Slideshow:
- Parameters used in
Linear Hashing:
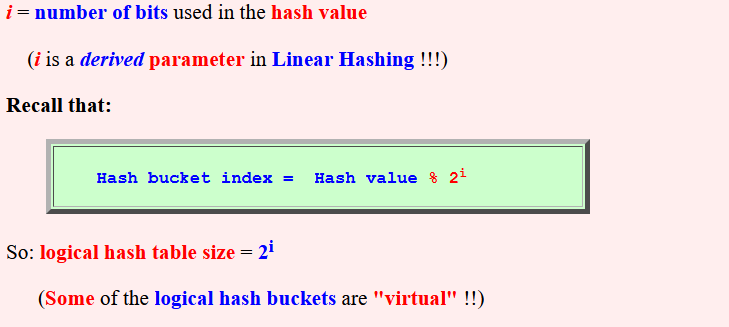
- i =
number of bits
used in the
hash value
(i is a derived parameter in Linear Hashing !!!)
Recall that:
Hash bucket index = Hash value % 2iSo: logical hash table size = 2i
(Some of the logical hash buckets are "virtual" !!)
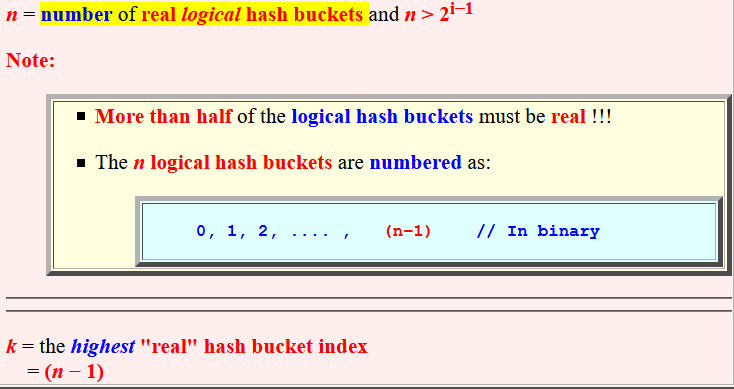
- n =
number
of
real
logical hash buckets
and
n > 2i−1
Note:
- More than half of the
logical hash buckets must be
real !!!
- The n logical hash buckets are
numbered as:
0, 1, 2, .... , (n−1) // In binary
- More than half of the
logical hash buckets must be
real !!!
- k = the
highest
"real" hash bucket index
= (n − 1)
- i =
number of bits
used in the
hash value
- Note:
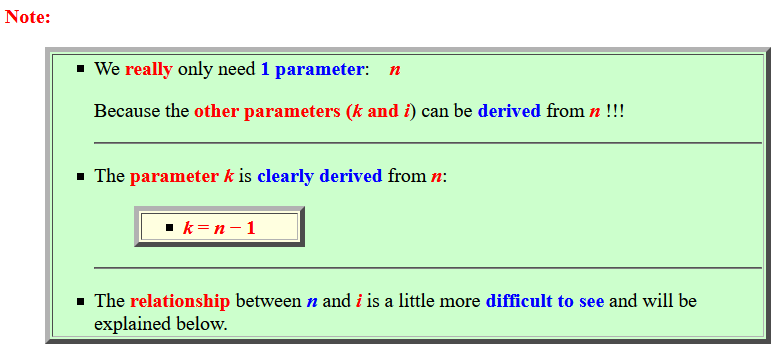
- We really only need
1 parameter:
n
Because the other parameters (k and i) can be derived from n !!!
- The parameter k is
clearly derived from
n:
- k = n − 1
- The relationship between n and i is a little more difficult to see and will be explained below.
