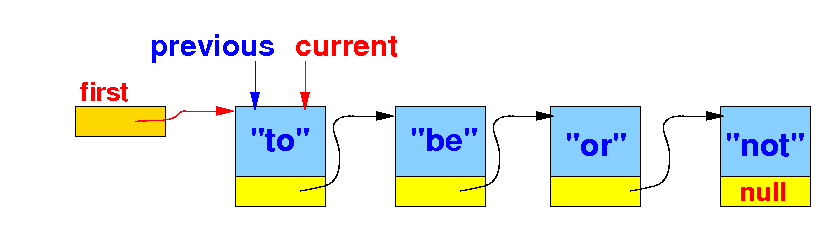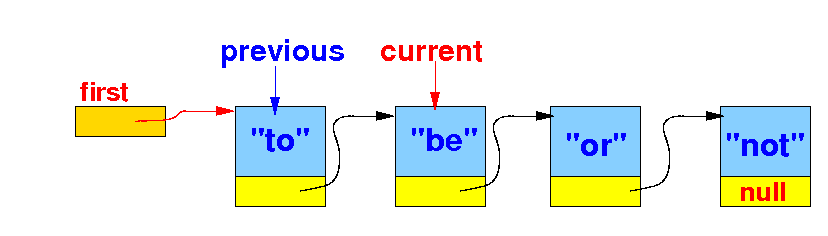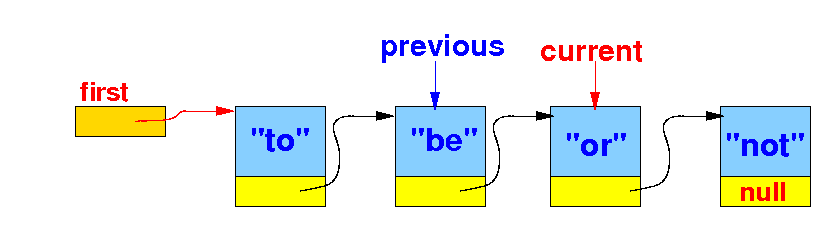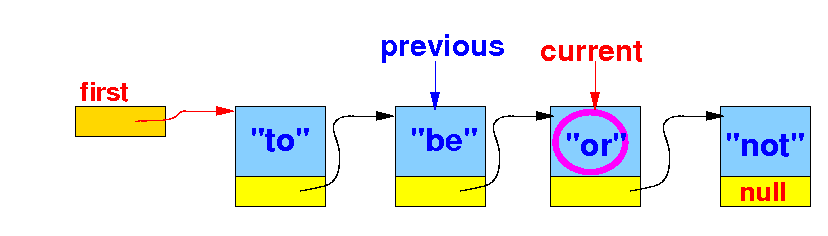
The effect of remove(key) --- removing the (first) item from a linked list that contains a item==key:
|
Note: the technique for step (1) is similar to that in the removeLast() algorithm !!!
|
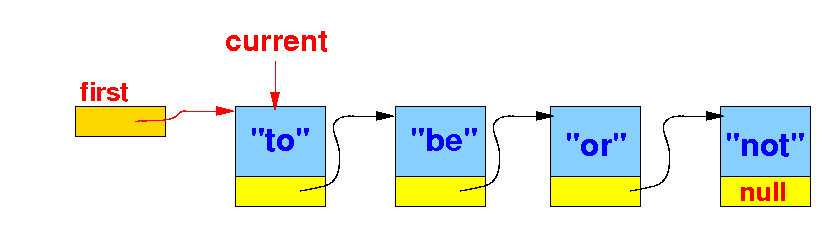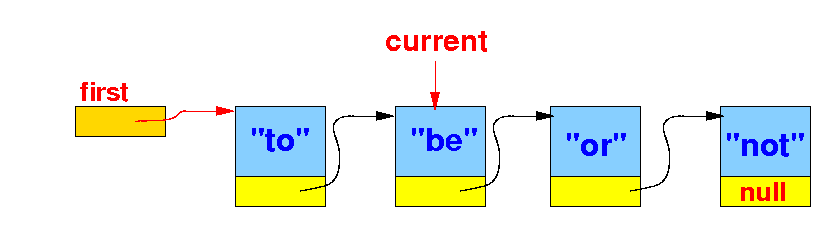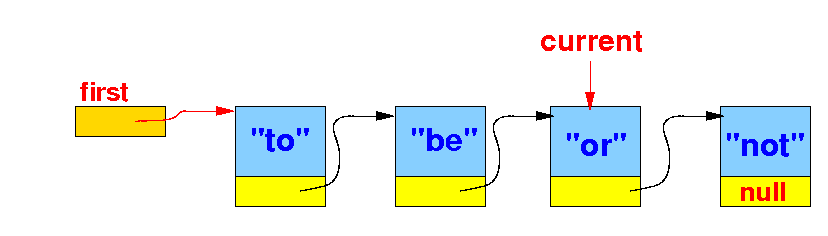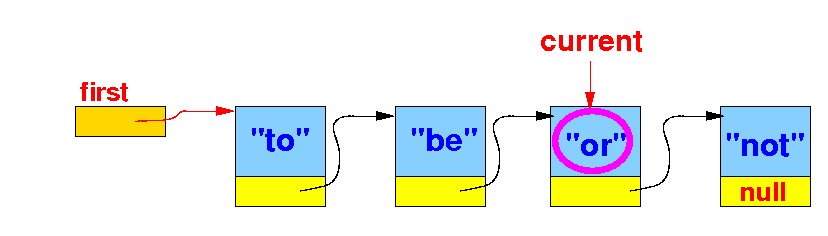
We stop when current.item is equal to the key:
|

The algorithm is usually written as:
|
|
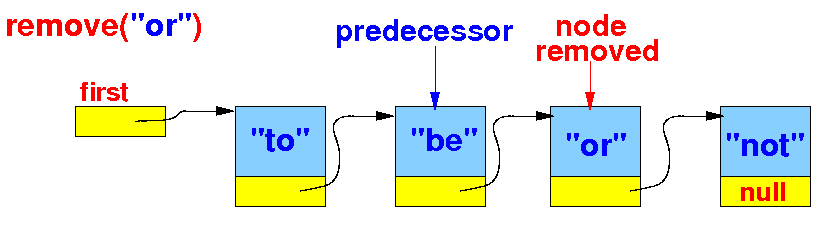
Let's implement the remove(key) method:
// Delete the node that contains key
public void remove(T key)
{ // General case (take care of edge cases later)
// Find the previous node of the node that contains key
Node<T> current = first;
Node<T> previous = first;
(1) Find the predecesor node of the node containing item==key
while( current!=null && !current.item.equals(key) )
{
previous = current;
current = current.next;
}
if( current == null )
{ // key not found
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
(2) Unlink the targeted node from its predecesor node
}
|

(1) Find the predecesor node of the node containing item==key:
// Delete the node that contains key
public void remove(T key)
{ // General case (take care of edge cases later)
// Find the previous node of the node that contains key
Node<T> current = first; // Initialize
Node<T> previous = first;
while( current != null && !current.item.equals(key) )
{
previous = current; // Keep track of the previous node
current = current.next; // Moev to next node
}
// previous points to the predecessor node of current
// current points to the node containing the given key
// or current == null: not found
(2) Unlink the targeted node from its predecesor node
}
|

(2a) If key is not found, we report an error (throw an exception):
// Delete the node that contains key
public void remove(T key)
{ // General case (take care of edge cases later)
// Find the previous node of the node that contains key
Node<T> current = first; // Initialize
Node<T> previous = first;
while( current != null && !current.item.equals(key) )
{
previous = current; // Keep track of the previous node
current = current.next; // Moev to next node
}
if( current == null )
{ key not found
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
(2) Unlink the targeted node from its predecesor node
}
|
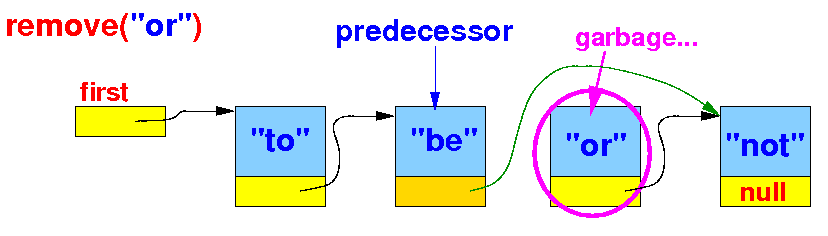
(2b) If the key was found in the linked list, we unlink the node from its predecessor node:
// Delete the node that contains key
public void remove(T key)
{ // General case (take care of edge cases later)
// Find the previous node of the node that contains key
Node<T> current = first; // Initialize
Node<T> previous = first;
while( current != null && !current.item.equals(key) )
{
previous = current; // Keep track of the previous node
current = current.next; // Moev to next node
}
if( current == null )
{ key not found
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
previous.next = current.next; // Unlink the current node from list
}
|
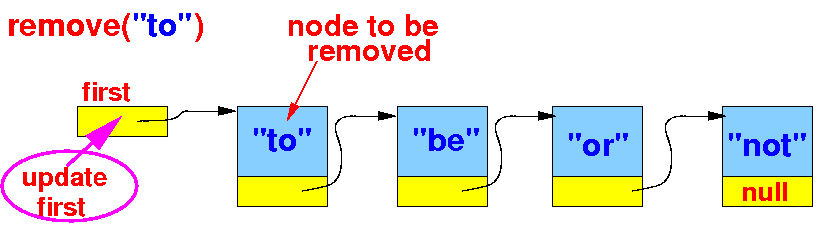
There are 2 edge cases: (1) the empty list and (2) the first node contains the key (updates first)
// Delete the node that contains key
public void remove(T key)
{
if ( edge case 1 )
{
...
}
else if ( edge case 2 )
{
... must update first
}
else
{
// General case updates previous.next
...
Omitted for brevity
previous.next = current.next; // Unlink the current node from list
}
}
|

Detect and handle edge case 1: the empty list
// Delete the node that contains key
public void remove(T key)
{
if ( first == null )
{
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
else if ( edge case 2 )
{
... must update first
}
else
{
// General case updates previous.next
...
Omitted for brevity
previous.next = current.next; // Unlink the current node from list
}
}
|
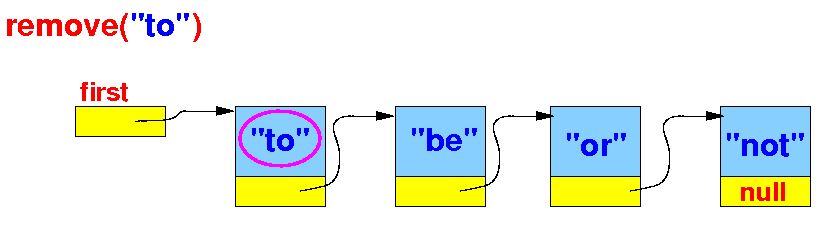
Detecting the edge case 2: the first node contains the given key
// Delete the node that contains key
public void remove(T key)
{
if ( first == null )
{
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
else if ( first.item.equals(key) )
{
... must update first
}
else
{
// General case updates previous.next
...
Omitted for brevity
previous.next = current.next; // Unlink the current node from list
}
}
|
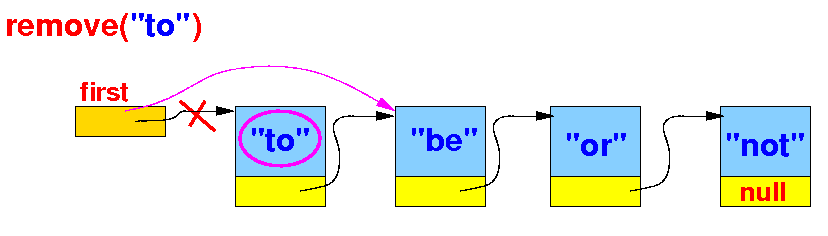
Handling the edge case 2: make the 2nd node into the first node of the list
// Delete the node that contains key
public void remove(T key)
{
if ( first == null )
{
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
else if ( first.item.equals(key) )
{
first = first.next; // The 2nd node is now the new 1st node
}
else
{
// General case updates previous.next
...
Omitted for brevity
previous.next = current.next; // Unlink the current node from list
}
}
|
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("Demo getFirst(), getLast(), get(pos)\n");
GenericLinkedList<Integer> intList = new GenericLinkedList<Integer>();
intList.addFirst(89);
intList.addFirst(78);
intList.addFirst(34);
intList.addFirst(23);
intList.addFirst(12);
System.out.println(intList); // 12 -> 23 -> 34 -> 78 -> 89
intList.remove(34);
System.out.println("After remove(34):");
System.out.println(intList);
intList.remove(89);
System.out.println("After remove(89):");
System.out.println(intList);
intList.remove(12);
System.out.println("After remove(12):");
System.out.println(intList);
System.out.println("remove(99): (not in list)");
intList.remove(12);
}
|
DEMO: demo/11-linked-list/05-remove-item/Demo.java + GenericLinkedList.java