- (Cartesian) Product operator:
R × S - Example (Cartesian) Product:
R = {1, 2}; S = {2, 4}; R × S = { (1,2), (1,4), (2,2), (2,4) }
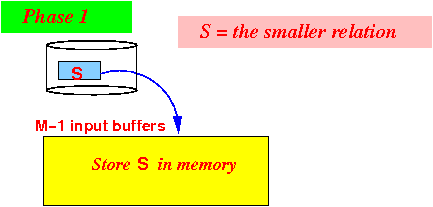
- Phase 1:
use M−1 buffers to
read the
smaller relation in
memory:
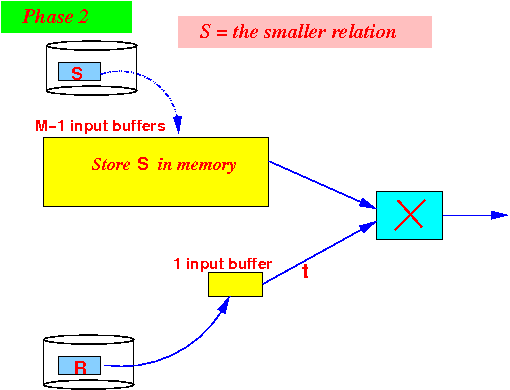
- Phase 2: use
1 buffer to
read the
larger relation -
one block at a time -
and output
R × S:
- Cost:
read S and
R once:
- Cost(one-pass ×) = B(R) + B(S) (Clustered relations)
- Constraint:
store S
completely
in memory and
use 1 buffer to
read
R:
- M(one-pass ×) ≥ B(S) + 1 (Clustered relations)
- Fact:
- The cartesian product is a very simple operation that does not need to use search data structures (e.g.: hash lookup table) for processing
- The one-pass algorithm can be
generalized to
compute the
cartesian product if
M < B(S) + 1:
Nested-loop cartesian-product algorithm:
Let M = # available buffers; /* ------------------------------------------- Outer loop: read M-1 block of S ------------------------------------------- */ while ( S has more data blocks ) { read M-1 data blocks of S; Reset R; /* ------------------------------------------- Innerloop: read through R and compute × ------------------------------------------- */ while ( R has more data blocks ) { read 1 data block of R; for ( each tuple s ∈ M-1 blocks of S and each tuple t ∈ 1 blocks of R ) do { output (s, t); } } }Graphically:
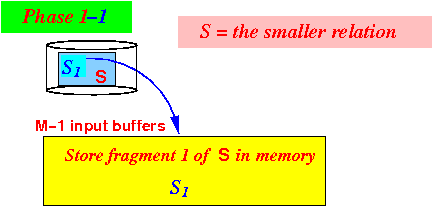
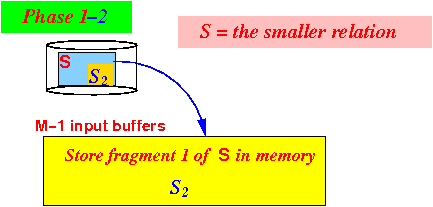
- Iteration 1:
- Use (M−1) blocks
to
read
the first fragment
S1 of
relation S
to memory:
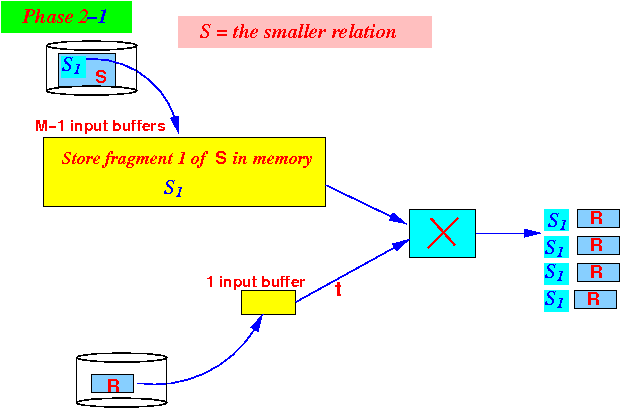
- Use
1 buffer to
read the
larger relation -
one block at a time -
and output
R ×
S1:
- Use (M−1) blocks
to
read
the first fragment
S1 of
relation S
to memory:
- Iteration 2:
- Use (M−1) blocks
to
read
the second fragment
S2 of
relation S
to memory:
- Use
1 buffer to
read the
larger relation -
one block at a time -
and output
R ×
S1:
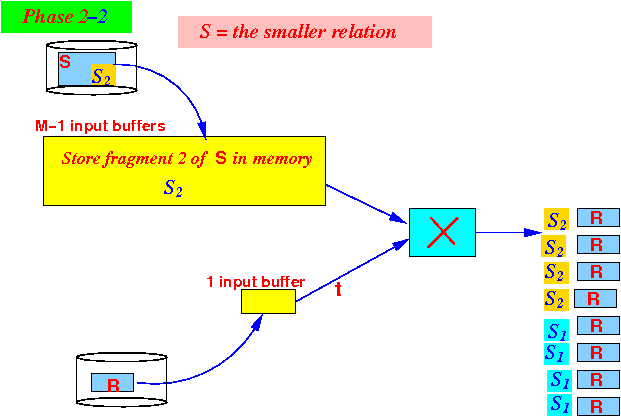
- Use (M−1) blocks
to
read
the second fragment
S2 of
relation S
to memory:
- And so on....
