- Sockets:
- (Network) socket =
= a program endpoint
for sending/receiving data
- A socket is
associated with a
network port
that is identified by
a socket address
- Socket address consists of:
- IP address of the host
- The port # of the kernet (UDP) port
- (Network) socket =
= a program endpoint
for sending/receiving data
- Data structure
in C used to store
Socket addresses
of an (Internet) UDB port:
struct sockaddr_in { sa_family_t sin_family; /* Socket's address family - Must contain the value AF_INET */ in_port_t sin_port; /* Socket's Internet Port # - a 2 bytes port number */ struct in_addr sin_addr; /* Socket's Internet Address (IP-address) - a 4 bytes IP address */ };Meaning of the variables:
- sin_family:
(Internet socket family)
- The sin_family must be set to the (constant) value AF_INET for the IP protocol
- sin_port:
(the data type of
this variable is
short --- Internet socket port#)
- If sin_port > 0 then:
- sin_port = the port# of some port in the Operating System
- If sin_port = 0 then:
- the system will pick an unassigned port for you
Very important:
- sin_port must be stored in network byte order (more later) !!!!
- If sin_port > 0 then:
- sin_addr:
(the data type of this
variable is a
struct ---
one of the field (s_addr
contains the IP address)
- sin_addr =
the 4 byte
IP address
Note:
- There is a special
wildcard IP address named:
INADDR_ANY
We will discuss this in the multi-homed IP host section later
- There is a special
wildcard IP address named:
INADDR_ANY
Very important:
- sin_addr must also be stored in network byte order (more later) !!!!
- sin_addr =
the 4 byte
IP address
- sin_family:
(Internet socket family)
- More on the
sin_addr field:
-
The sin_addr variable
is a struct typed variable
used to store an IP address:
/* Internet address. */ struct in_addr { uint32_t s_addr; /* 4 bytes IP address in network byte order */ } sin_addr;
-
The sin_addr variable
is a struct typed variable
used to store an IP address:
- Pre-liminary example:
how to
initialize
an
the IPv4 address structure
(1) We first define a socket address variable: struct sockaddr_in in_addr; (2) Then we initialize the socket address: in_addr.sin_family = AF_INET; /* Protocol domain is: Internet */ in_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = ....; /* IP address in netw byte order */ in_addr.sin_port = ....; /* Port # in netw byte order */(We will complete the example later after a discussion on byte ordering)
- Host
byte ordering:
- Host byte ordering = the byte ordering used by the host computer
- Recall
from CS255:
- A host computer can use
one of
2 different ways
to store serie of bytes
in the
memory of a computer:
- big endian and
- little endian.
Example:
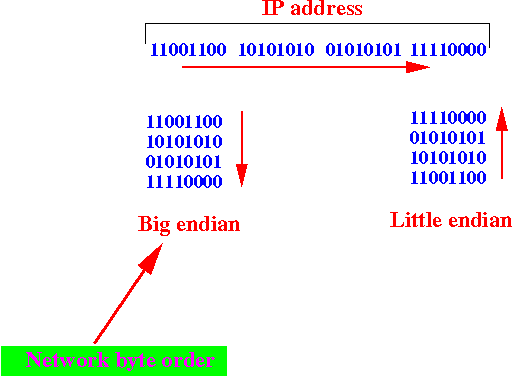
- A host computer can use
one of
2 different ways
to store serie of bytes
in the
memory of a computer:
- Network byte order:
- Network programming must always use the big endian order
- Specifically:
- These variables in
the socket Internet address
structure
- sin_port (Socket's Internet Port number)
- sin_addr.s_addr (Socket's Internet Address)
must use the network byte ordering !!!
- These variables in
the socket Internet address
structure
- Converting from
host ordering to
network ordering:
- int htonl(int):
(host to network long)
- input = 4 bytes in host ordering
- output = 4 bytes in network ordering
Example usage:
struct sockaddr_in in_addr; int IP = 170*256*256*256 + 140*256*256 + 150*256 + 1; // 170.140.150.1 in_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(IP);
- short htons(short):
(host to network long)
- input = 2 bytes in host ordering
- output = 2 bytes in network ordering
Example usage:
struct sockaddr_in in_addr; in_addr.sin_port = htons(8000);
- int htonl(int):
(host to network long)
- Example: setting up an
IPv4 socket address structure
with
- IP address = 170.140.150.1
- Port # = 8000
Program code:
/* =============================================== Define a socket address variable =============================================== */ struct sockaddr_in in_addr; /* ====================================================================== Initialize the socket address ====================================================================== */ in_addr.sin_family = AF_INET; /* Protocol domain is: Internet */ int IP = 170*256*256*256 + 140*256*256 + 150*256 + 1; // IP address is in host byte order !!! in_addr.sin_addr.s_addr = htonl(IP); /* IP address in network byte order */ in_addr.sin_port = htons(8000); /* Port # in network byte order */
- Fact:
- If we want to print
the IP address or the
port # stored in
an socket address variable:
- We must first convert the network byte order representation to host byte order before printing !!!
- If we want to print
the IP address or the
port # stored in
an socket address variable:
- Converting from
network ordering to
host ordering:
- int ntohl(int):
(network to host long)
- input = 4 bytes in network ordering
- output = 4 bytes in host ordering
Example usage:
struct sockaddr_in in_addr; int IP; IP = ntohl(in_addr.sin_addr.s_addr); /* ========================================================== If you need to use (e.g., print) the value, you need to convert it to HOST order first ========================================================== */ printf("%d", IP); // Prints the integer repr of the IP address // Computer program statements always use "host ordering" !!
- short ntohs(short):
(host to network long)
- input = 2 bytes in network ordering
- output = 2 bytes in host ordering
Example usage:
struct sockaddr_in in_addr; short portNum; portNum = ntohs(in_addr.sin_port);
- int ntohl(int):
(network to host long)