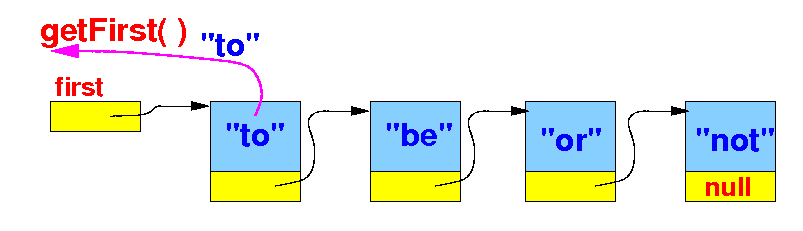
Retrieving the
first item stored in
the simple
linked list
- The
getFirst( )
method
retrieves the
item stored in the
first
list element (= node) in
the linked list:
- The Implementation of the
getFirst() method
is as follows:
// Returns the first element (item) in the list
// returns generic type
public T getFirst()
{
if(isEmpty())
{
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
return first.item; // Retrieves item in first node
}
|
|
Retrieving the
first item stored in
the simple
linked list
- When the linked list is
empty, there is
no item to
retrieve....
In this case, we will
report an
error:

- The Implementation of the
getFirst() method
is as follows:
// Returns the first element (item) in the list
// returns generic type
public T getFirst()
{
if ( isEmpty() )
{
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
return first.item; // Retrieves item in first node
}
|
|
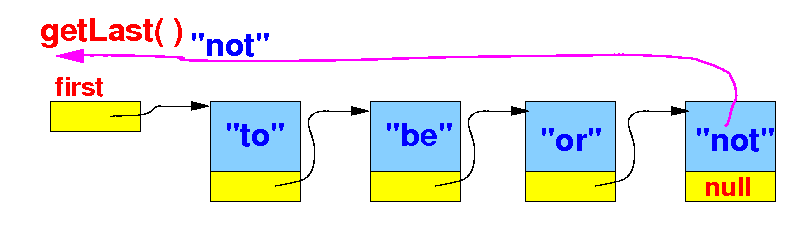
Retrieving the
last item stored in
the simple
linked list
- The
getLast( )
method
retrieves the
item stored in the
last
list element (= node) in
the linked list:
- The Implementation of the
getLast() method
is as follows:
public T getLast()
{
if ( isEmpty() )
{
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
// (1) Find the last node
Node current = first;
while(current.next!=null)
{
current = current.next;
}
// (2) return item stored in this node
}
|
|
Retrieving the
last item stored in
the simple
linked list
- We first
traverse
the linked list and
find the
last node:

- The Implementation of the
getLast() method
is as follows:
public T getLast()
{
if ( isEmpty() )
{
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
// (1) Find the last node
Node<T> current = first;
while ( current.next != null )
{
current = current.next;
}
// (2) return item stored in this node
}
|
|
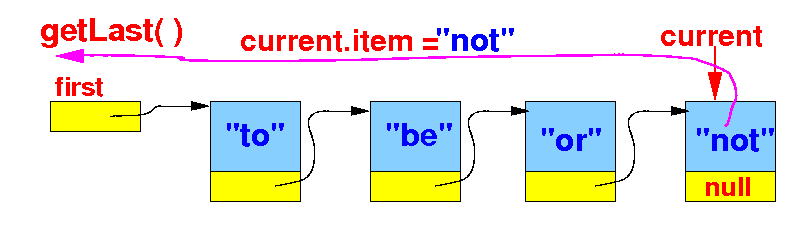
Retrieving the
last item stored in
the simple
linked list
- Then return the
item in
the last node:
- The Implementation of the
getLast() method
is as follows:
public T getLast()
{
if ( isEmpty() )
{
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
// (1) Find the last node
Node<T> current = first;
while ( current.next != null )
{
current = current.next;
}
return current.item; // (2) return item
}
|
|
Retrieving the
last item stored in
the simple
linked list
-
When the linked list is
empty, there is
no item to
retrieve....
In this case, we will
report an
error:

- The Implementation of the
getLast() method
is as follows:
public T getLast()
{
if ( isEmpty() )
{
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
Node<T> current = first;
while ( current.next != null )
{
current = current.next;
}
return current.item; // (2) return item
}
|
|
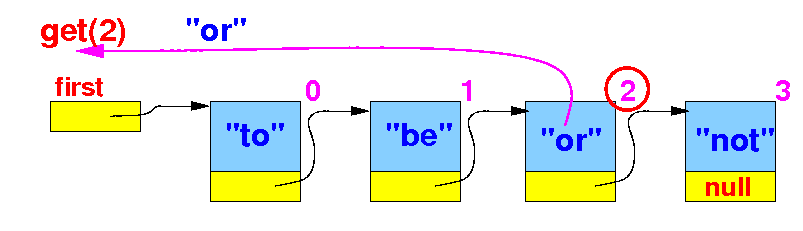
Retrieving the item
in node at
position pos in
the simple
linked list
- The
get(pos)
method
retrieves the
item stored in the
list element (= node) at the
position
pos
in
the linked list:
public T get(int pos)
{
// General case: (handle edge case(s) later....)
int i = 0;
Node<T> current = first;
while( current != null )
{
if ( i == pos )
break;
i++;
current = current.next;
}
if(current == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return current.item;
}
|
|
Retrieving the item
in node at
position pos in
the simple
linked list
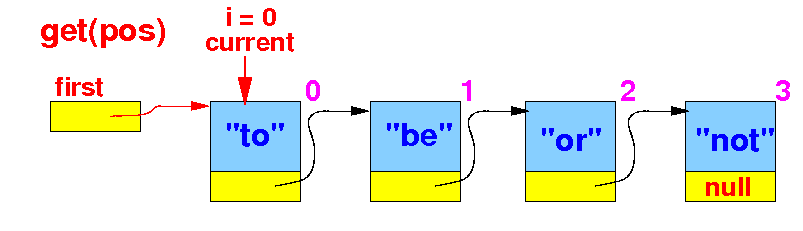
- We must
traverse the
linked list
while
keeping a
count
Start with the
current node = first node
with count
i = 0:
public T get(int pos)
{
// General case: (handle edge case(s) later....)
int i = 0;
Node<T> current = first;
while( current != null )
{
if ( i == pos )
break;
i++;
current = current.next;
}
if(current == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return current.item;
}
|
|
Retrieving the item
in node at
position pos in
the simple
linked list
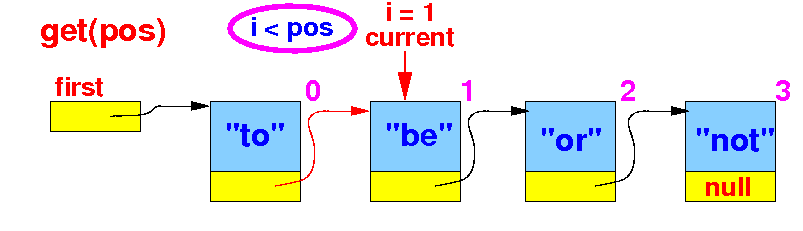
- When we have reached
the designated node
(
i == pos),
we exits
the loop
Otherwise,
we increment the
count and
move to the
next node.
public T get(int pos)
{
// General case: (handle edge case(s) later....)
int i = 0;
Node<T> current = first;
while( current != null )
{
if ( i == pos )
break;
i++;
current = current.next;
}
if(current == null)
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return current.item;
}
|
|
Retrieving the item
in node at
position pos in
the simple
linked list
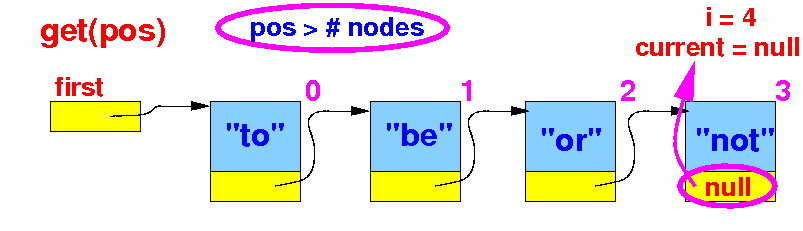
- The requested position
pos
can be too large and
current will
become
null
In this case, we report
an error:
public T get(int pos)
{
// General case: (handle edge case(s) later....)
int i = 0;
Node<T> current = first;
while( current != null )
{
if ( i == pos )
break;
i++;
current = current.next;
}
if ( current == null )
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return current.item;
}
|
|
Retrieving the item
in node at
position pos in
the simple
linked list
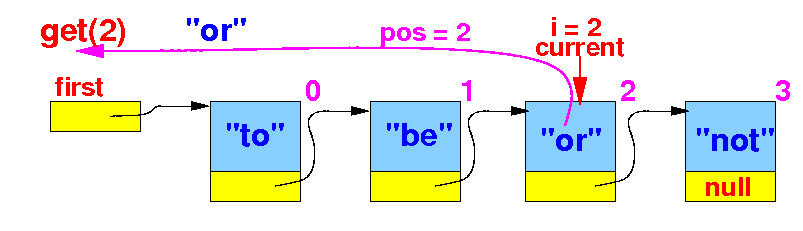
- Otherwise,
we return the
item in the
current node:
public T get(int pos)
{
// General case: (handle edge case(s) later....)
int i = 0;
Node<T> current = first;
while( current != null )
{
if ( i == pos )
break;
i++;
current = current.next;
}
if ( current == null )
throw new NoSuchElementException();
return current.item;
}
|
|
Retrieving the item
in node at
position pos in
the simple
linked list
-
When the linked list is
empty, there is
no item to
retrieve....
In this case, we will
report an
error:

public T get(int pos)
{
// Edge case
if ( isEmpty() )
{
throw new NoSuchElementException();
}
// General case (omitted for brevity)
...
...
}
|
|
Demo program
- Demo program:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
GenericLinkedList stringList = new GenericLinkedList();
stringList.addFirst("E");
stringList.addFirst("D");
stringList.addFirst("C");
stringList.addFirst("B");
stringList.addFirst("A");
System.out.println(stringList); // A -> B -> C -> D -> E
String s;
s = stringList.getFirst();
System.out.println("getFirst(): s = " + s);
s = stringList.getLast();
System.out.println("getLast(): s = " + s);
s = stringList.get(3);
System.out.println("get(3): s = " + s);
s = stringList.get(4);
System.out.println("get(4): s = " + s);
s = stringList.get(5);
System.out.println("get(5): s = " + s); // Crash...
}
|
|
DEMO:
demo/11-linked-list/04-get/Demo.java +
GenericLinkedList.java
❮
❯











