- We must distinguish between multicast forwarding over:
- One physical network (e.g., Ethernet, FDDI, etc)
- on the Internet (a logical network)
- Receiver specifies to join a multicast group using:
setsockopt(s, IPPROTO_IP, IP_ADD_MEMBERSHIP, (char *) &mreq, sizeof(mreq) ); - When the kernel processes this setsockopt system call,
it records the multicast address.
- Senders use an IP multicast address in the sendto system call
to send IP-multicast messages.
- IP multicast messages on a broadcast LAN is transmitted using
LAN broadcast.
For Ethernet, the IP multicast messages is transmitted in an Ethernet frame containing the broadcast address (FF:FF:FF:FF:FF:FF) as destination address.
There is
no ARPing used in IP multicast transmission in Ethernet to find the hosts' Ethernet interface addresses. - The multicast message is delivered to all hosts on the broadcast LAN but only those IP kernel that have been programmed to recognize the multicast group (by using the setsocketopt call) will process and forward the multicast packet when a matching IP multicast group address is found:

- The multicast message is delivered to all hosts on the broadcast LAN but only those IP kernel that have been programmed to recognize the multicast group (by using the setsocketopt call) will process and forward the multicast packet when a matching IP multicast group address is found:
- Multicasting on a single LAN requires a change in the OS kernel
and it is relatively simple to do.
- When you want to perform multicast over the Internet,
you cannot achieve it by changing OS kernels...
Even if you change every OS kernel in every computer, the Internet will NOT perform multicasting...
The reason is:
-
The Internet was NOT designed to perform
multicasting !!!
- Recall the IP forwarding algorithm:

- IP multicast address will contain destination addresses
that do not pertain to any host or network
IP multicast addresses will not be found in the routing table data structure....
- When a router encounters an IP address that it does not recognize
(no entry in the routing table) and it does not have a default router,
it will drop the packet.
Note: routers on the backbone of the Internet do not use default routers (they must know how to get to everyone).
- Therefore, when Deering started to implement IP multicasting,
routers on the Internet will drop multicast packets....
In fact, there are still plenty of routers on the Internet that do not recognize class D (multicast) addresses.
- Multicast packets will not reach their destinations with the existing IP routing software (in 1993).
- A router that recognize and can process multicast packets
(i.e., IP packets with Class D - multicast - addresses)
is called
multicast enabled.
-
Right now, multicast enabled routers are available and quite common.
(But there are still many multicast unaware routers, and even if a company has multicast enabled routers, they often choose not to enable multicast because of the high bandwidth demand of many multicast applications (which are usually multi-media - like video and audio conferencing))
- But back in 1993 when multicast was being developed,
not a single router recognize Class D addresses.
When a multicast IP packet arrives at such router, the packet is dropped like a brick...
- In order to make multicast happen with routers that are multicast
unaware, Deering used tunneling (what else ?)
to transfer IP multicast packets over the Internet:
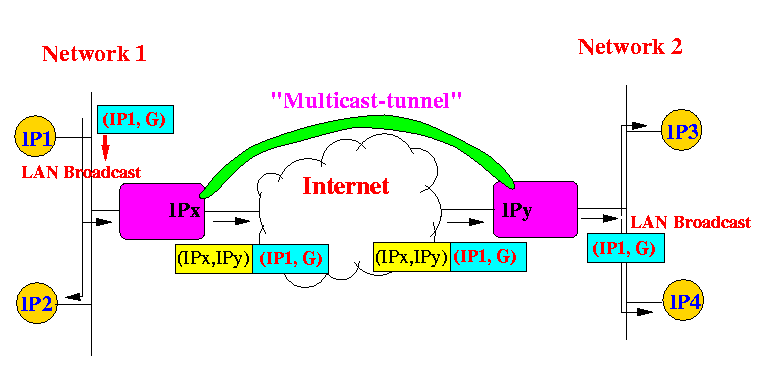
- Initially, Deering tested his multicast tunneling distribution
between a small number of sites, but quickly,
purely out of enthusiasm, most academic sites
obtained and install the tunneling software.
By 1994, a logical network has been built on top of the Internet (which itself is a logical network...) consisting of multicast enabled IP routers:
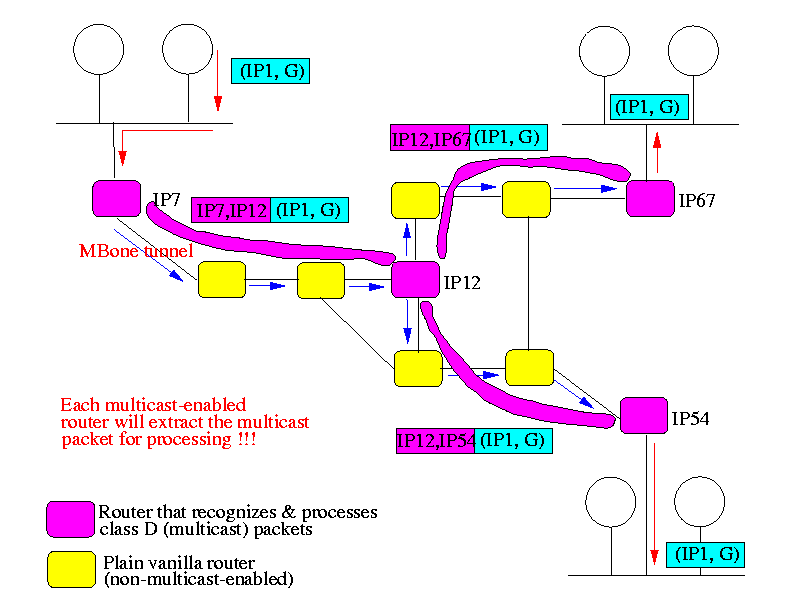
This logical multicast enable network is called the MBone - for Multicast Backbone.
- Internet 2
- The information that ate being multicasted over the Internet are
usually multimedia (video and audio) and they require high bandwidth
to achieve good performance.
- Due to the popularity of the Internet (DOT COMs), the Internet
is often overused.
Multicast applications will perform poorly over the ordinary Internet.
- Due to overcrowding, a new Internet network has been established
for research purposes, the Internet 2:
click here
- Since multicasting is one of the premier research area in networking,
most routers on Internet 2 are multicast enabled, i.e.,
these routers recognize multicast addresses and have
multicast forwarding software
that processes the multicast packets (discussed later)
So you don't need tunnels for multicasting in Internet 2.
- The information that ate being multicasted over the Internet are
usually multimedia (video and audio) and they require high bandwidth
to achieve good performance.
- You cannot do anything without information...
So also, you need information to perform multicast forwarding.
- Multicast enabled routers maintains in addition to
the unicast routing table, an additional
multicast routing table.
More on multicast routing information on the next few webpages....