|
|
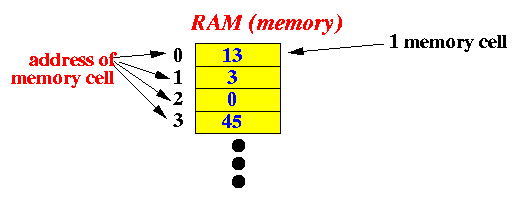
Byte memory (or "byte" for short):
|
Each byte memory can store one of the following 256 possible patterns of binary numbers:
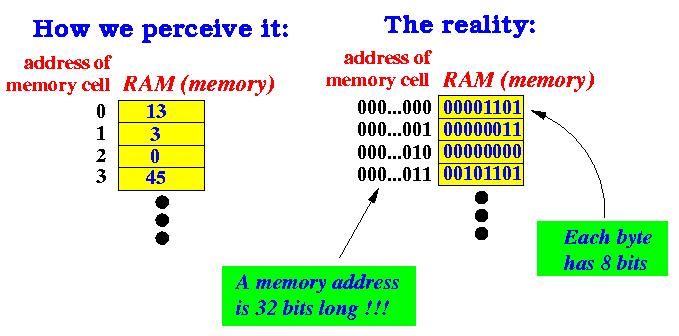
00000000 00000001 00000010 00000011 00000100 00000101 00000110 00000111 00001000 00001001 00001010 00001011 00001100 00001101 00001110 00001111 00010000 00010001 00010010 00010011 00010100 00010101 00010110 00010111 00011000 00011001 00011010 00011011 00011100 00011101 00011110 00011111 00100000 00100001 00100010 00100011 00100100 00100101 00100110 00100111 00101000 00101001 00101010 00101011 00101100 00101101 00101110 00101111 00110000 00110001 00110010 00110011 00110100 00110101 00110110 00110111 00111000 00111001 00111010 00111011 00111100 00111101 00111110 00111111 .... (And so on... too many to list) |
(1 bit can store 21 = 2 patterns. So 1 byte (= 8 bits) can store 28 = 256 patterns.)
Humans are
very flexible and can use
many (different) methods to
store
data/information.
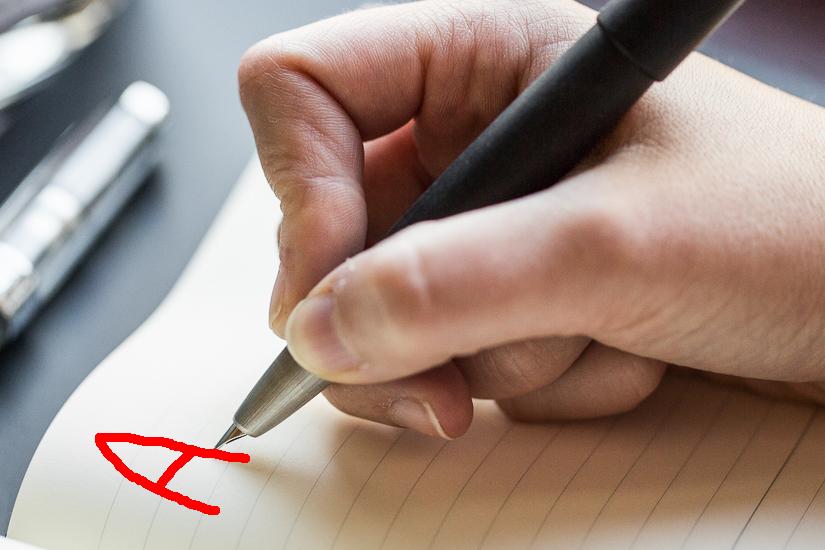
Example: a commonly used
human method to
save
data/information:

Computers
can
only
store
data/information as
binary numbers
(using electrical switches)
This is how a
computer
(must)
stores (= "writes") the
letter A
(which is
01000001):

BTW: an international committee decided that 01000001 represents the letter A long time ago...
|
|