Why do Programming Languages have methods ?
- Methods
are used to
encapsulate
(= put in a capsule)
a series of
operations
used to solve
a complex problem
- Methods allow
programmers to work
with
higher level
of abstraction
-
Low level of
abstraction =
when
we can see a
lot of detail
-
High level of
abstraction =
when
we can see
less detail
and the
"big picture"
-
Abstraction is
a commonly used technique
to
solve
complex problems
|
|
Methods are
useful, but
not necessary
for programming
- Your life
with
methods:
public class WithMethod
{
public static int sum( int start, int end )
{
int s = 0;
for ( int i = start; i <= end; i++ )
s = s + i;
return s;
}
public static void main(String[] args)
{
System.out.println("sum(1, 10) is: " + sum(1,10) );
System.out.println("sum(25, 30) is: " + sum(25,30) );
System.out.println("sum(40, 50) is: " + sum(40,50) );
}
|
|
Methods are
useful, but
not necessary
for programming
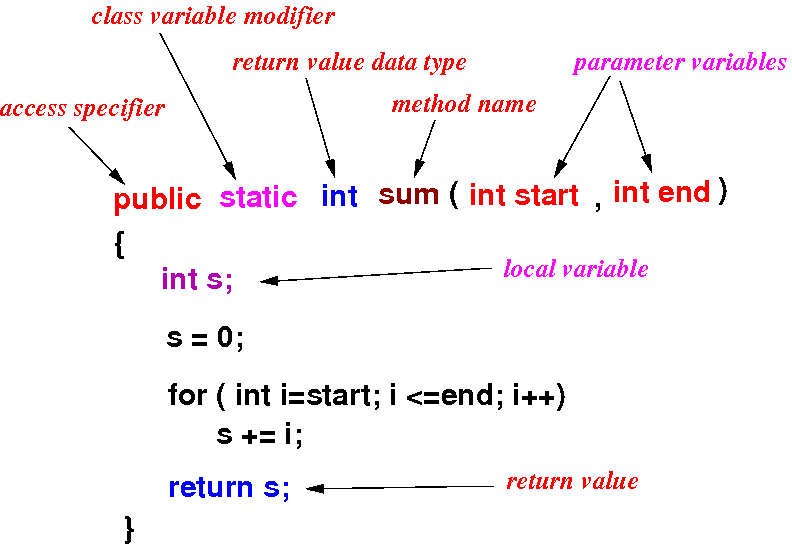
Java method definition
- Components in a
method definition:
|
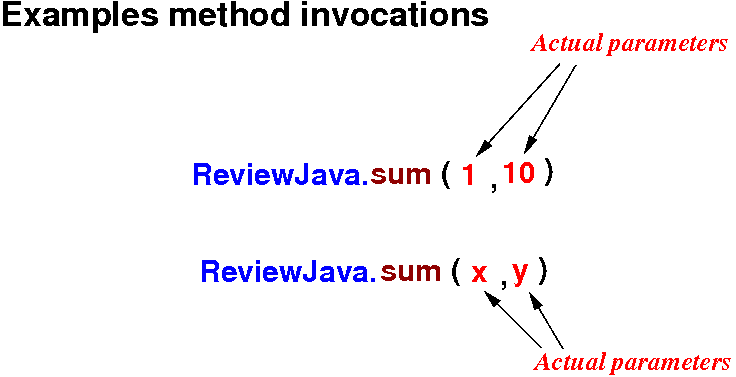
Using/calling/invoking a method
- Invoking a
method:
-
Very important:
- The
values of the
actual parameters (= "arguments")
are
passed (= copied)
to
the
parameter variables
of
the method
|
|
Java method definition
- The
signature of a
method =
method name +
data type of
the parameters
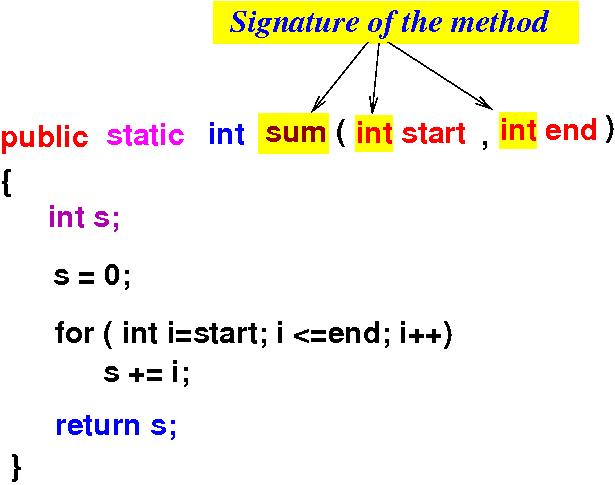
- Java uses
the method signature to
select
which method to
invoke
|
Method overloading
-
Overloaded method
= when there are
multiple
methods
in the class with
the
same
method name but
different
signature
Example:
public class Overload
{
public static void meth( int x )
{
System.out.println("Running: meth( int x ) ");
}
public static void meth( double x )
{
System.out.println("Running: meth( double x ) ");
}
public static void meth( int x, int y )
{
System.out.println("Running: meth( int x, int y ) ");
}
}
|
|
DEMO:
02-review/Overload.java
❮
❯


