It is safe to use a superclass reference variable to reference to a subclass object:
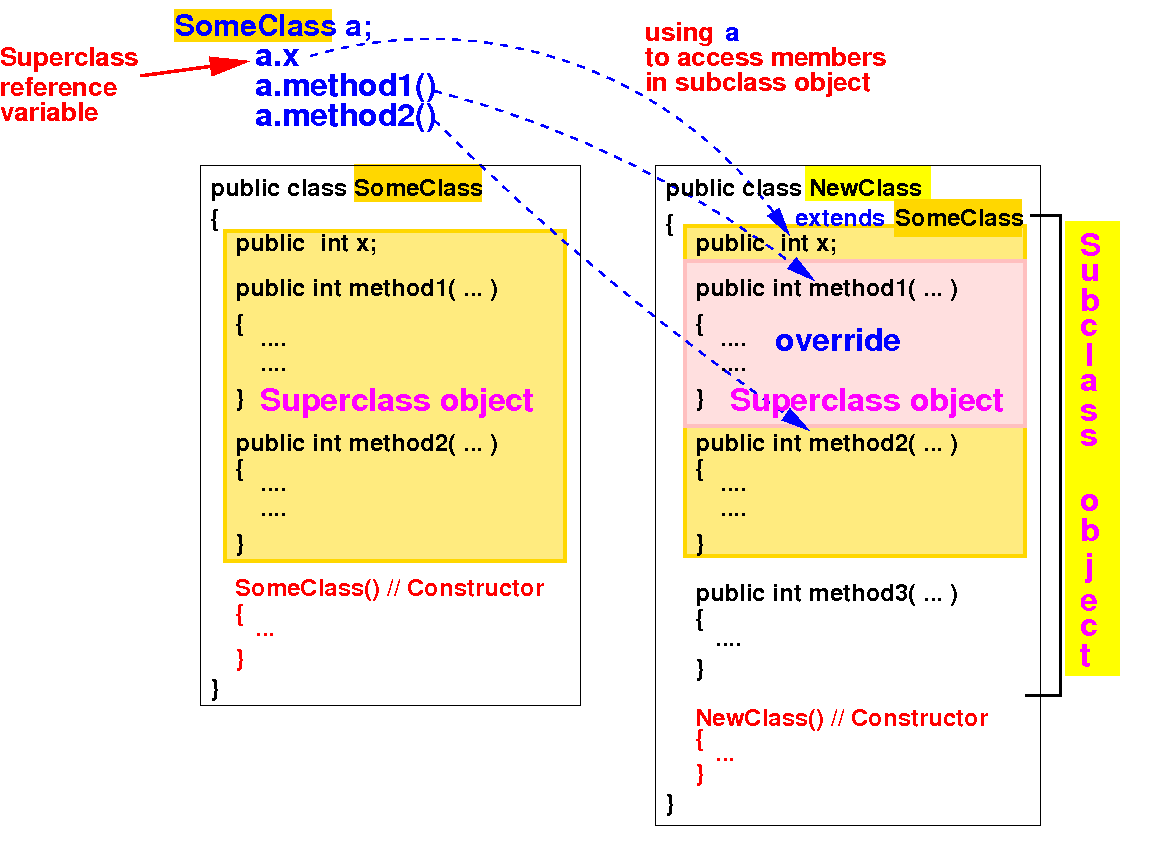
Because any request (action) that you make using a superclass variable a can be satisfied
|
DEMO: demo/04-inheritance/21-casting/Demo.java --- compile and show no error
It is unsafe to use a subclass reference variable to reference to a superclass object:
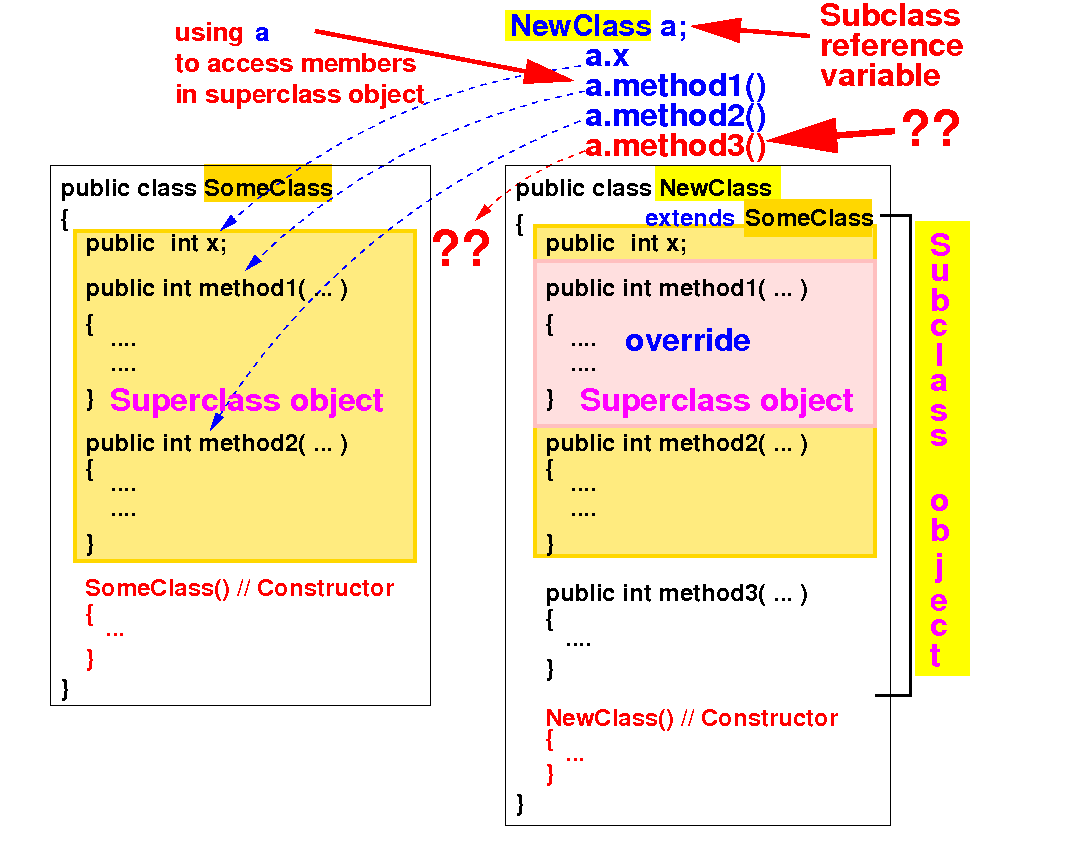
E.g.: user can make the illegal request to execute a.method3() (the superclass object cannot perform method3())
|
DEMO: demo/04-inheritance/21-casting/Demo2.java --- compile and show compile error
|
DEMO: demo/04-inheritance/21-casting/Demo3.java
|
|
|
DEMO: demo/04-inheritance/21-casting/Demo4.java
|
DEMO:
demo/04-inheritance/21-casting/Demo5.java
DEMO:
demo/04-inheritance/21-casting/Demo5b.java
(what happens if you cast to the wrong subtype)
|
|
DEMO: demo/04-inheritance/21-casting/Demo6.java
Skeletal code to downcast an unspecified superclass type to its correct subclass types:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
GeometricObject a = (can be a Circle or Rectangle object)
// Upcasting
if ( a is a Circle )
{
print its radius
}
else if ( a is a Rectangle )
{
print its width and height
}
else
print "invalid subclass type"
}
|
If a references to a Circle object, then downcast (convert) and assign to a Circle variable:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
GeometricObject a = (can be a Circle or Rectangle object)
// Upcasting
if ( a instanceof Circle )
{
Circle b = (Circle) a; // Downcast to a Circle
System.out.println(b.getRadius());
}
else if ( a is a Rectangle )
{
print its width and height
}
else
print "invalid subclass type"
}
|
If a references to a Rectangle object, then downcast (convert) and assign to a Rectangle variable:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
GeometricObject a = (can be a Circle or Rectangle object)
// Upcasting
if ( a instanceof Circle )
{
Circle b = (Circle) a; // Downcast to a Circle
System.out.println(b.getRadius());
}
else if ( a instanceof Rectangle )
{
Rectangle b = (Rectangle) a; // Downcast to a Rectangle
System.out.println(b.getWidth());
System.out.println(b.getHeight());
}
else
print "invalid subclass type"
}
|
Otherwise (it can be a GeometricObject !), print the warning message:
public static void main(String[] args)
{
GeometricObject a = (can be a Circle or Rectangle object)
// Upcasting
if ( a instanceof Circle )
{
Circle b = (Circle) a; // Downcast to a Circle
System.out.println(b.getRadius());
}
else if ( a instanceof Rectangle )
{
Rectangle b = (Rectangle) a; // Downcast to a Rectangle
System.out.println(b.getWidth());
System.out.println(b.getHeight());
}
else
System.out.println("Invalid subclass type");
}
|
Demo demo/04-inheritance/21-casting/Demo7.java
|