- We really only need
1 parameter:
n
- Let me show the
relationship with
a few
concrete examples first:
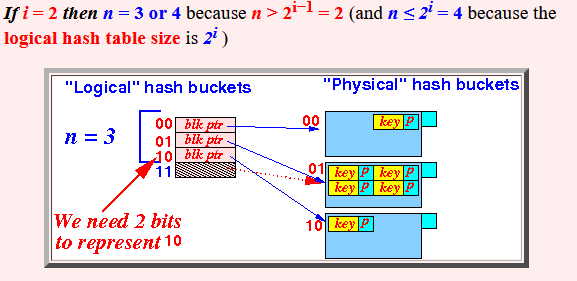
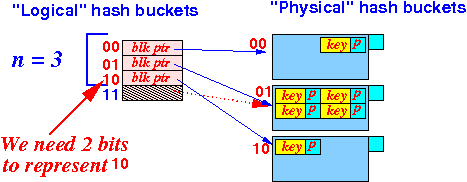
- If i = 2
then
n = 3 or 4
because
n > 2i−1 = 2
(and n ≤ 2i = 4
because
the
logical hash table size is
2i )
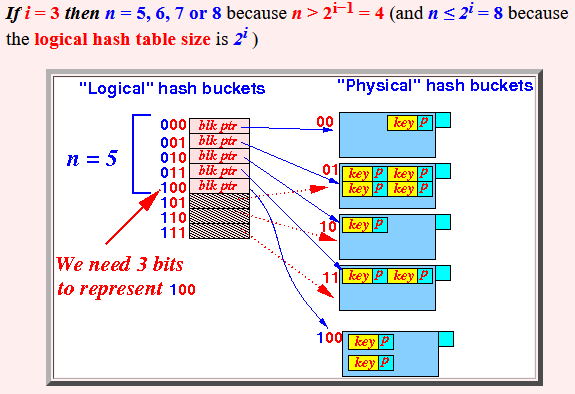
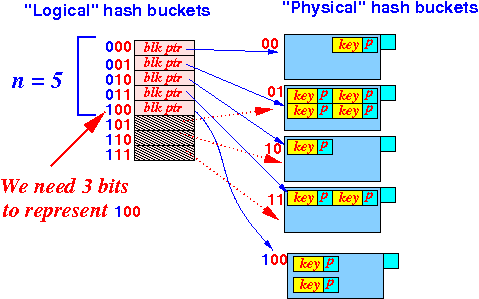
- If i = 3
then
n = 5, 6, 7 or 8
because
n > 2i−1 = 4
(and n ≤ 2i = 8
because
the
logical hash table size is
2i )
- If i = 2
then
n = 3 or 4
because
n > 2i−1 = 2
(and n ≤ 2i = 4
because
the
logical hash table size is
2i )
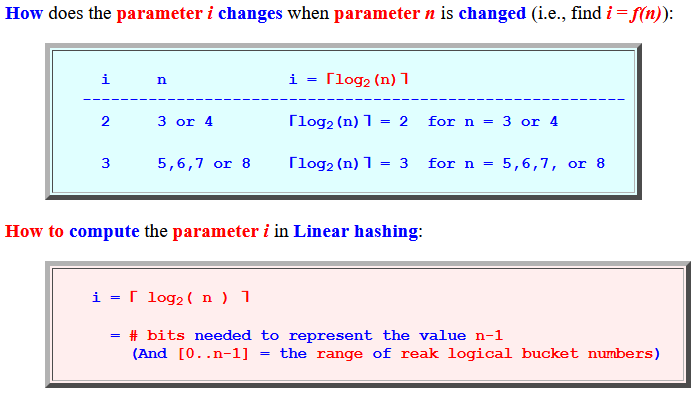
- How does
