- Direct link:
- Direct link =
a communication line that
connects 2 nodes directly
Graphically:
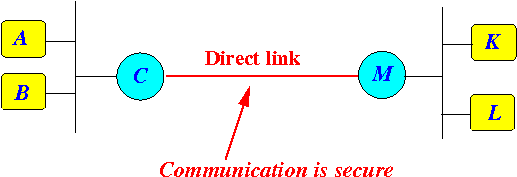
- Communication through a
direct link owned by
the same company is
very secure
(from eave dropping)
- To eave drop, the intruder will have to tap the direct link
- Direct link =
a communication line that
connects 2 nodes directly
- Tunnel ----
Virtual direct link:
- Tunnel = a
virtual "direct" link
- The messages
are transmitted over
many nodes
- The nodes can belong to different owners
- The messages transmitted through the (insecure) tunnel is made secure through encryption technqiues
Graphically:
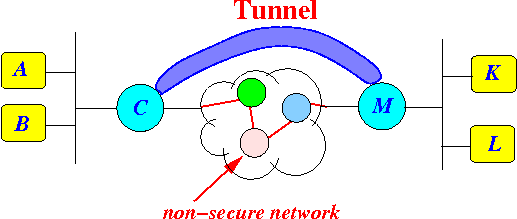
- The messages
are transmitted over
many nodes
- Tunnel = a
virtual "direct" link
- Suppose a company has
offices in
2 locations:
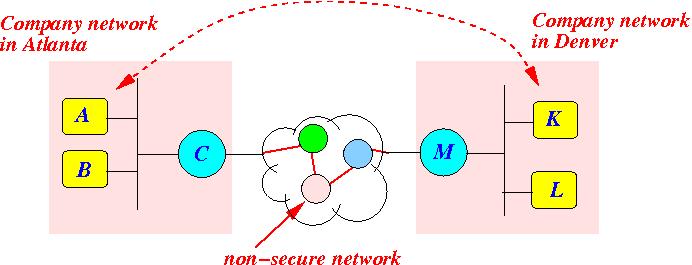
- Suppose we want to
setup
a secure tunnel between
the
company networks:
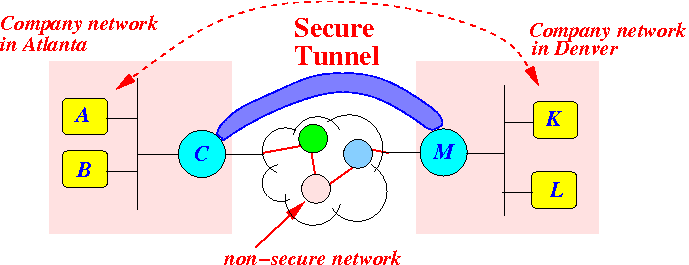
In other words:
- IP packets sent on a
(any) company network
can be plain (= not-secured)
- IP packets sent from
C ⇒ M must be
secured
(= encrypted
I.e.:
- The content of the IP packets sent from C ⇒ M must not be plain
Graphically:
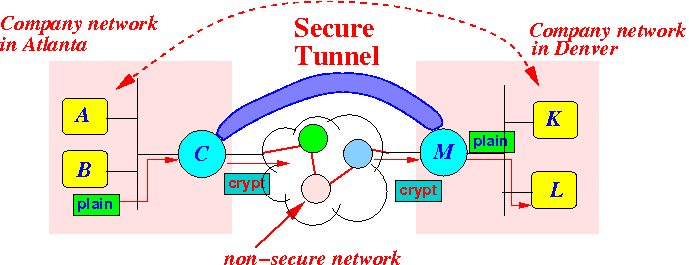
- IP packets sent on a
(any) company network
can be plain (= not-secured)
- How to
realize the
secure transmission
between
2 networks:
- Host A sends a
(plain) IP packet
to its router C:
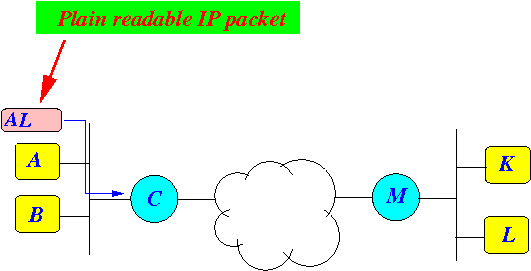
- The router C
processes the (plain) IP packet
as follows:
- Router C encrypts the (plain) IP packet
- Router C then transmits the encrypted IP packet inside a new IP packet to destination router M
Graphically:
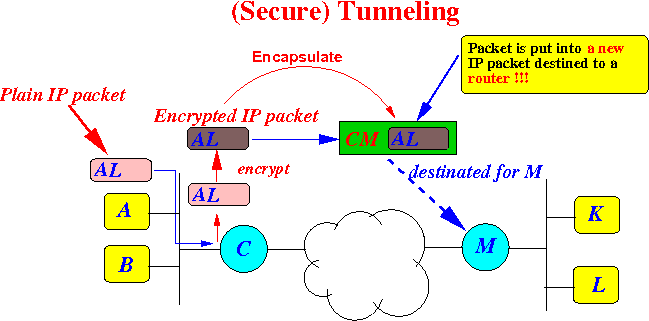
Postponed discussion:
- We will discuss
how
the router C
can know when to
perform encapsulate
later
- The discussion is given here: click here
(Obviously, router C should not do this all the time !!!)
