More details of the structure of a CPU
A CPU (processor) consists of
a chip on a
casing with
many connection pins:

The CPU (processor) is
inserted into a
CPU socket on a
mother board
(and connects to the
motherboard
by it pins):

Buses on the motherboard
The motherboard
contains wiring (= buses)
that connects the
CPU
to other components
(= memory and IO devices) of the computer:

Pins and signal names
- The pins on a
CPU chip are
used as
inputs and outputs
to the CPU.
- Each pin
signals
a specific:
- data bit
- address bit or
- a command/status
|
- Each pin of the
CPU is
connected to
one wire on the
motherboard
- Every pin
on the CPU
has a signal name
E.g.:
- MREQ (memory request)
- READ (read operation)
- etc
|
|
Terminology: asserted
- Asserted:
- We say that a
signal
is "asserted"
if the CPU is requesting
the
operation that is
conveyed by
the signal.
-
Important fact:
-
Signal is asserted ≠
signal value = 1 !!!
- To assert
a request, the manufacturer of the CPU
can choose
either
the
value 0 or
the
value 1
for the signal !!
|
|
|
How to denote that a
signal is asserted using the
value 1
A signal that is
asserted when the
signal value = 1 is
denoted by:
SignalName
Example:

How to denote that a
signal is asserted using the
value 0
A signal that is
asserted when the
signal value = 0 is
denoted by:
SignalName
Example:

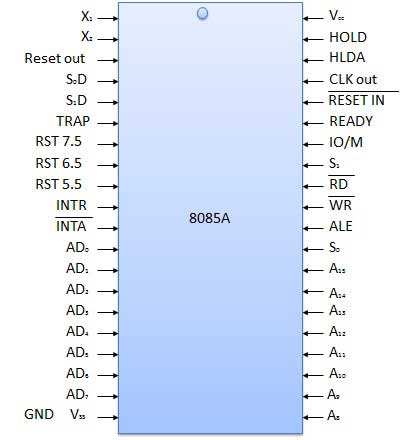
Example of
signal names (the 8085A CPU)
Notice that
some signals are
asserted by 1 (e.g.:
INTR) and
other signals are
asserted by 0 (e.g.:
INTA)
The pins on a
CPU
There are 3 groups of
pins on a
CPU:

The pins on a
CPU
There are 3 groups of
pins on a
CPU:

The
Address pins
convey the address
of a memory location
The pins on a
CPU
There are 3 groups of
pins on a
CPU:

The
Address pins
can also convey the address
of an IO device
The pins on a
CPU
There are 3 groups of
pins on a
CPU:

The
Data pins
convey the data
transfered between
the CPU and
memory
or an IO device
The pins on a
CPU
There are 3 groups of
pins on a
CPU:

The
Control pins
convey command/status info
between
the CPU and
memory/IO device
Categories of
signals in the
control pin group
- Bus control:
- output pins
of the CPU
that are used to
send commands to
the memory and IO devices
|
- Processor status:
- output pins
given status information
of the CPU
(allows memory/IO-debice to
check if the CPU is
ready or not)
|
- Interrupt control:
- Signals used by
IO devices to
synchronize with the
CPU (discussed later)
|
- Bus arbitration:
- Signals used by
CPU and
IO devices to
request/acquire
the use of the
data bus for
transfer
|
- Co-processor signaling:
used in older processer to
communicate with a
(Math) co-processor
|
Sample (M68000) Processor and its signals
This is the data sheet of
the M68000 CPU:

Notice the
control signals on the
data sheet
❮
❯











