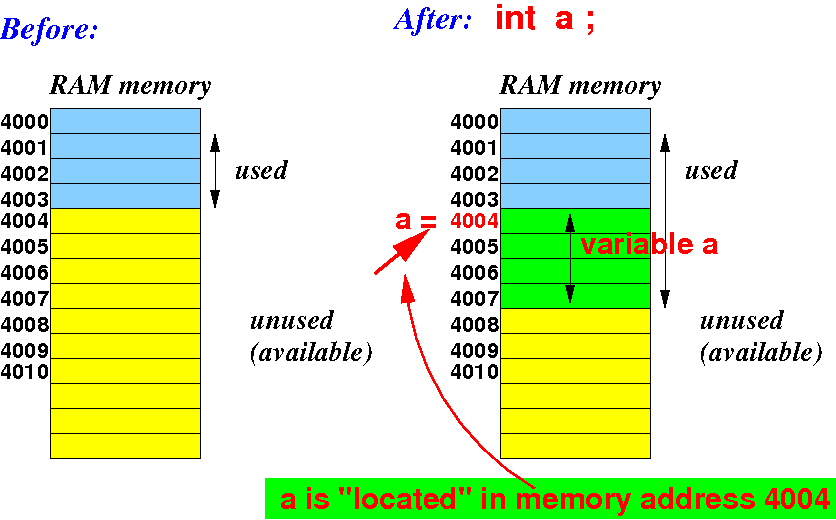
Defining variables
|
Data type of a
variable
|
Example that context in
necessary to
interpret
a number value
|
DEMO: demo/02-review/datatype.java
The reason why 65 is the letter A is the Unicode used to represent symbols:
Example of the
effect of
the context
in the English language
|
Example of the
effect of
the context
in the English language
|
Java's primitive data types
| Data type | Encoding method |
|---|---|
| byte | 2's complement encoding using 8 bits |
| short | 2's complement encoding using 16 bits |
| int | 2's complement encoding using 32 bits |
| long | 2's complement encoding using 64 bits |
| float | IEEE 754 encoding using 32 bits |
| double | IEEE 754 encoding using 64 bits |
| char | Unicode encoding using 16 bits |
| boolean | Enumeration encoding using 0 = false and 1 = true |
You will learn about these encoding methods in CS 255