- Prelim:
- Before you can delete an entry, you must find that entry first
- Preliminary Delete procedure:
Entry remove(Key k) { e = keySearch(k, root); // Find entry containing key k // starting with the root node if ( e == null ) return; // Not found, exit... Delete the entry e from the node that contains e. }
- The rest of this
webpage will discuss how to:
- Delete the entry e from the node that contains e.
- The easiest delete operation is:
- Deleting an entry in a leaf node with: ≥ 2 entries
- How to delete an entry e in
this case:
- Simply remove the entry e from the (containing) node p
- Example:
- Delete key 6 from this tree:

- Simply delete the
key 6 from the node
(and reshuffle the remaining keys
within the node):

- Delete key 6 from this tree:
- I have to draw larger 2,4-trees
and there is not enough space
to display the
entire node....
- Due to space limitation,
I will use a simplified way
to represent nodes in the
(2,4)-tree:

- The delete procedure for an
entry stored in a
non-leaf node is
similar to the one
used in
Binary Search Trees:
- Delete the entry
from the non-leaf node...
- Then:
- Replace the deleted entry with its successor or predecessor entry
Note:
- The successor/predecessor
entry will
always be stored inside
a leaf node !!!)
- Therefore:
- We will always end up "deleting" an entry stored inside a leaf node
Example:
- delete entry with
key = 12:

- Delete the entry:

- Replace the
deleted entry with
its successor
(or predecessor):

- Delete the entry
from the non-leaf node...
- How to find the
successor of some
entry:
- Where is the
successor entry:
- The left most entry in the right tree of an entry
- Example:

- Procedure: (just like the one used in the
Binary Search Tree)
- Go right once
- Go left all the way down
- Where is the
successor entry:
- How to find the
predecessor of some
entry:
- Where is the
successor entry:
- The right most entry in the left tree of an entry
- Example:

- Procedure: (just like the one used in the
Binary Search Tree)
- Go left once
- Go right all the way down
- Where is the
successor entry:
- Repeated example of deletion now with
successor location algorithm:
- Delete key 12 from this tree:

- First,
delete the
key 12 from the node
(do not
reshuffle the remaining keys
within the node):

Find the successor entry....
- Then,
replace the
deleted entry with
its
successor entry
(or its predecessor)

- Delete key 12 from this tree:
- Important fact:
- The deletion an
entry from an node with
internal children node
(i.e, from a
non-leaf node)
will eventually result
in:
- "moving" (deleting) an entry from a node with only external children nodes (= a leaf node) the lowest level
(This is exactly like a delete operation in a binary search tree)
- The deletion an
entry from an node with
internal children node
(i.e, from a
non-leaf node)
will eventually result
in:
- Note:
- The remainder of this webpage will assume that we are "deleting (or moving)" an entry from a node with only external children nodes
- Deleting an entry e from a
node p with
exactly 1 entry:
- will produce an
empty node....
- This condition is called an underflow
- will produce an
empty node....
- There are 2 methods used to
handle underflow:
- Transfer one entry from
an immediate sibling node
(and the parent node)
into the underflow (empty) node
- Merge the underflow node (with has 0 entries) with one of the immediate sibling nodes
- Transfer one entry from
an immediate sibling node
(and the parent node)
into the underflow (empty) node
- Detailed procedure
for handling an underflow situation in
the node p
(i.e., node p is now
empty):
- If one (left or right)
immediate sibling node of
node
has ≥ 2 entries:
- Transfer the
entry from node p's parent
to replace
the
deleted entry e
in node p,
and
- Transfer an entry from the immediately sibling to node p's parent
- Transfer the
entry from node p's parent
to replace
the
deleted entry e
in node p,
and
- If node p's
immediate sibling nodes
have 1 entry:
- Merge:
- Node p's parent entry
(1 entry)
- Node p's sibling node (with 1 entry in it)
into one single node
- Node p's parent entry
(1 entry)
Notice that:
- The merge operation will remove an entry from node p's parent node !
Consequently:
- Node p's parent node can itself become underflow (= empty) !!!
Solution:
- Repeat
the same procedure
at p's parent node
- In other words:
- Solve the same problem at a node higher up in the tree
- In yet other words:
- Use recursion !!!
- Merge:
- If one (left or right)
immediate sibling node of
node
has ≥ 2 entries:
- Terminology:
- Sibling nodes are
nodes that
share the same parent node
Example:

