Review: Array
- Recall:
- Program =
Algorithm +
Data Structure
|
- Array:
- The array is
one of the
fundamental data structures
in Computer Science
|
- How are
arrays used:
- Arrays are used to
organize
multiple data of
the
same type
- The
array size is
fixed after
creation
- Arrays provide
fast access to
the stored data
though an
index
- Searching in
an unsorted array takes
n steps
(linear search)
- Searching in
an sorted array takes
log(n) steps
(binary search)
|
|
Adding an element at the end of an array
Adding an element at the end of an array
- Add the
value 7
to the array x:
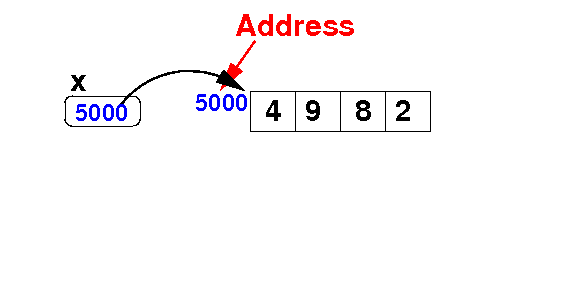
Algorithm:
temp = new int[ x.length + 1 ];
for ( int i = 0; i < x.length; i++ )
temp[i] = x[i];
temp[temp.length-1] = 7;
x = temp;
|
|
Adding an element at the end of an array
- Add the
value 7
to the array x:
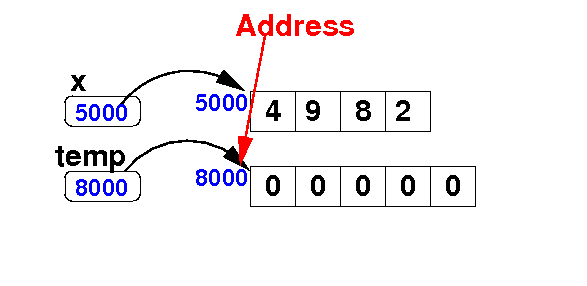
Algorithm:
int[] temp = new int[ x.length + 1 ];
for ( int i = 0; i < x.length; i++ )
temp[i] = x[i];
temp[temp.length-1] = 7;
x = temp;
|
|
Adding an element at the end of an array
- Add the
value 7
to the array x:
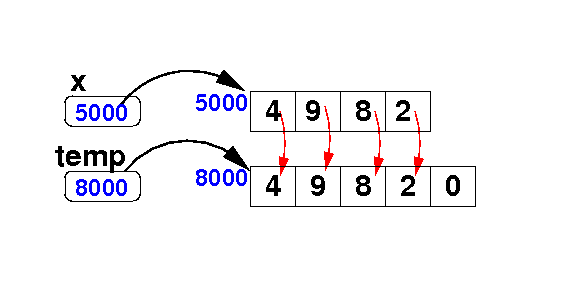
Algorithm:
int[] temp = new int[ x.length + 1 ];
for ( int i = 0; i < x.length; i++ ) // Copy
temp[i] = x[i];
temp[temp.length-1] = 7;
x = temp;
|
|
Adding an element at the end of an array
- Add the
value 7
to the array x:
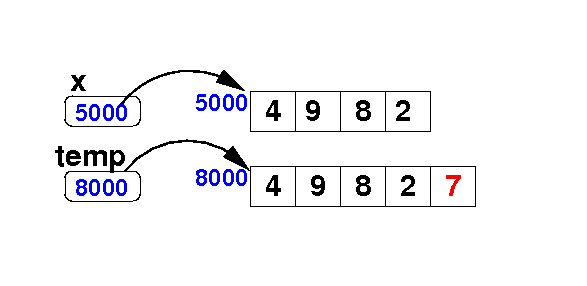
Algorithm:
int[] temp = new int[ x.length + 1 ];
for ( int i = 0; i < x.length; i++ ) // Copy
temp[i] = x[i];
temp[temp.length-1] = 7; // Add the new value
x = temp;
|
|
Adding an element at the end of an array
- Add the
value 7
to the array x:
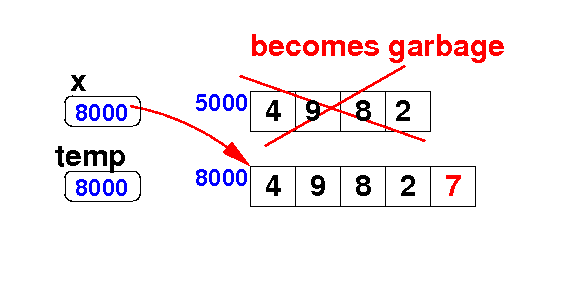
Algorithm:
int[] temp = new int[ x.length + 1 ];
for ( int i = 0; i < x.length; i++ ) // Copy
temp[i] = x[i];
temp[temp.length-1] = 7; // Add the new value
x = temp;
|
|
Adding an element at the end of an array
- Question:
how many
data copy statements
are
executed
by this algorithm ?

