Review:
objects in Java
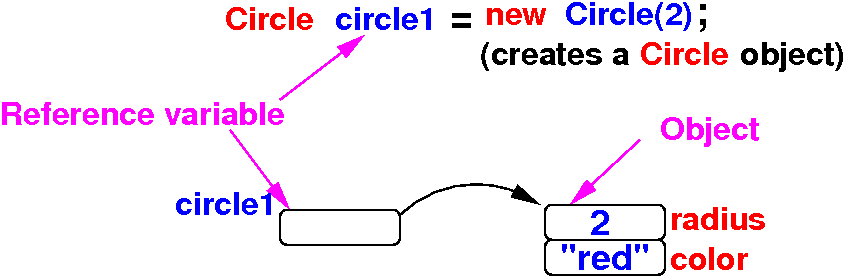
- In Java, an
object consists of
2 parts:
- An
object reference variable
(which is not an
object, but
references to
an object)
- The actual
object
which consists of a
number of
consecutive
instance variables
|
- Schematically:
|
What does it
mean to
copy an array
- Copy an
object means:
- Make a duplicate of
an object where
the duplicate object contains
the same data as
the original object
- Updating
the instance variables
in the duplicate object
must not affect
the values in the original object
|
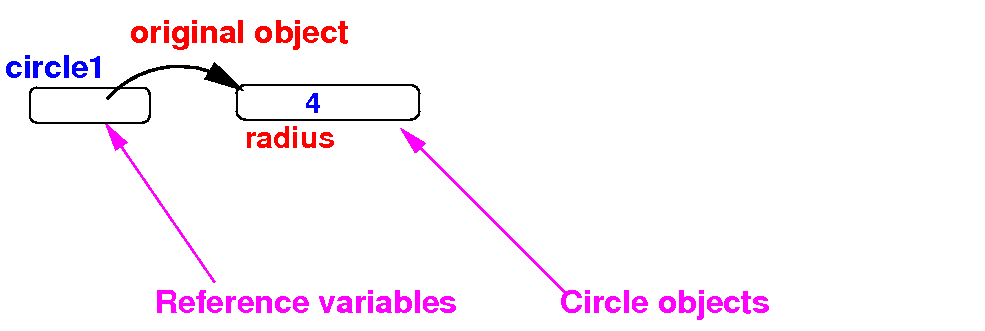
- Schematically:
before
making a copy of the
object circle1
|
What does it
mean to
copy an object
- Copy an
object means:
- Make a duplicate of
an object where
the duplicate object contains
the same data as
the original object
- Updating
the instance variables
in the duplicate object
must not affect
the values in the original object
|
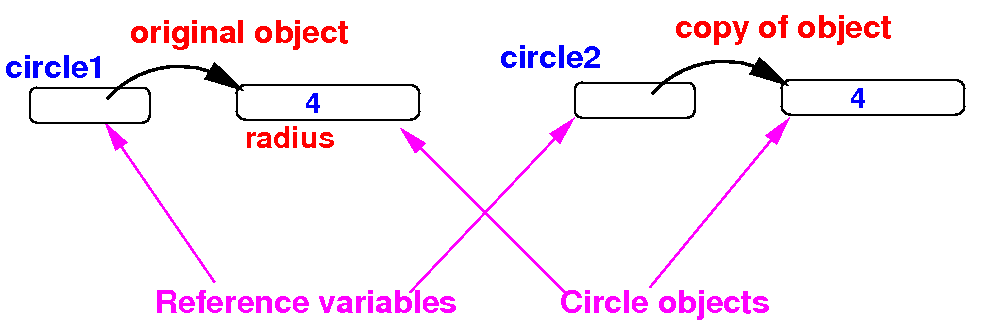
- Schematically:
after
making a copy of the
object circle1
|
How to
copy an object in
Java
step-by-step instructions
- Initial state:

public static void main(String[] args)
{
Circle circle1 = new Circle(4);
}
|
|
How to
copy an object in
Java
step-by-step instructions
- Step 1:
create an
object to
store the
copy
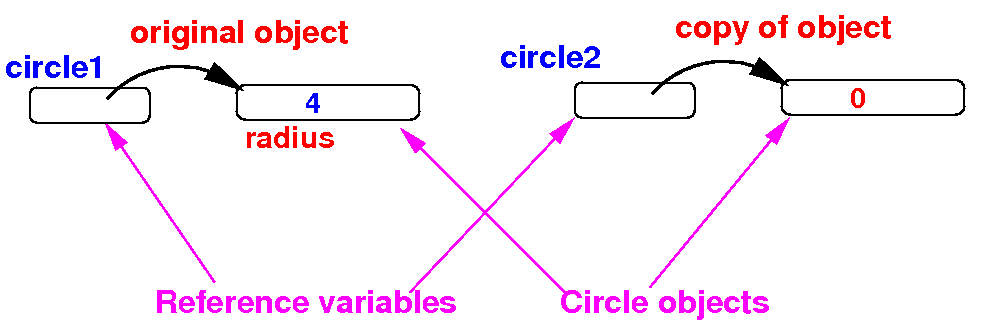
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Circle circle1 = new Circle(4);
Circle circle2 = new Circle();
}
|
|
How to
copy an object in
Java
step-by-step instructions
- Step 2:
copy the
instance variables to
the
copy object