- What I (not in text books)
call immediate sibling nodes, are
sibling nodes that are
next to each other
Example:


- Sibling nodes are
nodes that
share the same parent node
- How to find the
immediate sibling nodes:
- The immediate right sibling
node of a node p is
found at the
root of the
"next right" subtree
of
p's parent node
Example:

- The immediate left sibling
node of a node p is
found at the
root of the
"last left" subtree
of
p's parent node
Example:

- The immediate right sibling
node of a node p is
found at the
root of the
"next right" subtree
of
p's parent node
- Technique:
- If an underflow condition occurs
in a delete operation, and one of the
immediate sibling nodes
has ≥ 2 entries,
we can
solve the
underflow condition
by:
- A 3-way transfer
(of one entry) from:
sibling node ====> parent node ====> underflow (empty) node
- A 3-way transfer
(of one entry) from:
- If an underflow condition occurs
in a delete operation, and one of the
immediate sibling nodes
has ≥ 2 entries,
we can
solve the
underflow condition
by:
- Transfer with its
right sibling:
- Let's start with a delete operation
that caused an
underflow:
remove(6)

- Transfer:
- left most entry
in sibling node
⇒ "search key" entry in parent node
⇒ left most entry in underflow (empty) node
Graphically:

Note:
- In addition to transfering
the entries, we must also
transfer some references
- Specifically, we must also transfer the reference in red in the above figure
- left most entry
in sibling node
- Let's start with a delete operation
that caused an
underflow:
remove(6)
- Transfer with its
left sibling:
- Delete the
entry:

- Transfer:
- right most entry
in sibling node
⇒ "search key" entry in parent node
⇒ left most entry in underflow (empty) node
Graphically:

Note:
- In addition to transfering
the entries, we must also
transfer some references
- Specifically, we must also transfer the reference in red in the above figure
- right most entry
in sibling node
- Delete the
entry:
- Very important note:
- When we transfer a subtree
reference into another node,
we must:
- Update the parent reference of the root node in the subtree !!!
- Example:
- We will see later that
the delete operation can
cause cascaded transfers
up the tree.
We may have to perform a transfer where the red reference is a reference to a subtree:

- After the
transfer operation, the
parent node of
the subtree has changed:

- You must update the
parent reference
of the root node in the
subtree !!!

- We will see later that
the delete operation can
cause cascaded transfers
up the tree.
- When we transfer a subtree
reference into another node,
we must:
- Technique:
- If an underflow condition occurs
in a delete operation, and BOTH
immediate sibling nodes
have 1 entry,
we must
solve the
underflow condition
by:
- A 3-way merge
operation using
one of the sibling node + the parent key entry + underflow (empty) node (which has a reference)
- A 3-way merge
operation using
- If an underflow condition occurs
in a delete operation, and BOTH
immediate sibling nodes
have 1 entry,
we must
solve the
underflow condition
by:
- Example:

