Before we begin...
-
Do not memorize ---
understand what needs to be done and
how to achieve it
- Notations:
- I will
high light the
(reference) variable
that
must be
updated with
this color
|
- Handling
edge case(s):
- It happens
very often that
a
different
(reference) variable
must be
updated
for some
special ("edge")
cases
- We must look for (= test)
the edge cases and
handle (= process) them
separately
|
- Often,
the
edge cases are
- The empty
list
(
Test:
first == null
)
- A list that contains
only
1 element
(
Test:
first.next == null
)
|
|
|
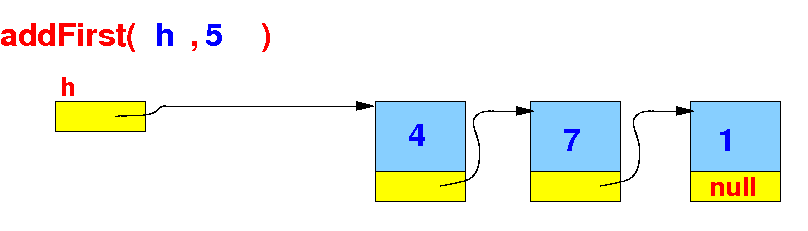
Inserting an item at the
front of the linked list
The effect of
addFirst(h, x) ---
inserting
x at the
front of
a linked list h:
Implementation of
addFirst()
The implementation of the
addFirst()
method:

- Let's write the
addFirst()
method:
(This is how to achieve it)
// Inserts a new node containg x
// at the beginning of the list at h
struct Node *addFirst(struct Node *h, int x)
{
Node<T> newNode = new Node<T>(item, oldFirst);
first = newNode;
}
|
|
Implementation of
addFirst()
The implementation of the
addFirst( )
method:
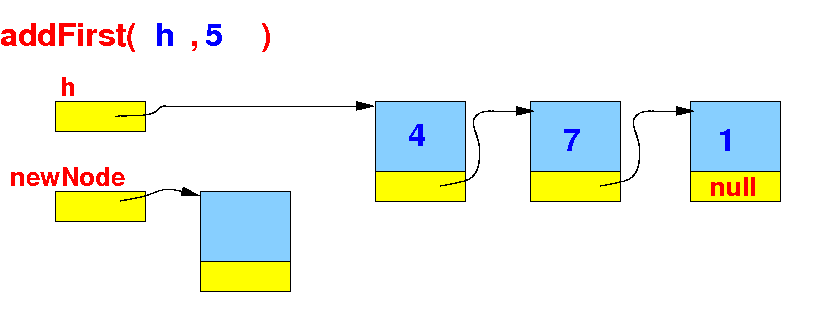
- Create a new Node:
// Inserts a new node containg x
// at the beginning of the list at h
struct Node *addFirst(struct Node *h, int x)
{
struct Node *newNode = malloc( sizeof(struct Node) );
first = newNode;
}
|
|
Implementation of
addFirst()
The implementation of the
addFirst( )
method:
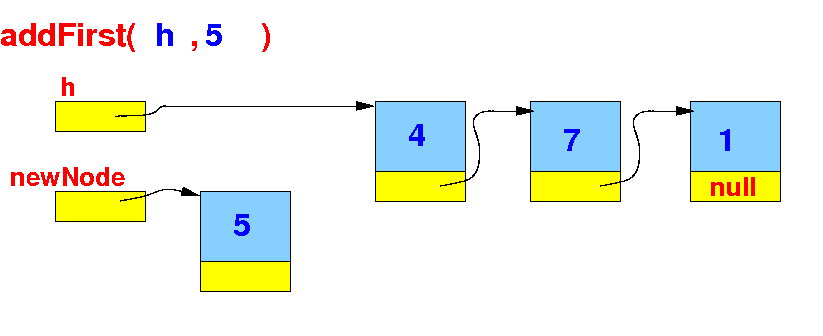
- Store the value
x in the
item field:
// Inserts a new node containg x
// at the beginning of the list at h
struct Node *addFirst(struct Node *h, int x)
{
struct Node *newNode = malloc( sizeof(struct Node) );
newNode->item = x; // Store x
first = newNode;
}
|
|
Implementation of
addFirst()
The implementation of the
addFirst( )
method:

