- How
to implement the
Internet protocol:
- A router or
computer
that implements
the Internet Protocol
contains software (program) that:
- process messages (= packets) in the IP packet format
- The software will:
- Find the
source/destination IP addresses in
the IP packet
- Lookup the
output interface based on the
destination address
- Transmit the IP packet on an output interface
- Find the
source/destination IP addresses in
the IP packet
- A router or
computer
that implements
the Internet Protocol
contains software (program) that:
- The Internet:
- Internet = a network of routers and computers that exchange messages ("packets") that conform to the IP packet format.
- There are nowadays
2 types of
IP packet formates:
- IP version 4 (IPv4) ---
this is the original IP format
- IP version 6 (IPv6) --- this is the new IP format that will replace IPv4 hopefully, one day in the future....
- IP version 4 (IPv4) ---
this is the original IP format
- The IPv4 packet consists of:
- The IPv4 header
- The header contains control information
- The payload
- The payload (= data portion)
is the message carried inside
an IP packet
- The most common payload
carried inside an
IP packet is:
- A TCP protocol message
- The payload (= data portion)
is the message carried inside
an IP packet
- The IPv4 header
- The IPv4 packet format:
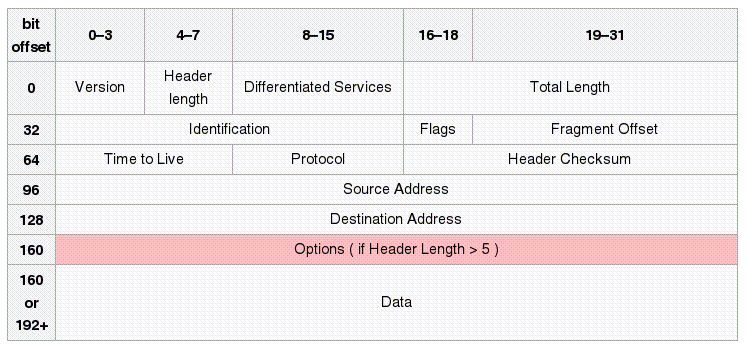
How the fields in the IP packet is used:
- Version:
- 0100 (4) (4 bits) - identifies the version of the IP protocol
- Header Length:
- number of 32-bit words in the header.
-
Type of Service (a.k.a: Differentiated Services):
- specify a preference for how the datagram would be handled (a kind of priority indicator)
Comment:
- This field is now defined by
RFC 2474 for
Differentiated services (DiffServ) and
- by RFC 3168 for Explicit Congestion Notification (ECN)
- Total Length:
- number of bytes of the entire IP datagram, in bytes (16 bits)
Comments:
- The smallest IP packet
with no data
(only the IP header) is
20 bytes long
- The largest IP packet has 65,535 (216 - 1) bytes (total length)
- Identification:
- This field is used in the
fragmentation operation
(See next webpage)
- This field is used in the
fragmentation operation
- Flags:
- The flags is
a three-bit field used to
control or identify fragments.
(See next webpage)
Comment:
- Bit 1: Reserved; must be zero (meaning: can't find a use for the bit yet :-))
- Bit 2: Don't Fragment (DF)
- Bit 3: More Fragments (MF) (explained below)
- The flags is
a three-bit field used to
control or identify fragments.
- Fragment Offset:
- specifies the offset of this fragment
relative to the beginning
of
the
original unfragmented IP datagram.
(Explained in the next webpage)
- specifies the offset of this fragment
relative to the beginning
of
the
original unfragmented IP datagram.
- Time To Live (TTL):
- Used to limits the range of the packet
How the TTL field is used:
- Each router
that routes an IP packet will
decrement the
TTL
field by one.
- When the TTL field
becomes zero,
the IP packet is
discarded.
- This feature will stop an IP packet from looping forever !!!
- Protocol:
- Specifies the Transport layer protocol (= type of message) that is carried in the data portion of the IP datagram.
Common "protocol" values:
- 6 = TCP
- 17 = UDP
More details, see: click here
- Header Checksum:
- This is the CRC code
Comment"
- Checks only the header
(Does not include the data portion in the check sum)
Note:
- Because the TTL field is decremented (changed) by the router, the checksum must be recomputed each time by the router.
- Source and Destination address:
- IP address of the source and destination
- Options:
- Extra fields --- such as additional header fields
(Not of interest to this course, will not discuss further)
- Version:
- The IPv6 packet format:

How the fields in the IPv6 packet is used: Notes:
- Version::
- 0110 (6) (4 bits) --- identifies verion 6
- Traffic class:
- contains the priority of this IP packet (8 bits)
- Flow label:
- Used to indicate the QoS (Quality of Service) management function (20 bits)
Comment:
- Originally created togive real-time (video) applications special service, but currently unused.
- Payload length:
- The size of the payload (= data portion) in # of bytes (16 bits).
- Next header:
- Contains the location of the
next protocol data
(8 bits).
- Normally (usually), the
next header will be
location of the
the transport layer protocol data
- Under special circumstances, the sender can add options to the IPv6 header
- Normally (usually), the
next header will be
location of the
the transport layer protocol data
- Contains the location of the
next protocol data
(8 bits).
- Hop limit:
- is the same filed as the time to live (TTL) field of IPv4 (8 bits).
- Source and destination addresses:
- same as IPv4, except the IPv6 addresses are 128 bits each.
- Version::
- Fact:
- The IPv6 header does
not contain
fragmentation/re-assembly
fields
- IPv6 does have
fragmentation/re-assembly:
- IPv6 provdies
fragmentation/re-assembly using
the
fragment option header
See: click here
- IPv6 provdies
fragmentation/re-assembly using
the
fragment option header
- The IPv6 header does
not contain
fragmentation/re-assembly
fields