Transfering an entry form the sibling node will cause an underflow at the sibling node itself !
- Solution:
- Merge entries
from your
parent node and
your sibling node
to create a
"new" node
- The "new" node will be the root node of the subtree formed from yourself and your sibling node
- Merge entries
from your
parent node and
your sibling node
to create a
"new" node
- The merge operation
(on node p that
contained entry 10):
- Node p's parent entry (here: 8)
- Node p's sibling entry (here: 6)
Result:
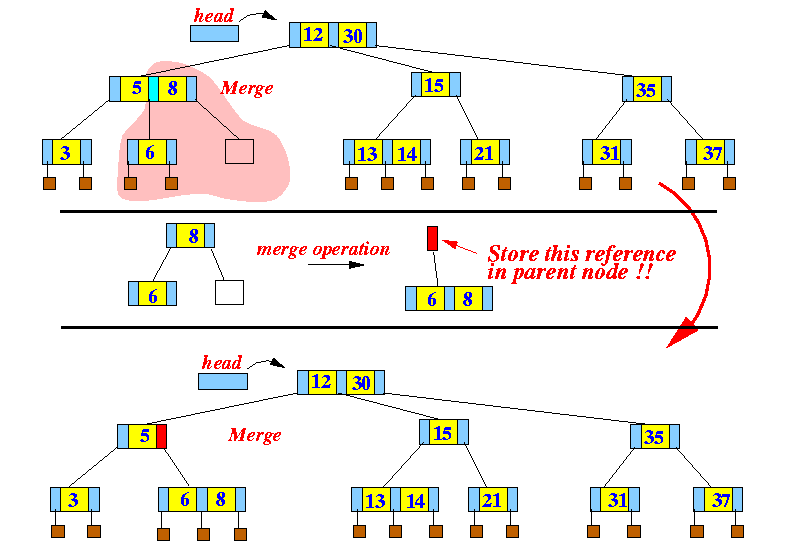
- Merging
with your left sibling:
- Graphically:

- The left merge
will replace:
- Your own subtree pointer p1
- The parent key
- Your left sibling subtree pointer p2
by one subtree pointer:

- Graphically:
- Merging
with your right sibling:
- Graphically:

- The right merge
will replace:
- Your own subtree pointer p1
- The parent key
- Your right sibling subtree pointer p2
by one subtree pointer:

- Graphically:
- Notice that:
- The ordering of the subtree links in the merged node are different in the left and the right merge operations !!!
- The merge operation will
"remove" one entry from
the parent node
- Underflow condition at the parent node:
- If the parent node of the delete target node contains one (1) entry, the parent node will suffer the underflow condition
- Example:
- Delete key entry 7:

- After the merge operation:

- Delete key entry 7:
- Handling the underflow
condition in the parent node:
- Exactly
the same method is used:
- If node has
a immediate sibling
with ≥ 2 entries, then:
- perform a transfer
Note:
- Here we will discuss how to copy the subtree links - because they are not null
- If node has
a immediate sibling
with only 1 entry, then:
- perform a merge
- If node has
a immediate sibling
with ≥ 2 entries, then:
- Exactly
the same method is used:
- Example:
- Note: transfer
with the
left sibling
- When you perform a
transfer operation
with your left sibling,
you will also
transfer the right most
subtree link
into the sibling node
- The right most
subtree link will occupy the
first slot
in the entry
- Example:

- When you perform a
transfer operation
with your left sibling,
you will also
transfer the right most
subtree link
into the sibling node
- Example:
- Notice that:
- The second merge operation
again
"removes" one entry from
the grand parent node
of the target delete node
- The grand parent node can
also suffer
a underflow condition....
- This cascaded underflow/merge
sequence will
eventually end
when an entry is removed
from the root node
- If the root node has
one (1) entry,
the removal will
can the root node to
become
empty
An empty root node is discarded
(and the previously merged node becomes the new root !)
- The second merge operation
again
"removes" one entry from
the grand parent node
of the target delete node
- An example
where a deletion
causes the root node
to underflow
(and then removed):
- Delete key entry 7:

There is an underflow....
- The sibling node has
1 entry
⇒
merge

There is another underflow....
- The sibling node has
1 entry
⇒
merge
(again)

There is another underflow.... now we reach the root node !!!
- The sibling node has
1 entry
⇒
merge
(yet again)

