Brief history of
GPU computing
- Before 2006:
- Graphics cards were
designed perform
specialized
graphics rendering
functions
- "Graphic Accerelation" Hardware
performs the
rendering algorithm
|
- Not
programmable
(i.e.: can
only
perform
image rendering)
|
-
2006:
introduction of
the
general purpose
Graphics Processing Unit
(GPGPU)
to save on
hardware cost:
- The GPU can now be
programmed using a
high-level programming language
(C)
- The rendering algorithm is
executed using
software
|
- Library functions were
provided to
support
GPU programming
|
|
For more info:
click here
The CUDA architecture
The CUDA architecture makes
the
GPU computer as a
subsystem of a
CPU (host) computer:

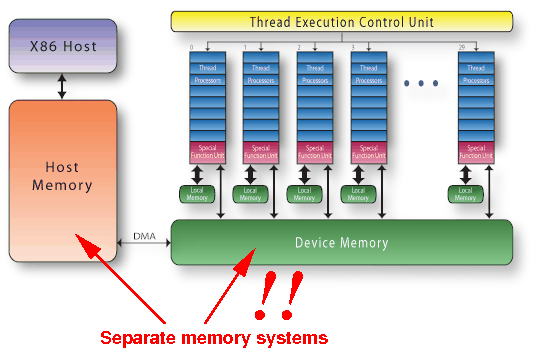
The CUDA architecture
The CPU system and
the GPU (sub)system have
their own (independent) memories:
The CUDA architecture
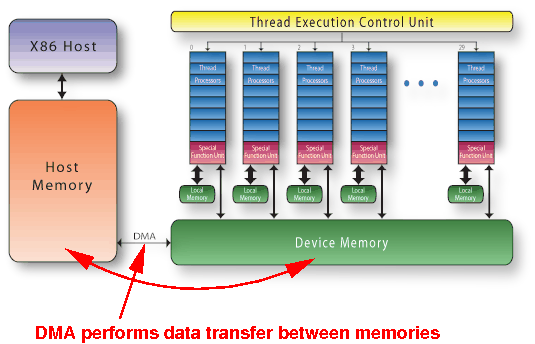
Consequently:
data must be
transfered between
RAM and
device memory
(using DMA):
CUDA programming
A
CUDA (computer) program consists
of 2 parts:

(1)
a
CPU part of
the
CUDA program
stored in
RAM
(and executed by
the CPU)
CUDA programming
A
CUDA (computer) program consists
of 2 parts:

(2)
a
GPU part of
the
CUDA program
stored in the
device memory
(and executed by the
GPU)
How to write the CPU program part of a
CUDA program
- The CPU program part
of a CUDA program is
typically
written in the C programming language
and can use
functions in the
C library
Example:
int main( )
{
printf("Hello World\n");
// Standard C programming statements
// Can use functions in C library
}
|
|
How to write the GPU program part of a
CUDA program
- The GPU program part
of a CUDA program in
written in the
"CUDA C" programming language
and can use
functions in the
"CUDA C" library
Example:
__global__ void hello( )
{
printf("Hello World\n");
// CUDA C code
// Uses printf( ) in CUDA C library !
}
|
|
Note:
CUDA C
is
designed to be
similar to
the C language to
make it easy to learn !!!
How does the
GPU execute a
CUDA function
- A CUDA function is
executed by
multiple threads
(of execution):
- All
threads will
execute the
same
series of
instructions
(
"SIMT")
|

- A
thread
is executed on
a
"core"
(a.k.a.
CUDA core)
--- explained next
- There can be more threads than
cores.
A core will then
alternate
executions
of different threads
|
❮
❯