the parameter i
changes
when parameter n is
changed
(i.e., find i = f(n)):
i n i = ⌈log2(n)⌉ ---------------------------------------------------------- 2 3 or 4 ⌈log2(n)⌉ = 2 for n = 3 or 4 3 5,6,7 or 8 ⌈log2(n)⌉ = 3 for n = 5,6,7, or 8How to compute the parameter i in Linear hashing:
i = ⌈ log2( n ) ⌉ = # bits needed to represent the value n-1 (And [0..n-1] = the range of reak logical bucket numbers)
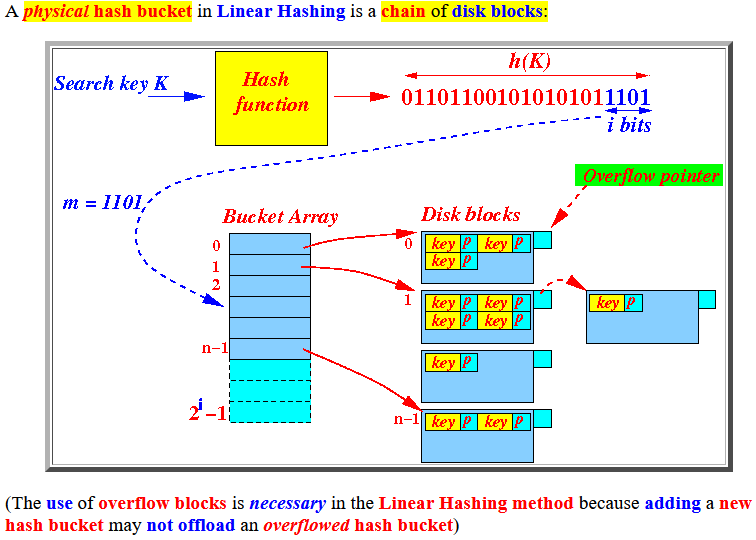
- A
physical hash bucket
in
Linear Hashing is
a
chain of
disk blocks:
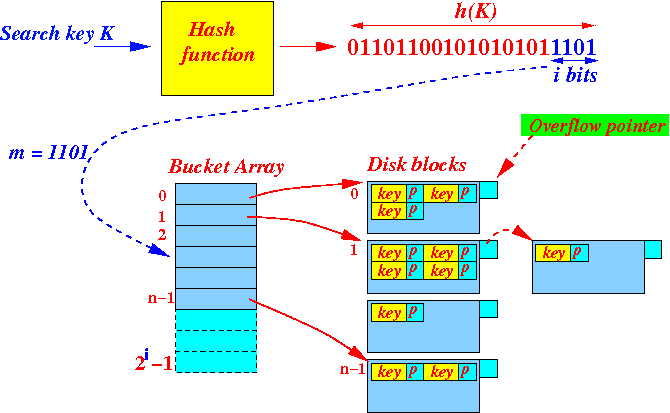
(The use of overflow blocks is necessary in the Linear Hashing method because adding a new hash bucket may not offload an overflowed hash bucket)