Algorithm:
int[] temp = new int[ x.length + 1 ];
for ( int i = 0; i < x.length; i++ ) // Copy
temp[i] = x[i];
temp[temp.length-1] = 7; // Add the new value
x = temp;
|
|
Adding an element at the end of an array
Deleting the last element from an array
Adding an element at the end of an array
- Delete the
last element
from the array x:

Algorithm:
temp = new int[ x.length + 1 ];
for ( int i = 0; i < x.length; i++ )
temp[i] = x[i];
temp[temp.length-1] = 7;
x = temp;
|
|
Adding an element at the end of an array
- Delete the
last element
from the array x:
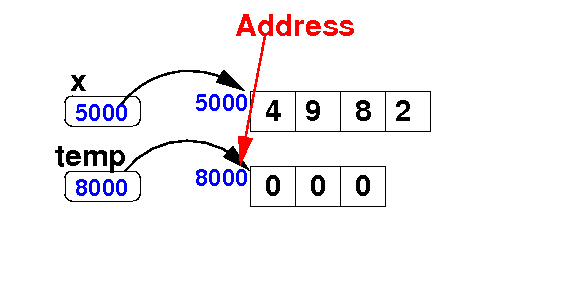
Algorithm:
int[] temp = new int[ x.length − 1 ];
for ( int i = 0; i < x.length; i++ )
temp[i] = x[i];
temp[temp.length-1] = 7;
x = temp;
|
|
Adding an element at the end of an array
- Delete the
last element
from the array x:
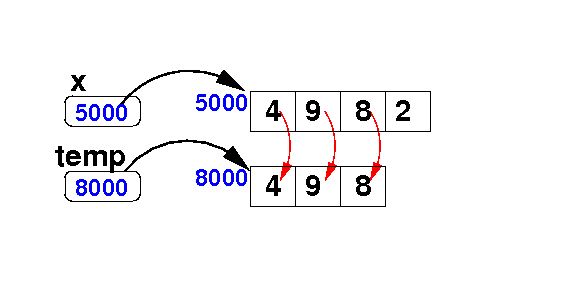
Algorithm:
int[] temp = new int[ x.length − 1 ];
for ( int i = 0; i < x.length-1; i++ ) // Copy
temp[i] = x[i];
temp[temp.length-1] = 7;
x = temp;
|
|
Adding an element at the end of an array
- Delete the
last element
from the array x:
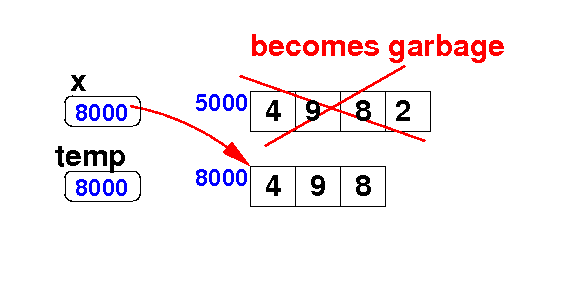
Algorithm:
int[] temp = new int[ x.length − 1 ];
for ( int i = 0; i < x.length-1; i++ ) // Copy
temp[i] = x[i];
x = temp;
|
|
Adding an element at the end of an array
- Delete the
last element
from the array x:

Algorithm:
int[] temp = new int[ x.length − 1 ];
for ( int i = 0; i < x.length-1; i++ ) // Copy
temp[i] = x[i];
x = temp;
Note: you can delete an element at a different location
with a similar algorithm
|
|
A better way to
add and delete elements in arrays
-
Dynamic
arrays
(a.k.a.
ArrayList in
Java) consists of:
- A (fixed size)
array
- A
count of
the actual number of
elements stored in
the array:
Schematically:

|
- The array is
increased
only when
the add( ) operation
encounters a
full array
- The array is
reduced when
the occupancy drops
below a
certain threshold
|
❮
❯