Insight on
how to improve the search performance of arrays
- Fact on
arrays:
- Array access is
(very) fast if
access uses
an
array index
|
- Fact on
dictionaries:
- Entries in
a dictionary are
looked up using
its
key
|
- The problem with
the ArrayMap
implementation of
the dictionary:
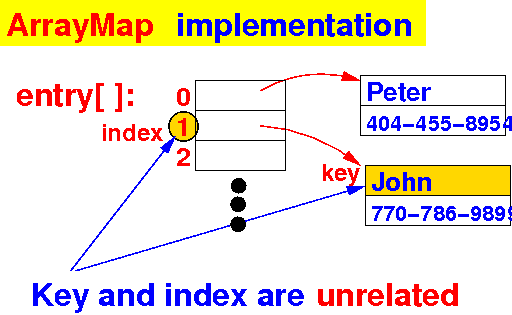
- Entries of
the dictionary are
stored
using an index that is
unrelated
to the
key
|
|
Insight on
how to improve the search performance of arrays
Hash functions
-
Hash function
H( ):
- A
hash function
is usually specified
as the composition of
2 functions:
where:
-
H1(k) =
the
hash code
function that
returns the
integer value of
the key k
-
H2(x) =
a
compression function
that
maps a
value
x
uniformly to
[0..(M-1)]
|
|
The hash code
of a key
- Fact:
- All
data inside a
computer is
stored as
a
binary number
|
- The
Object
class in
Java contains a
hashCode()
method that
returns the
data
stored in the Object as
an integer
- Examples:
- We can use the
hashCode()
method
as our
h1(k)
function
|
DEMO:
15-hashing/03-hashcode/HashCode.java
The compression function
h2(x)
- Notice from the
previous discussion on
the hash code H1(k):
- H1(k)
uses the data stored in the
key k to
compute (deterministically)
a hash code value
|
- The compression function
H2(x)
has 2 purpose:
- Make sure that the
return value is
in the range
[0..(M-1)]
(where M = size of array)
- Scatter/randomize the
input value
x = H1(k),
so that the value
H2(x) is
evenly/uniformly
distributed over the
range
[0..(M-1)]
|
- Why use
uniform randomization ?
- The array element used to store
the dictionary entry
(k, v) is:
array index = H(k) = H2( H1( k ) )
|
-
Uniform randomization will
minimize the
likelihood/chance that
2 different keys
being
hashed to the
same value (= array index)
(a.k.a.
collision)
|
|
Commonly used
compression function
- A commonly used
compression function is the
Multiply Add Divide (MAD) function:
H2(x) = ( ( ax + b ) % p ) % M where p = a prime number
^^^^^^^^^^^^^^
randomizes
|
- In my examples, I will use:
p = 109345121
a = 123
b = 456
|
Note:
- p must be
greater than
M
(i.e.:
p > M)
-- otherwise, you will not use the
full capacity of
the array
|
|
DEMO:
15-hashing/03-hashcode/HashValue.java
Summary on the
hashing technique
❮
❯