Comment:
- The generalized algorithm for
the cartesian product is
not a pure
one-pass algorithm:
- The generalized algorithm will
read
the relation S
once
- The generalized algorithm will read the relation S: B(S)/(M−1) times
- The generalized algorithm will
read
the relation S
once
- Iteration 1:
- # disk I/O used:
Algorithm read S once: # disk I/Os = B(S)
# fragments of S read = B(S) / (M−1) For each fragment of S: Algorithm reads R once: # disk I/Os = B(S)/(M−1) × B(R)
So: B(S) Total cost = B(S) + ------- B(R) M-1
- Memory requirement:
- M ≥ 2 buffer
!!!!!
- The generalized
cartesian product algorithm can
work with
only
2 buffers:
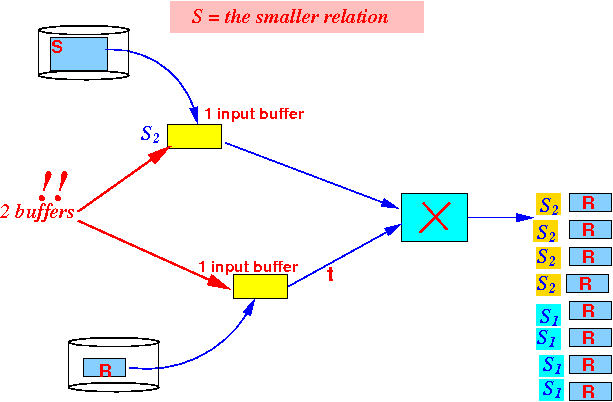
But the running time will be very large (you will read the relation R many times !!!)
- The generalized
cartesian product algorithm can
work with
only
2 buffers:
- M ≥ 2 buffer
!!!!!
- Fact:
- R × S is
a symmetric operation:
R × S = S × R
Observation:
- The (generalized) cartesian product implementation algorithm is not symmetric in behavior !!!
- R × S is
a symmetric operation:
- Example:
B(R) = 10,000 B(S) = 5,000 M = 101
- The cost to execute
the cartesian product
using
the smaller relation (S)
in the outer loop
is:
Configuration: (1) Use 100 buffers to hold tuples of S (2) Use 1 buffers to scan R
Read S once: # disk I/Os = B(S) = 5000 blocks
# fragments of S read = 5000/100 = 50 fragments for each fragment of S, read R once: # disk I/Os = 50 × B(R) = 50 × 10000 blocks
Total: 505,000 disk blocks
- The cost to execute
the cartesian product
using
the larger relation (R)
in the outer loop is:
Configuration: (1) Use 100 buffers to hold tuples of R (2) Use 1 buffers to scan S
Read R once: # disk I/Os = B(R) = 10000 blocks
# fragments of R read = 10000/100 = 100 fragments for each fragment of R, read S once: # disk I/Os = 100 × B(S) = 100 × 5000 blocks
Total: 510,000 disk blocks
- Note:
- The cost calculation does
not include the
output side
- We assume that the tuples are pipelined (through memory buffer) to the next query operator
- We will need include the
output disk I/O
in the cost
if we
know that the
result will be
materialized
(= written to disk) !!!
(E.g.: if we do not have sufficient memory buffers !!!)
- The cost calculation does
not include the
output side