- The root node
has underflowed
⇒
remove it

DONE !!!
- Delete key entry 7:
- Psuedo code of remove(k):
Entry remove(Key k) { Entry e; Node p; /* ----------------------- Find k to remove ----------------------- */ e = keySearch(k); /* ======================= Check if k exists... ======================= */ if ( e == null ) { return(null); // Not found, nothing to delete... } /* ------------------------------ Phase 1: remove entry e ------------------------------ */ p = node containing e; if ( p has an internal child node ) { /* ---------------------------- Replace e with e's successor ---------------------------- */ succ = successor entry of the deleted entry e; Swap p.e with succ entry; /* ----------------------------------------------------- The target entry is now in the successor's location ----------------------------------------------------- */ e = succ; p = node containing succ entry; } delete e from p and reshuffle entries in p; // Delete entry // Also: remember the old value /* *********************************************** Handle a possible underflow situation *********************************************** */ if ( p has ≤ 1 entry ) { handleUnderflow(p); // This is a recursive routine ! } return the old value in e; // No underflow; done }
- Java code:
public Integer remove(String k) { Entry e; Node p; int pos; /* ----------------------- Find k to remove ----------------------- */ e = keySearch(k); /* ======================= Check if k exists... ======================= */ if ( e == null ) { return(null); // Not found, nothing to delete... } Entry old = e; // Save for return value /* ---------------------------------------------------- Note: searchEndPos = node containing entry e ---------------------------------------------------- */ p = searchEndPos; /* ---------------------------------------------------- Find position of e inside p: p --> | T0 | e0 | T1 | e1 | T2 | e2 | T3 | Which of the e? is e ???? ---------------------------------------------------- */ for ( pos = 0; pos < 3; pos++ ) if ( p.e[pos] == e ) break; /* ---------------------------------------------------- Delete entry e from 2,4-tree ---------------------------------------------------- */ if ( p.child[0] == null /* => leaf node */ ) { /* ================================================== Delete entry e from node Note: this is done by MOVING right most entries into the slot containing e !!! ================================================== */ for ( int i = pos; i < 2; i++ ) p.e[i] = p.e[i+1]; p.e[2] = null; // The right most entry is for sure null ! } else { /* ------------------------------------------------ Non-leaf: replace e with e's successor ------------------------------------------------ */ Node q; /* ------------------------------------------------ Use q to traverse to p's successor ------------------------------------------------ */ System.out.println("pos = " + pos); q = p.child[pos+1]; // Go right while ( q.child[0] != null ) q = q.child[0]; // Go left all the way down. /* ------------------------------------------------ Delete e ------------------------------------------------ */ System.out.println("Replace " + p.e[pos] + " with: " + q.e[0]); p.e[pos] = q.e[0]; // Replace e by e's successor for ( int i = 0; i < 2; i++ ) // Delete e's successor in q q.e[i] = q.e[i+1]; q.e[2] = null; /* ----------------------------------------------------- The target entry is now the successor's location ----------------------------------------------------- */ p = q; // node where entry was deleted System.out.println("Result: p = " + p); } /* *********************************************** Check for a possible underflow situation *********************************************** */ if ( p.e[0] == null ) { handleUnderflow(p, null); // Node p is empty // Second parameter is a subtree // hung under p } return old.value; // Return old value }