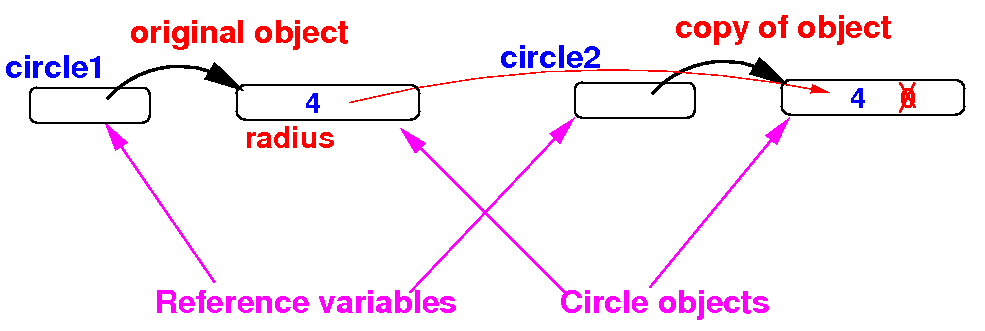
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Circle circle1 = new Circle(4);
Circle circle2 = new Circle();
circle2.radius = circle1.radius;
}
|
|
How to
copy an object in
Java
step-by-step instructions
- Result:
updates on
the object copy will
not affect the
original object:
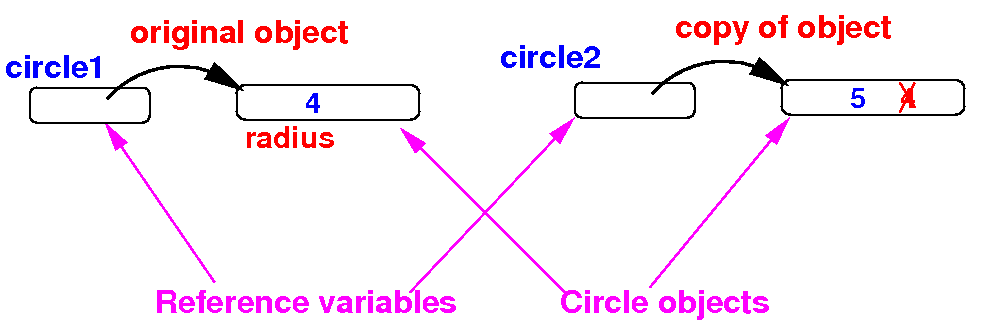
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Circle circle1 = new Circle(4);
Circle circle2 = new Circle();
circle2.radius = circle1.radius;
circle2.radius++; // Will not affect circle1.radius
}
|
|
Demo:
demo/03-classes/10-copy
A
common error
in object copy
- Variables of
primitive data types
(such as int,
double, etc)
can be
copied with
an
assignment:
int x = 4;
int xCopy;
xCopy = x; // Copies x to xCopy
|
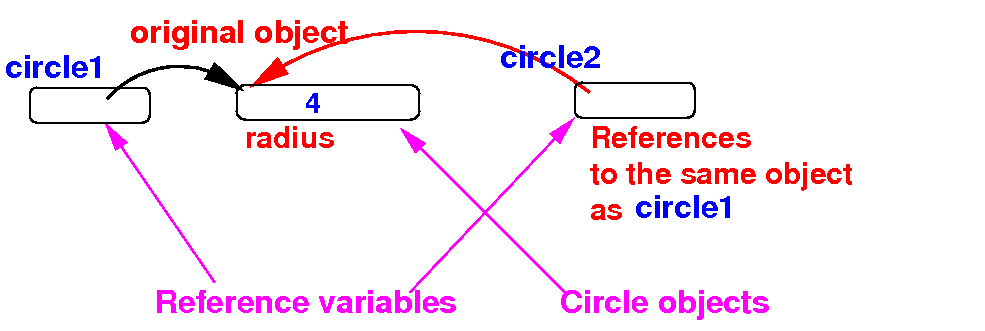
- However,
in Java,
the
assignment operation will
not
copy
objects of
non-primitive
data types:
Circle circle1 = new Circle(4);
Circle circle2;
circle2 = circle1; // Does not copy an object
// ** This copies the reference
// ** in circle1 to circle2
|
|
The effect of
assignment
with a
reference variable
- Initially we
have the object
circle1:
Circle circle1 = new Circle(4);
|
Schematically:

|
The effect of
assignment
with a
reference variable
- The definition
Circle
circle2
defines another
reference variable:
Circle circle1 = new Circle(4);
Circle circle2;
|
Schematically:
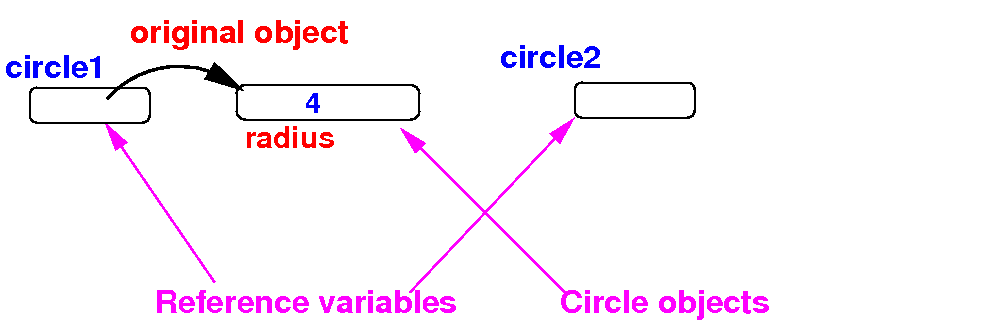
|
The effect of
assignment
with a
reference variable
The effect of
assignment
with a
reference variable
Demo:
demo/03-classes/10-copy/Demo2.java
❮
❯