Useful (summation) formula in algorithm analysis
|
Derivation of the
triangular sum formula
S = 1 + 2 + 3 + ... + (N-3) + (N-2) + (N-1) + N
= [1 + N] + [2 + (N-1)] + [3 + (N-2)] ...
<------------------------------------------>
N/2 terms
= N/2 (N+1)
= N(N+1)/2
|
Derivation of the
geometric sum formula 1
S = 1 + 2 + 4 + 8 + .... + N
2S = 2 + 4 + 8 + .... + N + 2N
--------------------------------------------
2S - S = 2N - 1
S = 2N - 1
|
Derivation of the
geometric sum formula 2
S = 1 + 1/2 + 1/4 + 1/8 + .... + 1/N
(1/2)S = 1/2 + 1/4 + 1/8 + .... + 1/N + 1/(2N)
-----------------------------------------------------------
S - (1/2)S = 1 - 1/(2N)
(1/2)S = 1 - 1/(2N)
S = 2 - 1/N
|
Derivation of the
Harmonic sum formula
S = 1 + 1/2 + 1/3 + 1/4 + .... + 1/N ≈ log(N)
|
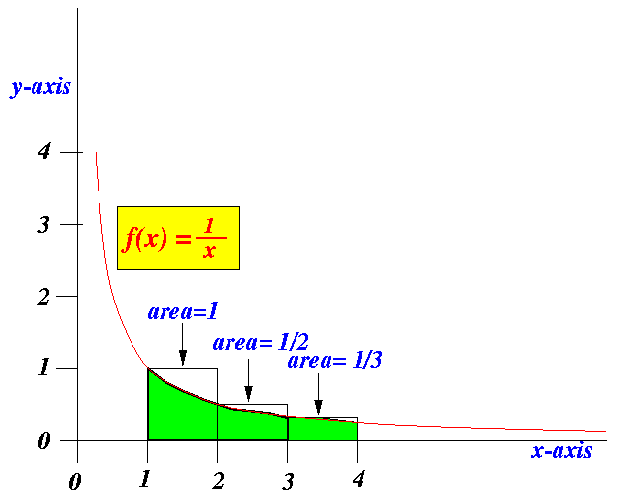 The sum of the squares = 1 + 1/2 + 1/3 + 1/4 + .... + 1/N
The area under f(x) = log(N)
The sum of the squares = 1 + 1/2 + 1/3 + 1/4 + .... + 1/N
The area under f(x) = log(N)