- Psuedo code of handleUnderflow(Node p):
/* ------------------------------------------------------- handleUnderflow(p): handle the overflow condition in node p (p = empty !) Node format: p: {p1, k1, p2, k2, p3, k3, p4} k1, k2, k3 are keys (with values) p1, p2, p3, p4 are subtree pointers Node p (input) is empty - i.e., it has NO keys BUT: p.p1 points to the subtree of the underflow node ------------------------------------------------------- */ void handleUnderflow(Node p) { /* ---------------------------- Check if p is the root ---------------------------- */ if ( p == root ) { root = p.p1; // New root... return; // DONE ! } /* ------------------------------------------------------------- Solve underflow with a TRANSFER against your right sibling ------------------------------------------------------------- */ if ( p.right_sibling != null && p.right_sibling has >= 2 entries ) { /* ------------------------------------- Transfer p1 and k1 from right sibling See: click here ------------------------------------- */ s = p.right_sibling; pa = p.parent; i = index of subtree p in parent pa; // i = 1, 2 or 3 /* -------------------------------------------------- Example: if i == 1, then: pa: | p1 | k1 | p2 | k2 | p3 | k3 | p4 | / \ p s (s is right sibling of p) --------------------------------------------------- */ /* ----------------------
Transfer data into p
---------------------- */
p.k1 = pa.ki; // Transfer entry from parent
p.p2 = s.p1; // Transfer left most subtree from sibling
/* -----------------------------
Transfer data into parent pa
----------------------------- */
pa.ki = s.k1; // Transfer left most key from sibling
delete p1 and k1 from s;
return; // DONE...
}
/* -------------------------------------------------------------
Solve underflow with a TRANSFER against your left sibling
------------------------------------------------------------- */
else if ( p.left_sibling != null && p.left_sibling has >= 2 entries )
{
/* ------------------------------------------------
Transfer p(Last) and k(Last) from left sibling
See: click here
------------------------------------------------ */
s = p.left_sibling;
pa = p.parent;
i = index of subtree p in parent pa; // i = 2, 3 or 4
/* ----------------------------------------------
Example:
if i == 3, then:
pa: | p1 | k1 | p2 | k2 | p3 | k3 | p4 |
/ \
s p
(s is left sibling of p)
----------------------------------------------- */
/* ----------------------
Transfer data into p
---------------------- */
p.k1 = pa.ki; // Transfer entry from parent
p.p2 = s.p1; // Transfer left most subtree from sibling
/* -----------------------------
Transfer data into parent pa
----------------------------- */
pa.ki = s.k1; // Transfer left most key from sibling
delete p1 and k1 from s;
return; // DONE...
}
/* -------------------------------------------------------------
Solve underflow with a TRANSFER against your left sibling
------------------------------------------------------------- */
else if ( p.left_sibling != null && p.left_sibling has >= 2 entries )
{
/* ------------------------------------------------
Transfer p(Last) and k(Last) from left sibling
See: click here
------------------------------------------------ */
s = p.left_sibling;
pa = p.parent;
i = index of subtree p in parent pa; // i = 2, 3 or 4
/* ----------------------------------------------
Example:
if i == 3, then:
pa: | p1 | k1 | p2 | k2 | p3 | k3 | p4 |
/ \
s p
(s is left sibling of p)
----------------------------------------------- */
 /* ----------------------
Transfer data into p
---------------------- */
p.k1 = pa.k(i-1); // Transfer entry from parent
p.p2 = p.p1; // Green link
p.p1 = s.p(Last); // Cyan link
/* -----------------------------
Transfer data into parent pa
----------------------------- */
pa.k(i-1) = s.k(Last);
delete p(Last) and k(Last) from s;
return; // DONE...
}
/* -------------------------------------------------------------
