A commonly used
parallel programming pattern
- A commonly used
parallel programming
pattern:
main( )
{
Prepare data1;
Spawn N "worker" threads to process data1;
Wait for all threads to complete processing
Prepare data2;
Spawn N "worker" threads to process data2;
Wait for all threads to complete processing
....
}
|
- Graphical
depiction of
each step:
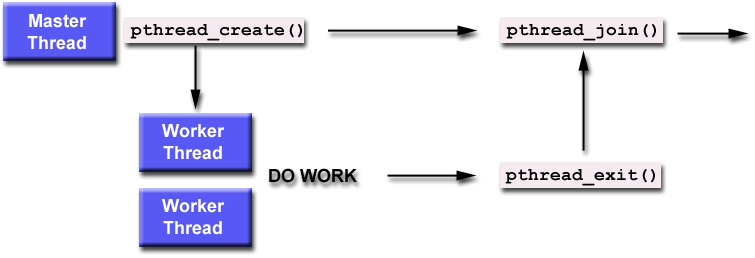
|
Detached and
Joinable
threads
- There are
2 kinds of
threads in
the PThread API:
- Detached
threads
- Joinable
threads
|
-
Detached
threads:
- A detached
thread is an
"independent"
thread
- When a
detached
thread
terminates, its
resources
are
released back
to the system
immediately
|
-
Joinable
threads:
- A joinable
thread is a
"dependent"
thread
- When a
joinable
thread
terminates, its
resources
are
retained until
the thread
joins
with its
creator thread
|
- The
default
setting of
pthread_create( ) will
create a
joinable
thread
|
How to
"join" (= wait for) a
joinable thread
to finish
- When the main thread
creates a
"worker" thread, it must
record its
thread ID:
pthread_t tid;
if ( pthread_create(&tid, NULL, worker, &n) != 0 ) // Create thread
{
perror("pthread_create"); // Print error message
exit(1);
}
|
- The main thread can
"join" (= wait for)
a joinable thread with the
pthread_join( )
call:
pthread_join(pthread_t threadID, void **retval);
threadID = the thread ID returned by pthread_create( )
retval = return value returned by the exiting thread
Example:
pthread_join( tid, NULL ); // NULL = ignore the return value
|
|
Example on using
thread_join( )
- Consider the following
program where
main( ) does
not
join with the
worker thread:
void *worker( )
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 10000000; j++); // Slow thread down...
printf("*");
fflush(stdout);
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
pthread_t tid;
if ( pthread_create(&tid, NULL, worker, NULL) != 0 ) // Create thread
{
perror("pthread_create"); // Print error message
exit(1);
}
// Do NOT join (wait)
}
|
- Result:
nothing is
printed
(because
main( )
exited before
worker
prints)
|
DEMO:
demo/pthread/join01.c
Example on using
thread_join( )
- We change it so
main( ) will
pthread_join( ) with the
worker thread:
void *worker( )
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 10000000; j++); // Slow thread down...
printf("*");
fflush(stdout);
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
pthread_t tid;
if ( pthread_create(&tid, NULL, worker, NULL) != 0 ) // Create thread
{
perror("pthread_create"); // Print error message
exit(1);
}
pthread_join(&tid, NULL); // Join with (wait for) worker to finish
}
|
- Result:
********** is
printed
(because
main( )
waited for
worker( )
exit)
|
DEMO:
demo/pthread/join01b.c
How to wait for
multiple worker threads
to complete execution
- Program that
creates a
group of
worker
threads:
void *worker(int *id) // Not syntactically correct, but easier to code...
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 10000000; j++); // Slow thread down...
printf("%d", *id);
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
pthread_t tid[4];
int arg[4];
for ( int i = 0; i < 4; i++ )
{
arg[i] = i;
if ( pthread_create(&tid[i], NULL, worker, &arg[i]) != 0 ){
perror("pthread_create"); // Print error message
exit(1);
}
}
for ( int i = 0; i < 4; i++ )
pthread_join(tid[i], NULL);
}
|
|
How to wait for
multiple worker threads
to complete execution
-
Create the
group of
threads and
save each
thread ID:
void *worker(int *id) // Not syntactically correct, but easier to code...
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 10000000; j++); // Slow thread down...
printf("%d", *id);
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
pthread_t tid[4];
int arg[4];
for ( int i = 0; i < 4; i++ )
{
arg[i] = i;
if ( pthread_create(&tid[i], NULL, worker, &arg[i]) != 0 ){
perror("pthread_create"); // Print error message
exit(1);
}
}
for ( int i = 0; i < 4; i++ )
pthread_join(tid[i], NULL);
}
|
|
How to wait for
multiple worker threads
to complete execution
-
Wait for
every
thread to
finish:
void *worker(int *id) // Not syntactically correct, but easier to code...
{
for (int i = 0; i < 10; i++)
{
for (int j = 0; j < 10000000; j++); // Slow thread down...
printf("%d", *id);
}
}
int main(int argc, char *argv[])
{
pthread_t tid[4];
int arg[4];
for ( int i = 0; i < 4; i++ )
{
arg[i] = i;
if ( pthread_create(&tid[i], NULL, worker, &arg[i]) != 0 ){
perror("pthread_create"); // Print error message
exit(1);
}
}
for ( int i = 0; i < 4; i++ )
pthread_join(tid[i], NULL);
}
|
|
DEMO:
demo/pthread/join02.c
❮
❯