- Make the
correct
linkage:
// Inserts a new node containg x
// at the beginning of the list at h
struct Node *addFirst(struct Node *h, int x)
{
struct Node *newNode = malloc( sizeof(struct Node) );
newNode->item = x; // Store x
newNode->next = h; // Make it point to h
first = newNode;
}
|
|
Implementation of
addFirst()
The implementation of the
addFirst( )
method:
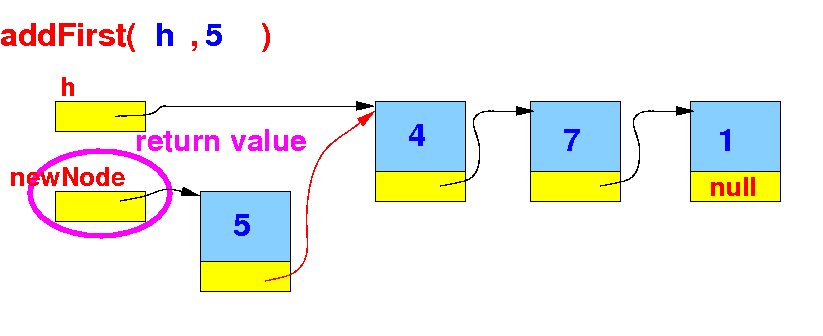
- Return the
new
first node:
// Inserts a new node containg x
// at the beginning of the list at h
struct Node *addFirst(struct Node *h, int x)
{
struct Node *newNode = malloc( sizeof(struct Node) );
newNode->item = x; // Store x
newNode->next = h; // Make it point to h
return newNode;
}
|
|
Implementation of
addFirst()
Check if
algorithm is
correct for
edge case(s):

- Run the
code for the
edge case(s):
// Inserts a new node containg x
// at the beginning of the list at h
struct Node *addFirst(struct Node *h, int x)
{
struct Node *newNode = malloc( sizeof(struct Node) );
newNode->item = x; // Store x
newNode->next = h; // Make it point to h
return newNode;
}
|
|
Implementation of
addFirst()
Check if
algorithm is
correct for
edge case(s):

- Step 1:
create node and
store value
// Inserts a new node containg x
// at the beginning of the list at h
struct Node *addFirst(struct Node *h, int x)
{
struct Node *newNode = malloc( sizeof(struct Node) );
newNode->item = x; // Store x
newNode->next = h; // Make it point to h
return newNode;
}
|
|
Implementation of
addFirst()
Check if
algorithm is
correct for
edge case(s):
Demo program
struct Node
{
int item;
struct Node *next;
};
int main()
{
struct Node *head = NULL;
int k;
printList(head);
for (k = 1; k < 5; k++ )
{
head = addFirst(head, k);
printList(head);
}
}
|
DEMO:
demo/C/Linked-list/addFirst.c
Alternate solution: pass
head by
reference
(so we can update head)
Alternately: we can
pass the
head variable
by reference:
struct Node
{
int item;
struct Node *next;
};
int main()
{
struct Node *head = NULL;
int k;
printList(head);
for (k = 1; k < 5; k++ )
{
addFirst(&head, k); // Pass head by reference
printList(head);
}
}
|
DEMO:
demo/C/Linked-list/addFirst-byRef.c
Alternate solution: pass
head by
reference
(so we can update head)
We change the
parameter type
of h in
addFirst and
we can now update the
the head using
*h (alias !!)
struct Node
{
int item;
struct Node *next;
};
// Inserts a new node containg x at the beginning of the list at h
// We pass the variable "struct Node *h" by reference
void addFirst(struct Node **h, int x)
{
struct Node *newNode = malloc( sizeof(struct Node) );
newNode->item = x; // Store x
newNode->next = *h; // Make it point to head
// WAS: return newNode;
*h = newNode; // Update "head" in main using the alias *h
}
|
DEMO:
demo/C/Linked-list/addFirst-byRef.c
❮
❯