Solve underflow with a MERGE with your right sibling
------------------------------------------------------------- */
else if ( p.right_sibling != null )
{
/* ---------------------------
Merge with right sibling
See: click here
---------------------------*/
s = p.right_sibling;
pa = p.parent;
i = index of subtree p in parent pa; // i = 1, 2 or 3
/* --------------------------------------------------
Example:
if i == 1, then:
pa: | p1 | k1 | p2 | k2 | p3 | k3 | p4 |
/ \
p s
(s is right sibling of p)
--------------------------------------------------- */
/* ----------------------
Transfer data into p
---------------------- */
p.k1 = pa.k(i-1); // Transfer entry from parent
p.p2 = p.p1; // Green link
p.p1 = s.p(Last); // Cyan link
/* -----------------------------
Transfer data into parent pa
----------------------------- */
pa.k(i-1) = s.k(Last);
delete p(Last) and k(Last) from s;
return; // DONE...
}
/* -------------------------------------------------------------
Solve underflow with a MERGE with your right sibling
------------------------------------------------------------- */
else if ( p.right_sibling != null )
{
/* ---------------------------
Merge with right sibling
See: click here
---------------------------*/
s = p.right_sibling;
pa = p.parent;
i = index of subtree p in parent pa; // i = 1, 2 or 3
/* --------------------------------------------------
Example:
if i == 1, then:
pa: | p1 | k1 | p2 | k2 | p3 | k3 | p4 |
/ \
p s
(s is right sibling of p)
--------------------------------------------------- */
 p.k1 = pa.ki
p.p2 = s.p1;
p.k2 = s.k1;
p.p3 = s.p2;
pa.pi = p;
delete pa.ki and pa.p(i+1) from pa;
}
else
{
/* ---------------------------
Merge with left sibling
See: click here
---------------------------*/
s = p.left_sibling;
pa = p.parent;
i = index of subtree p in parent pa; // i = 2, 3 or 4
/* ----------------------------------------------
Example:
if i == 3, then:
p(i-1) pi
pa: | p1 | k1 | p2 | k2 | p3 | k3 | p4 |
/ \
s p
(s is left sibling of p)
----------------------------------------------- */
p.k1 = pa.ki
p.p2 = s.p1;
p.k2 = s.k1;
p.p3 = s.p2;
pa.pi = p;
delete pa.ki and pa.p(i+1) from pa;
}
else
{
/* ---------------------------
Merge with left sibling
See: click here
---------------------------*/
s = p.left_sibling;
pa = p.parent;
i = index of subtree p in parent pa; // i = 2, 3 or 4
/* ----------------------------------------------
Example:
if i == 3, then:
p(i-1) pi
pa: | p1 | k1 | p2 | k2 | p3 | k3 | p4 |
/ \
s p
(s is left sibling of p)
----------------------------------------------- */
 s.k2 = pa.k(i-1);
s.p3 = p.p1;
pa.p(i-1) = s;
delete pa.k(i-1) and pa.pi from pa;
}
/* ---------------------------------------------
Check if the merged node has underflowed...
--------------------------------------------- */
if ( pa has 0 entry )
{
handleUnderflow(pa); // Recurse...
}
}
s.k2 = pa.k(i-1);
s.p3 = p.p1;
pa.p(i-1) = s;
delete pa.k(i-1) and pa.pi from pa;
}
/* ---------------------------------------------
Check if the merged node has underflowed...
--------------------------------------------- */
if ( pa has 0 entry )
{
handleUnderflow(pa); // Recurse...
}
}
- Java code:
public void handleUnderflow(Node p, Node Z) { /* ================================================ Check if the root node is empty Note: This is a base case of the recursion.... ================================================ */ if ( p == root ) { root = Z; // Delete the empty root node p return; } /* ------------------------------------------------------------- Find the position of p inside p's parent node p's parent --> | T0 | e0 | T1 | e1 | T2 | e2 | T3 | ^ ^ ^ ^ | | | | pos=0 pos=1 pos=2 pos=3 Which of the T? is p ???? (pos = 0, 1, 2, or 3) ---------------------------------------------------- */ Node parent; int pos; parent = p.parent; for ( pos = 0; pos < 4; pos++ ) { if ( parent.child[pos] == p ) break; } /* ------------------------------------------------------------- TRY a TRANSFER with your RIGHT sibling ------------------------------------------------------------- */ if ( (pos <= 2 && parent.child[pos+1] != null) /* p has a right sibling */ && parent.child[pos+1].e[1] != null /* R sibling has >= 2 entries */) { /* ----------------------------------------------------------- Legend to understand the transfer operation: (assume pos=1) pos pos+1 | | V V parent --> | T0 | e0 | T1 | *e1* | T2 | e2 | T3 | | | p R_sibling Entry sandwiched between pos and pos+1 is moved into p !!! ----------------------------------------------------------- */ Node R_sibling = parent.child[pos+1]; System.out.println("Underflow !!!! ===> Transfer with R sibling " + R_sibling); p.child[0] = Z; // Hang Z if ( Z != null ) Z.parent = p; p.e[0] = parent.e[pos]; // Transfer parent's entry p.child[1] = R_sibling.child[0]; // Transfer sibling's subtree if ( p.child[1] != null ) p.child[1].parent = p; parent.e[pos] = R_sibling.e[0]; // Move sibling entry to parent /* =================================== Delete e[0] in R_sibling =================================== */ for ( int i = 0; i < 2; i++ ) // ... accomplish by shifting { R_sibling.e[i] = R_sibling.e[i+1]; R_sibling.child[i] = R_sibling.child[i+1]; } R_sibling.e[2] = null; // e[2] is now empty R_sibling.child[3] = null; // child[3] is now empty return; // Done } /* ------------------------------------------------------------- TRY a TRANSFER with your LEFT sibling ------------------------------------------------------------- */ else if ( pos > 0 /* p has a left sibling */ && parent.child[pos-1].e[1] != null /* L sibling has >= 2 entries */) { /* ----------------------------------------------------------- Legend to understand the transfer operation: (assume pos=1) pos-1 pos | | V V parent --> | T0 | *e0* | T1 | e1 | T2 | e2 | T3 | | | L_sibling p Entry sandwiched between pos-1 and pos is moved into p !!! ----------------------------------------------------------- */ Node L_sibling = parent.child[pos-1]; int last; System.out.println("Underflow !!!! ===> Transfer with L sibling " + L_sibling); /* ------------------------------------- Find the last entry in L_sibling ------------------------------------- */ for ( last = 0; last < 3; last++ ) if ( L_sibling.e[last] == null ) break; if ( last >= 3 || L_sibling.e[last] == null ) last--; p.child[0] = L_sibling.child[last+1]; // Transfer sibling's subtree if ( p.child[0] != null ) p.child[0].parent = p; p.e[0] = parent.e[pos-1]; // Transfer parent's entry p.child[1] = Z; // Hang Z if ( Z != null ) Z.parent = p; parent.e[pos-1] = L_sibling.e[last]; // Move sibling entry to parent /* =================================== Delete e[lst] in L_sibling =================================== */ L_sibling.e[last] = null; L_sibling.child[last+1] = null; return; // Done } /* ======================================================== We MUST use a merge operation Legend of the position of p inside p's parent node p's parent --> | T0 | e0 | T1 | e1 | T2 | e2 | T3 | ^ ^ ^ ^ | | | | pos=0 pos=1 pos=2 pos=3 ======================================================== */ /* ------------------------------------------------------------- TRY a MERGE with your RIGHT sibling ------------------------------------------------------------- */ else if ( pos != 3 /* No Right sibling possible */ && parent.child[pos+1] != null /* There is a right sibling */) { /* ----------------------------------------------------------- Legend to understand the merge operation: (assume pos=1) pos pos+1 | | V V parent --> | T0 | e0 | T1 | *e1* | T2 | e2 | T3 | | | p R_sibling Entry sandwiched between pos and pos+1 is moved into p !!! ----------------------------------------------------------- */ Node R_sibling = parent.child[pos+1]; // R_sibling has ONLY 1 entry ! System.out.println("Underflow !!!! ===> MERGE with R sibling " + R_sibling); p.child[0] = Z; // Hang Z if ( Z != null ) Z.parent = p; p.e[0] = parent.e[pos]; // Transfer parent's entry p.child[1] = R_sibling.child[0]; // Transfer sibling's subtree if ( p.child[1] != null ) p.child[1] .parent = p; p.e[1] = R_sibling.e[0]; // Transfer sibling (ONLY) entry p.child[2] = R_sibling.child[1]; // Transfer sibling's subtree if ( p.child[2] != null ) p.child[2] .parent = p; /* ====================================== Delete parent.e[pos] in parent node ====================================== */ for ( int i = pos; i < 2; i++ ) { parent.e[i] = parent.e[i+1]; parent.child[i+1] = parent.child[i+2]; } parent.e[2] = null; parent.child[3] = null; if ( parent.e[0] == null ) handleUnderflow(parent, p); } else // pos == 3, we must merge LEFT ... { /* ----------------------------------------------------------- Legend to understand the transfer operation: (assume pos=1) pos-1 pos | | V V parent --> | T0 | *e0* | T1 | e1 | T2 | e2 | T3 | | | L_sibling p Entry sandwiched between pos-1 and pos is moved into p !!! ----------------------------------------------------------- */ Node L_sibling = parent.child[pos-1]; // L_sibling has 1 entry ! System.out.println("Underflow !!!! ===> MERGE with L sibling " + L_sibling); L_sibling.e[1] = parent.e[pos-1]; // Transfer parent's entry L_sibling.child[2] = Z; // Hang Z if ( Z != null ) Z.parent = p; /* ====================================== Delete parent.e[pos] in parent node ====================================== */ for ( int i = pos-1; i < 2; i++ ) { parent.e[i] = parent.e[i+1]; parent.child[i+1] = parent.child[i+2]; } parent.e[2] = null; parent.child[3] = null; if ( parent.e[0] == null ) handleUnderflow(parent, L_sibling); } }
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- The Tree24.java Prog file: click here
- The Node.java Prog file: click here
- The Entry.java
Prog file:
click here
- A test program TestProg.java Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link(s) and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac TestProg.java
- To run: java TestProg
Sample output:
Legend: red denotes the next deleted entry darkred denotes the entries involved in op darkgreen shows when the involved entries end up 2:((m,6),(-),(-)) 3:((ka,6),(l,6),(-)) 1:((kb,6),(-),(-)) 0:((j,6),(k,6),(-)) 1:((h,8),(-),(-)) 2:((g,7),(-),(-)) 0:((e,5),(f,6),(-)) 0:((ba,6),(d,4),(i,9)) 1:((ca,6),(-),(-)) 1:((c,3),(-),(-)) 0:((bb,6),(-),(-)) 3:((b,2),(-),(-)) 2:((ae,6),(af,6),(-)) <--- will be replaced by (ae,6) 0:((ab,6),(ad,6),(ax,6)) 1:((ac,6),(-),(-)) 0:((a,1),(aa,6),(-)) ================================================================== == After remove(ad): 2:((m,6),(-),(-)) 3:((ka,6),(l,6),(-)) 1:((kb,6),(-),(-)) 0:((j,6),(k,6),(-)) 1:((h,8),(-),(-)) 2:((g,7),(-),(-)) 0:((e,5),(f,6),(-)) 0:((ba,6),(d,4),(i,9)) 1:((ca,6),(-),(-)) 1:((c,3),(-),(-)) 0:((bb,6),(-),(-)) 3:((b,2),(-),(-)) 2:((af,6),(-),(-)) 0:((ab,6),(ae,6),(ax,6)) 1:((ac,6),(-),(-)) 0:((a,1),(aa,6),(-)) <---- will TRANSFER with Left sibling ==================================================== Underflow !!!! ===> Transfer with L sibling ((a,1),(aa,6),(-)) == After remove(ac): 2:((m,6),(-),(-)) 3:((ka,6),(l,6),(-)) 1:((kb,6),(-),(-)) 0:((j,6),(k,6),(-)) 1:((h,8),(-),(-)) 2:((g,7),(-),(-)) 0:((e,5),(f,6),(-)) 0:((ba,6),(d,4),(i,9)) 1:((ca,6),(-),(-)) 1:((c,3),(-),(-)) 0:((bb,6),(-),(-)) 3:((b,2),(-),(-)) 2:((af,6),(-),(-)) <---- will MERGE with Left sibling 0:((aa,6),(ae,6),(ax,6)) 1:((ab,6),(-),(-)) 0:((a,1),(-),(-)) ======================================== Underflow !!!! ===> MERGE with L sibling ((af,6),(-),(-)) == After remove(b): 2:((m,6),(-),(-)) 3:((ka,6),(l,6),(-)) 1:((kb,6),(-),(-)) 0:((j,6),(k,6),(-)) 1:((h,8),(-),(-)) 2:((g,7),(-),(-)) 0:((e,5),(f,6),(-)) 0:((ba,6),(d,4),(i,9)) 1:((ca,6),(-),(-)) 1:((c,3),(-),(-)) 0:((bb,6),(-),(-)) 2:((af,6),(ax,6),(-)) 0:((aa,6),(ae,6),(-)) 1:((ab,6),(-),(-)) 0:((a,1),(-),(-))