- The encapsulated IP packet is
then routed
using IP forwarding to the
destination M:
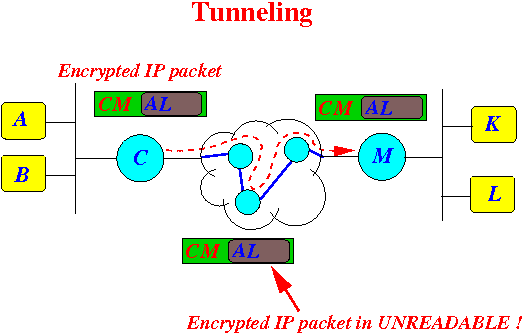
Notice that:
- Nodes can
forward the
IP packet to the
destination M using the
outer IP packet:
- Destination IP address of outer packet is router M !!!
- But the
nodes
can not decrypt
(= decode and read) the
encrypted inner IP packet !!!
So it feels like the packet transmission is on a direct link:

- Nodes can
forward the
IP packet to the
destination M using the
outer IP packet:
- When the destination router M
receives the
(encapsulated) IP packet:
- Router M
detects that the
IP packet contains
its own IP address
M !!!
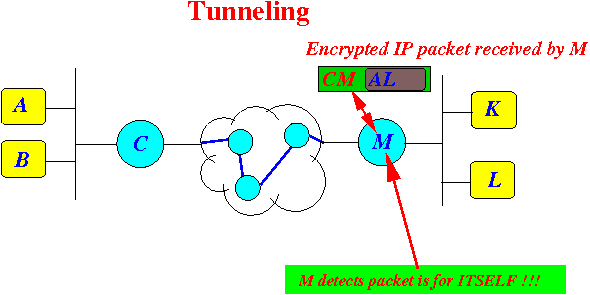
Note:
- This is not normal:
- IP packets
(so far in the course) contains
destination addresses of
host (= computers)
- IP packets are not transmitted to routers !!!
- IP packets
(so far in the course) contains
destination addresses of
host (= computers)
Creative usage:
- When destination IP address is
equal to
a router IP address:
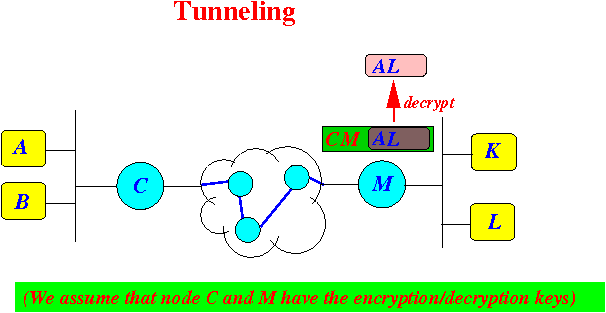
- The router will perform a de-capsulation operation !!!
In this example:
- The router M will first decrypt the inner IP packet and
- Then the router M will forward the de-crypted packet
- Router M
detects that the
IP packet contains
its own IP address
M !!!
- Router M
decrypts the inner IP packet:
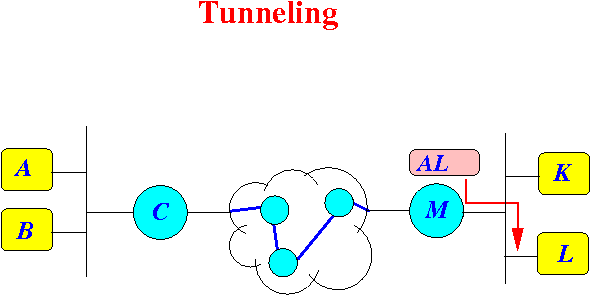
- And finally, the router M
forwards the
decrypted IP packet to
the final destination L:
- Host A sends a
(plain) IP packet
to its router C:
- Summary:
- The following diagram shows the
regions where the
IP packet are
readable/unreadable:
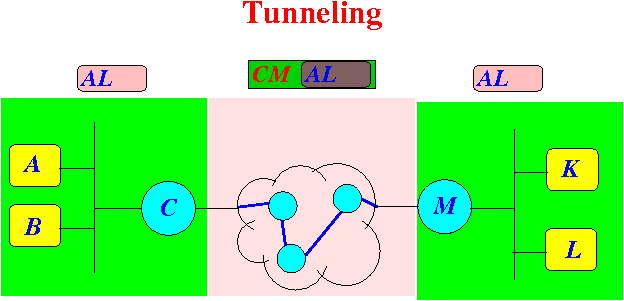
- It feels like there is a
secure tunnel between
C and
M:
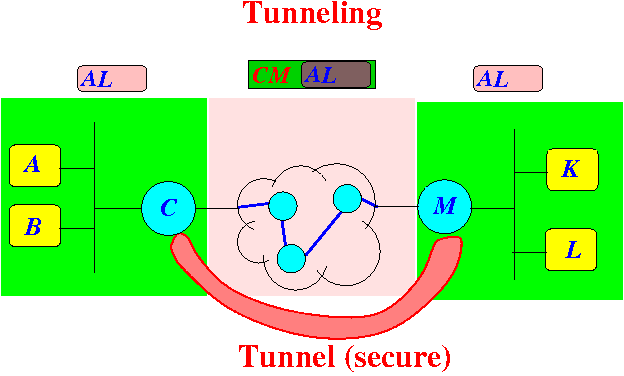
- The following diagram shows the
regions where the
IP packet are
readable/unreadable: