is
always inserted
in a node that contains
only external nodes
- In other words:
- A new entry is always inserted into a leaf node
- A new entry is
always inserted
in a node that contains
only external nodes
- Example 1:
- Before insert(18):

- After insert(18):

- Before insert(18):
- Example 2: we may need to
move some elements inside
a node !!!
- Before insert(7):

- After insert(7):

- Before insert(7):
- Simplest case of the insert operation:
- When an entry is inserted into a (leaf) node that contains ≤ 3 entries, the new entry is simply added in that node
Note:
- We have seen 2 examples already (see above !!!)
- Teaching note:
- I will now do a
"evolving" example:
- I start with an empty
2,4-tree
- I will keep inserting entries into the 2,4-tree and see how the 2,4-tree changes
- I start with an empty
2,4-tree
- I will now do a
"evolving" example:
- Examples: inserting into
a 2,4-tree
starting with an empty tree

Comments:
- The first insert (insert(4))
will create a node
- The next 2 insert operations
will simply add entries
to this node
These are what I call easy cases:
- when the (leaf) node has space to hold one entry, you just add the entry in the node.
- The first insert (insert(4))
will create a node
- Overflow in the root node:
- The
root node has
3 entries
and will
overflow
when another entry is inserted
Example:

Comment:
- A node with
4 entries
does not exist.
- I drew a node with 4 entries to show you how the keys must be distributed !!!
- The
root node has
3 entries
and will
overflow
when another entry is inserted
- Handling an overflow situation:
- Let the keys and
links
in the overflow root node be
as follows:

(Notice that p1, p2, p3, p4 and p5 can be references to subtrees !!!)
- Create a new nodes
and copy into this new node:
p4 k4 p5while leaving the entry k3 out:

- Create a new root node
using the entry k3 and
make the other 2 nodes the
subtrees:

- Let the keys and
links
in the overflow root node be
as follows:
- This operation is called
splitting.... (quite obvious)
- Note:
- The height of the
2,4-tree is
increased by 1 when
the root node is
split !!!
- In fact, the only time that the height of of a 2,4-tree will increased is when the root node is split
- The height of the
2,4-tree is
increased by 1 when
the root node is
split !!!
- Example:

- We need to insert
more entries to
get to another node split:

- When we do an
insert(5),
we need to
split the
non-root node (3,4,6):

- Splitting a
non-root node
(pay special attention to the
node references):
- Node p overflows and
needs to be split:

- Create a new node and
move (p4, e4, p5)
into the new node
while leaving
the entry
e3 out:

Note:
- The subtrees p4 and p5 have a new parent node !!!
- Insert the
left over entry e3 into
the parent node
along with the new node as
it's
right subtree:

- Node p overflows and
needs to be split:
- Result:
- Insert(5):

- 2,4-tree after node split:

Repeated warning:
- Notice that subtrees p4 and p5 have a new parent node !!!
- Insert(5):
- Comment:
- You have now
learn everything you
need to insert a new entry
into a 2,4-tree
- I will explain
cascaded node splitting
next ---
which is not a new technique....
You just repeat the node splitting at a high level in the tree.
- I will explain
cascaded node splitting
next ---
which is not a new technique....
- Here a summary on what's ahead:
- You will always insert
a new entry into a
leaf node
- If the leaf node has
≤ 2 entries, you insert the new
entry and you are done
Otherwise:
- Split the node
- If you splitted a node
in the previous step,
an entry would have been
inserted into
the parent node !!!
If the parent node has ≤ 2 entries, you insert the new entry and you are done
Otherwise:
- Split the parent node !!!
And so on !!!
(Can you smell recursion ???)
- You will always insert
a new entry into a
leaf node
- You have now
learn everything you
need to insert a new entry
into a 2,4-tree
- This is like the
calm before the
storm...
- Let's fill the the tree some more...
These insertion are of the simple type:

- We node do insert(11), causing
a node to split and
fill up its
parent node:

- The split operation:
(we have seen this twice already...)

- Notice that:
- We added one new node
- The new node
is the right child of
the key 10 that
was moved upward (into the parent node)
- The 2,4 - tree has a full internal node (the root node with the 3 entries (5, 10, 12)) and it is ripe for a cascaded split !!!
- We added one new node
- OK, now the fire works...
Cascading splits/insertions:
- An insert operation that
causes an overflow
not only split the overflow node,
but
will also:
- Perform an insert operation in the parent node of the overflow node
- The insert operation
in the parent node
can again cause an
overflow
in the parent node
This will cause:
- The parent node to
split
- Perform an insert operation in the parent's parent node of the overflow node
- The parent node to
split
- And so on...
- An insert operation that
causes an overflow
not only split the overflow node,
but
will also:
- Note:
- The process will eventually
stop:
- When a node that receives a
new entry has
≤ 2 entries
- Or if all parent nodes towards the
root nodes are
all filled (= 3 entries),
the split process will reach
the (full) root node and
causes the root node to split
- When the root node splits,
we create a new root node:

- The new root node
will only contain
one key...
and the height of the 2,4-tree is increased by 1 !!!
- When the root node splits,
we create a new root node:
- When a node that receives a
new entry has
≤ 2 entries
- The process will eventually
stop:
- Fact:
- The height of a 2,4-tree is increased (by 1) only when the root node is split !!!
- Example: cascaded splits/insertions
- insert(17) causes
a node to
overflow:

- The split operation
causes an insertion in the
parent node...
....and the parent node overflows:
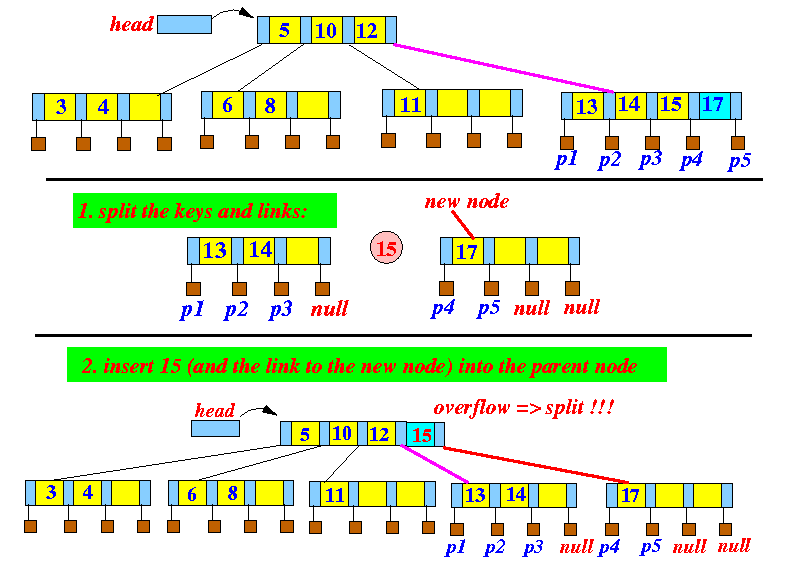
- insert(17) causes
a node to
overflow:
- Split
the parent node...
Because the parent node is the root node, the split operation will create a new root node:
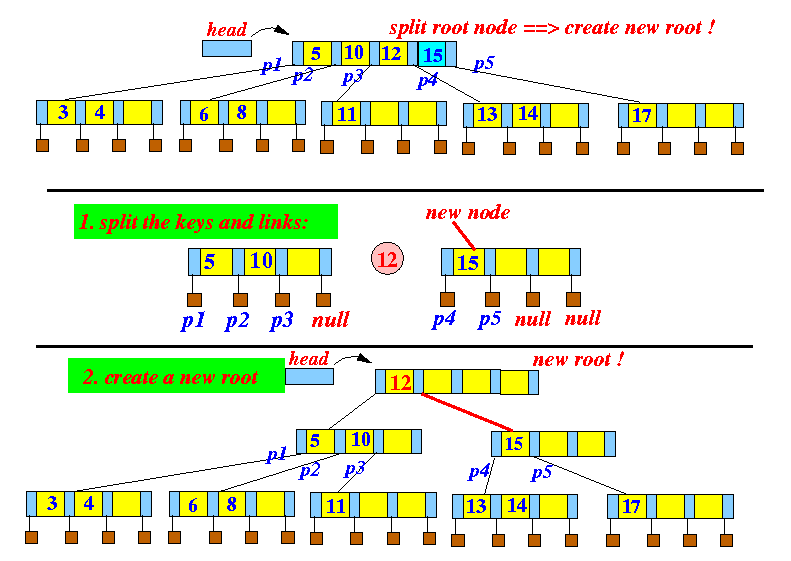
- put(k,v) pseudo code:
Entry put(Key k, Value v) { /* ------------------------- Special case: empty tree ------------------------- */ if ( root == null ) { root = create new root node; root.entry[0] = (k,v); return(null); } /* ----------------------------------- Find key k in the tree.... ----------------------------------- */ p = keySearch(k); // keySearch: see click here /* ----------------------------------- Handle the case when key k is found ----------------------------------- */ if ( p != null && p.key == k ) { p.value = v; return (old Value in p); // Done... } /* ------------------------------------------------ Key k not found... Then: keySearch(k) ended at a node p with only external children node ------------------------------------------------ */ p = Node of (2,4)-tree where keySearch(k) ended; // This is a node with only external children node e = new Entry(k, v); // Create entry using k and v /* ------------------------------------------------ Invoke a recursive insert procedure (It MUST be recursive because we may need to REPEAT the procedure further up the tree !!! (That is when a node overflows and splits !!!) ------------------------------------------------ */ insertEntryInThisNode(e, null (the right subtree), p); // Parameters: // e = the new entry that is inserted // second parameter = the RIGHT subtree of e // p = node used to insert e }Java code:
/* ================================================ put(k): insert (k,v) ================================================ */ Integer put(String k, Integer v) { Node p; Entry e; /* ------------------------ Special case: empty tree ------------------------ */ if ( root == null ) { p = new Node(); p.e[0] = new Entry(k, v); root = p; p.parent = p; // Parent(root) == root return(null); } /* ------------------------ Other cases ------------------------ */ e = keySearch(k); // keySearch sets "searchEndPos = last node visited /* ------------------------ key found, update value ------------------------ */ if ( e != null && k.compareTo(e.key) == 0 ) { Integer oldValue; System.out.print("*** Update value of " + k + " in entry " + e); oldValue = e.value; e.value = v; return(oldValue); } /* ------------------------------------------ key not found: insert (k,v) in node "searchEndPos" ------------------------------------------ */ e = new Entry(k,v); insertEntryInThisNode(e, null, searchEndPos); return(null); }
- insertEntryInThisNode(e, rightSubTree, p):
the recursive help function
that inserts
[e=(k,v), e's rightSubTree]
into the node p:
(Pseudo code):
/* ----------------------------------------------------------- insertEntryInThisNode( e, rightSubTree, p ): inserts: [e, e's rightSubTree] into node p Note: Since p contains multiple entries, we must insert e in the correct position inside p !!! This will require moving some elements in an array !! ------------------------------------------------------------ */ void insertEntryInThisNode(Entry e, Node rightSubTree, Node p) { /* ---------------------------------------------- Case 1: node p has space left for new entry ---------------------------------------------- */ if ( # enties in p <= 2 ) { insert [e, rightSubTree] in the correct position inside p return; } /* ------------------------------------------------------------- Case 2: node p is full - split node, and recurse up the tree Situation: p's parent / / p: [ p1 k1 p2 k2 p3 k3 p4 ] is full ^ | k is inserted into p Note: node p is already PART of the 2,4-tree and will remain under the SAME parent A NEW node q will be created that will contain the RIGHT half of the overflow entries. The NEW node q has the SAME parent node as p ------------------------------------------------------------- */ q = new Node(); // Make a new node to hold entries // stored in the RIGHT half of the split Sort the 3 entries and 4 links in node p p: (full) -------------------- p1 k1 p2 k2 p3 k3 p4 and the inserted entry k and its rightSubTree link as follows: if ( k < k1 ) { Split into: p1 k rightSubTree k1 p2 k2 p3 k3 p4 ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ ^^^^^^^^ p contains: p1 k rightSubTree k1 p2 q contains: p3 k3 p4 n = k2 (Note: q is n's right tree) } else if ( k < k2 ) { Split into: p1 k1 p2 k rightSubTree k2 p3 k3 p4 ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ ^^^^^^^^ p contains: p1 k1 p2 k rightSubTree q contains: p3 k3 p4 n = k2 (Note: q is n's right tree) } else if ( k < k3 ) { Split into: p1 k1 p2 k2 p3 k rightSubTree k3 p4 ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ p contains: p1 k1 p2 k2 p3 q contains: rightSubTree k3 p4 n = k (Note: q is n's right tree) } else { Split into: p1 k1 p2 k2 p3 k3 p4 k rightSubTree ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ ^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^^ p contains: p1 k1 p2 k2 p3 q contains: p4 k rightSubTree n = k3 (Note: q is n's right tree) } # Before: # p's parent # / # / # p: [ p1 k1 p2 k2 p3 k3 p4 ] is full # ^ # | # k is inserted into p # # Now: # # p's parent # / q is n's RIGHT child !!! # / # p: [ p1 k1' p2 k2' p3 ] q: [ p3 k3' k4 ] # # To complete the insert operation: insert [ n q (= n's RIGHT tree)] in p's parent ! # I.e., we must make this tree: # # # [ .. p .. n q ...] # / \ # / \ # p: [ p1 k1' p2 k2' p3 ] q: [ p3 k3' k4 ] /* ---------------------------------------------- Handle p = root DIFFERENTLY!!! ---------------------------------------------- */ if ( p == root ) { /* --------------------------------------------------------------- Special case: SPLIT the root node (tree wil grow in height !!! --------------------------------------------------------------- */ newRoot = new Node(); newRoot = p n q; // p = left subtree, n = key, q = right subtree p.parent = newRoot; q.parent = newRoot; root = newRoot; // New root node } else { /* ------------------------------------------------- Make this link: p.parent: [ .. p .. n q ...] | ^ / \ / \ p: [ p1 k1' p2 k2' p3 ] q: [ p3 k3' k4 ] -------------------------------------------------- */ q.parent = p.parent; // q is p's parent's child... /* ----------------------------------------------------- Insert [n q] in p.parent, i.e., make this happen: p.parent: [ .. p .. n q ... ] / \ / \ p: [ p1 k1' p2 k2' p3 ] q: [ p3 k3' k4 ] ------------------------------------------------------- */ insertEntryInThisNode(n, q, p.parent); } }
- Java code:
/* ======================================================= insertEntryInThisNode(e, rightSubTree, p): 1. insert "e" and its "rightSubTree" in node p 2. if over flow, split and insert in parent ======================================================= */ public void insertEntryInThisNode(Entry e, Node rightSubTree, Node p) { int i; Node q; Entry n; if ( p.e[2] == null ) { /* ----------------- There is space ----------------- */ insertEntryDirectlyInNode(e, rightSubTree, p); // Find the spot for (e, rightSubTree) inside p // We may need to move array elements !!! } else { /* ----------------------------------------------- There is no more space .... Split insert !!! ----------------------------------------------- */ /* ======================================= Make a virtual node with 4 keys (It's easier to sort in an array !!!) ======================================= */ Entry[] x_e = new Entry[4]; Node[] x_child = new Node[5]; x_child[0] = p.child[0]; /* ================================== 1. Fill with keys < k ================================== */ i = 0; while ( i < 3 && p.e[i].key.compareTo(e.key) < 0 ) { x_e[i] = p.e[i]; x_child[i+1] = p.child[i+1]; i++; } /* ================================================= 2. Then fill it with e and it's RIGHT subtree ================================================== */ x_e[i] = e; x_child[i+1] = rightSubTree; /* ======================================================== 3. Finally, fill it with the rest (these keys are > k) ======================================================== */ while ( i < 3 ) { x_e[i+1] = p.e[i]; x_child[i+2] = p.child[i+1]; i++; } /* ===================================== Distribute keys into p and q p: first 2 keys q: last key ===================================== */ p.child[0] = x_child[0]; p.e[0] = x_e[0]; // first key p.child[1] = x_child[1]; p.e[1] = x_e[1]; // second key p.child[2] = x_child[2]; p.e[2] = null; p.child[3] = null; n = x_e[2]; // n = 3rd key q = new Node(); // Make a new node to hold the RIGHT half /* ============================================= Move entries and substrees into NEW node q ============================================= */ q.child[0] = x_child[3]; q.e[0] = x_e[3]; // Last key q.child[1] = x_child[4]; /* ============================================= Change the PARENT links of these subtrees !!! ============================================= */ if ( q.child[0] != null ) // I forgot these 2 if-statements and q.child[0].parent = q; // has a hard time finding this bug... if ( q.child[1] != null ) q.child[1].parent = q; /* ---------------------------------------------- Handle p = root DIFFERENTLY!!! ---------------------------------------------- */ if ( p == root ) { /* Split root */ Node newRoot = new Node(); newRoot.child[0] = p; newRoot.e[0] = n; newRoot.child[1] = q; p.parent = newRoot; q.parent = newRoot; root = newRoot; } else { // ************************* Recurse ! q.parent = p.parent; insertEntryInThisNode(n, q, p.parent); } } }
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- The Tree24.java Prog file: click here
- The Node.java Prog file: click here
- The Entry.java
Prog file:
click here
- A test program TestProg.java Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link(s) and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac TestProg.java
- To run: java TestProg
Sample output:
vvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvv Enter a key: a Enter a value: 1 put(a,1): == After put(a,1): 0:(a,(-),(-)) vvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvv cheung@home6(377)> java TestProg vvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvv Enter a key: a Enter a value: 1 put(a,1): == After put(a,1): 0:((a,1),(-),(-)) vvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvv Enter a key: b Enter a value: 2 put(b,2): Insert b in node ((a,1),(-),(-)) == After put(b,2): 0:((a,1),(b,2),(-)) vvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvv Enter a key: b Enter a value: 4 put(b,4): *** Update value of b in entry (b,2) == After put(b,4): 0:((a,1),(b,4),(-)) vvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvv Enter a key: c Enter a value: 7 put(c,7): Insert c in node ((a,1),(b,4),(-)) == After put(c,7): 0:((a,1),(b,4),(c,7)) vvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvvv Enter a key: d 4 Enter a value: put(d,4): *** Split insert ! ---- Transitional node = a b (c) d == After put(d,4): 1:((d,4),(-),(-)) 0:((c,7),(-),(-)) 0:((a,1),(b,4),(-))