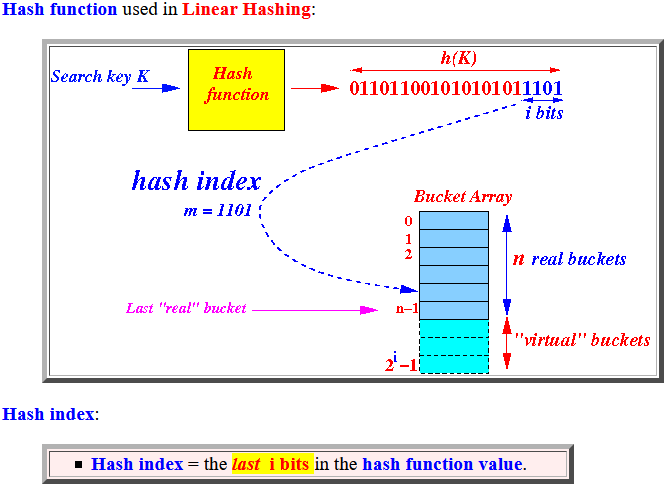
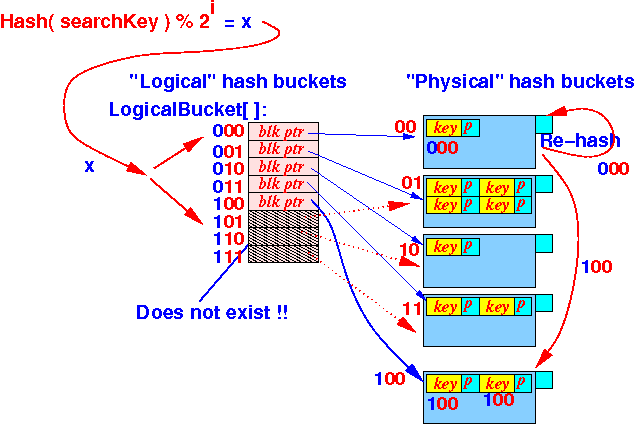
- Hash function used in
Linear Hashing:
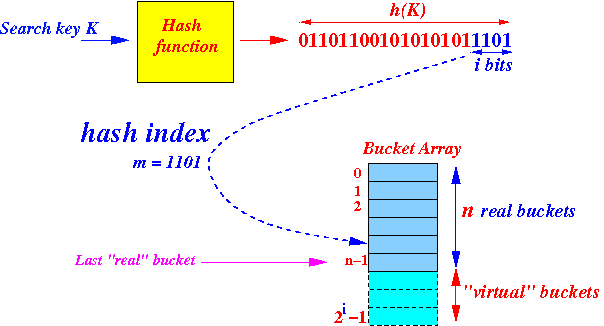
Hash index:
- Hash index = the last i bits in the hash function value.
-
Note: as
we have seen before
- A hash index can be > (n − 1) !!!
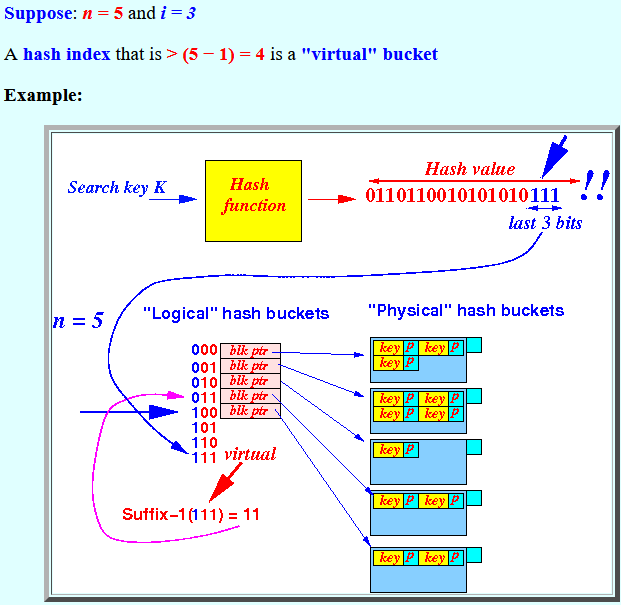
Example:
- Suppose:
n = 5
and i = 3
A hash index that is > (5 − 1) = 4 is a "virtual" bucket
Example:
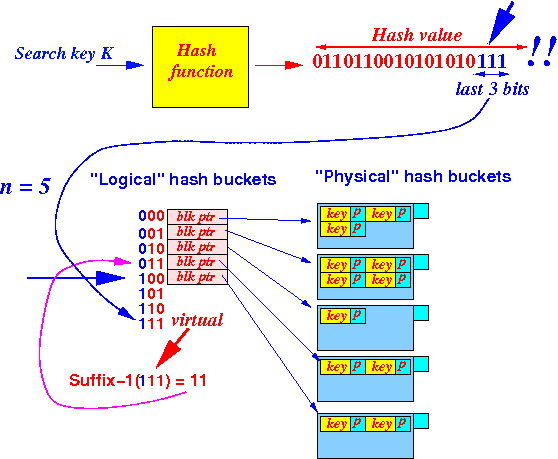
If the hash index is > (n − 1), then it is a virtual hash bucket
- We must map the hash index with the Suffix-1( • ) !!!
- Mapping
"virtual" hash buckets:
- We use the Suffix-1( )
mapping function
to
map
a virtual hash bucket:
Let x = a hash index if ( x ≤ (n − 1) ) { Use Bucket[ x ] to find the physical hash bucket } else { // "ghost" bucket !! Use Bucket[ Suffix-1(x) ] to find the physical hash bucket }
- We use the Suffix-1( )
mapping function
to
map
a virtual hash bucket:
Parameter: n = current number of buckets in use
i = ⌈ log(n) ⌉
Lookup( x )
{
k = hash(x); // k = hash function value
m = k % 2i; // Hash index (last i bits of k)
/* =============================================
Check if m is a real or virtual hash bucket
============================================= */
if ( m ≤ n−1 )
{
/* =========================================
m is a "real" bucket
========================================= */
Read Bucket[ m ] from disk;
Search (x, recordPtr(x)) in Bucket[m]
(including the overflow block);
}
else
{
/* =========================================
m is a "virtual" bucket
Use Suffix-1(m) to map !!
========================================= */
m' = Suffix-1(m);
// I.e.: m = 1xxxxxxxxxx
// m' = 0xxxxxxxxxx
// Note: m' is a "real" bucket !!!
Read Bucket[ m' ] from disk;
Search (x, recordPtr(x)) in Bucket[m']
(including the overflow block);
}
}
|
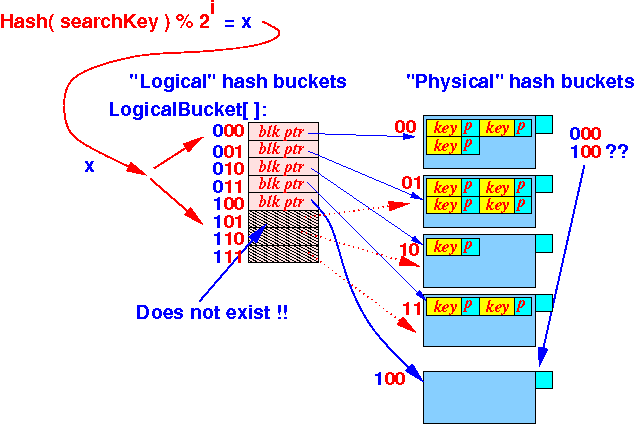
- Effect of
increasing the
physical hash table size:
- Adding a
new
physical hash bucket
can
reduce
the chain length
of the overflow blocks:
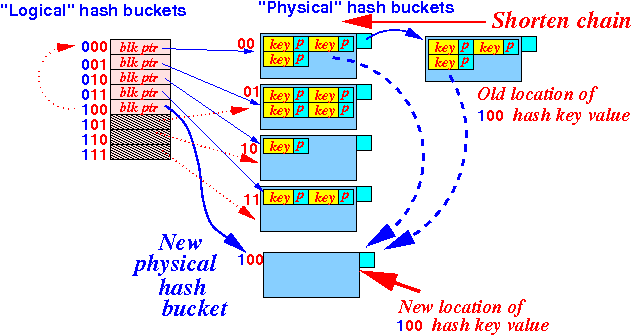
- Adding a
new
physical hash bucket
can
reduce
the chain length
of the overflow blocks:
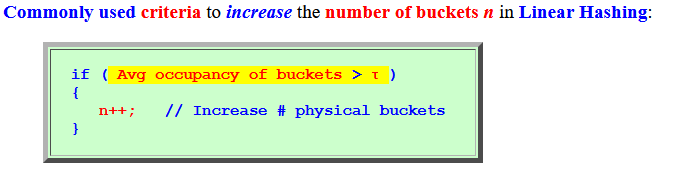
- Commonly used
criteria to
increase
the number of buckets n
in Linear Hashing:
if ( Avg occupancy of buckets > τ ) { n++; // Increase # physical buckets }
- How to determine
average occupancy of
buckets:
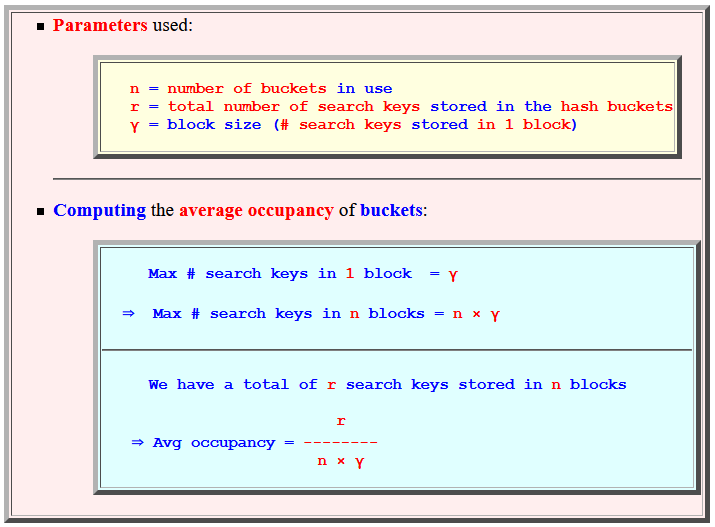
- Parameters used:
n = number of buckets in use r = total number of search keys stored in the hash buckets γ = block size (# search keys stored in 1 block)
- Computing the
average occupancy of
buckets:
Max # search keys in 1 block = γ ⇒ Max # search keys in n blocks = n × γ
We have a total of r search keys stored in n blocks r ⇒ Avg occupancy = -------- n × γ
Example:
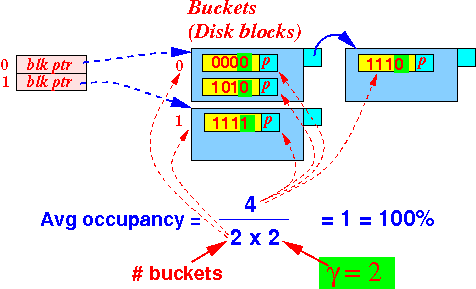
- Parameters used:
- Bucket increase criteria in
Linear hashing:
r if ( -------- > τ ) n × γ { n++; }
- Insert Algorithm:
Parameter: n = current number of buckets in use Insert( x , recordPtr(x) ) { i = ⌈ log(n) ⌉ // Using last i bits in hash value k = h(x); // h(x) = RandomNumGen(x) m = k % 2i ; // Last i bits = Linear hash function value /* --------------------------------------------------- Insert search key (x, recordPtr(x)) in "bucket m" --------------------------------------------------- */ if ( m ≤ n−1 ) { /* ========================================= m is a "real" bucket ========================================= */ Read disk block Bucket[ m ]; Insert (x, recordPtr(x)) into Bucket[m] (If overflow, use an overflow block) Write disk block Bucket[ m ]; } else { /* ========================================= m is a "virtual" bucket ========================================= */ m' = Suffix-1(m); // I.e.: m = 1xxxxxxxxxx // m' = 0xxxxxxxxxx // Note: m' is for sure a "real" bucket !!! Read disk block Bucket[ m' ]; Insert (x, recordPtr(x)) into Bucket[m] (If overflow, use an overflow block) Write disk block Bucket[ m' ]; } /* ============================================= Check if we need to add a new bucket ============================================= */ if ( r/(n*γ) > τ ) // Average occupancy > threshold { /* =========================================== Create a new physical hash bucket =========================================== */ Allocate a new disk block (for hash bucket); Bucket[n] = new disk block; // Bucket[n] is now real n' = Suffix-1(n); // Bucket[n'] was used to store // search keys belonging to Bucket[n] /* ================================================ Re-hash all keys in Bucket[n'] into: Bucket[n'] and Bucket[n] ================================================ */ j = ⌈ log(n+1) ⌉ ; // The range of hash bucket index is now [0..n] // j = number of binary digits to express n for ( every search key k ∈ Bucket[ n'] ) do { if ( (last j bits of k) == n ) { move search key k into the new Bucket[n]; (Allocate overflow blocks if necessary) } } n++; // One more "real" hash bucket } }