- Binary Search Trees
was discussed in CS171
- Here are the CS171 notes from
last semester:
- BST slides, part 1: click here
- BST slides, part 2: click here
- I will not cover the
material in the webpage in detail.
I put it here in case you need to refresh your knowledge - as always, I added my personal touch to the material....
- Structure of a binary search tree:
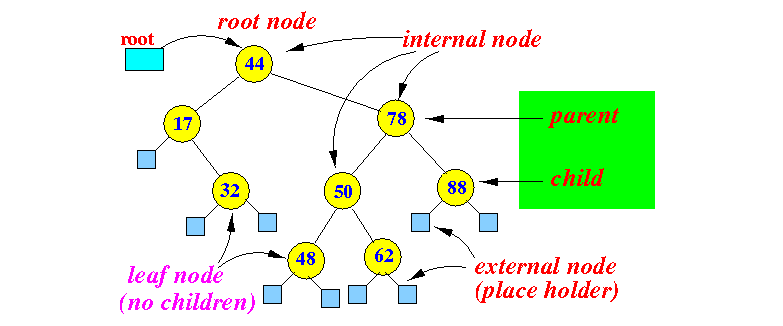
For simplicity, I will omit the external nodes and draw the binary search tree as:

- Properties:
- The keys stored in the left subtree of any node n are < n.key
- The keys stored in the right subtree of any node n are > n.key
Examples:
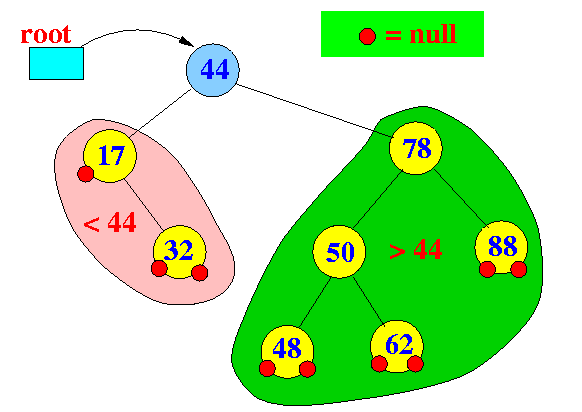
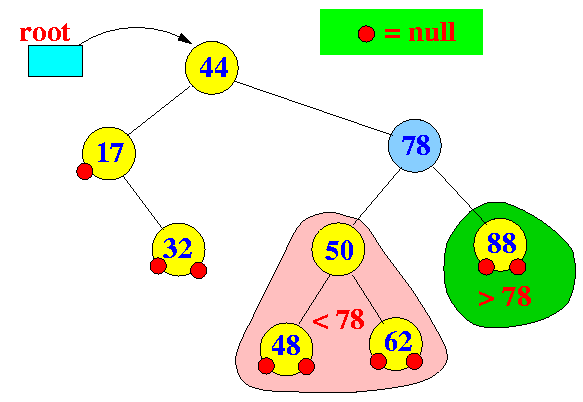
- The structure of
an entry:
/* =========================== Entry structure =========================== */ public class BSTEntry { // ******** The "payload *************************** public String key; // I use concrete data type again.... public Integer value; // Links that let you traverse UP and DOWN the BST public BSTEntry parent; // Parent node public BSTEntry left; // Left child node public BSTEntry right; // Right child node }
- The BSTEntry.java file:
public class BSTEntry { public String key; public Integer value; public BSTEntry parent; public BSTEntry left; public BSTEntry right; public BSTEntry(String k, Integer v) // Constructor { key = k; value = v; parent = null; left = null; right = null; } }For brevety sake, I left out the methods:
- getKey()
- getValue()
(I can do that because I made the variables public). It's very easy to write these methods....
- Fact:
- A tree is a generation of a linked list
Therefore:
- Just like in a linked list
(where you have no idea where all the nodes in a list are),
you have no idea where
all the nodes in a
tree are !!!
- All you have is information on where to start looking for the nodes !!!
- Information used to
represent a
BST:
public class BST { public BSTEntry root; // Reference to the root node of the BST }
- Constructor that make an
empty tree:
public class BST { public BSTEntry root; // Reference to the root node of the BST // Constructor public BST() { root = null; } }
- Often seen fact about
get(), put() and remove():
- You should know by now that
all these 3 operations
must first find
the approriate entry
- Furthermore,
the put() method is
a bit different in that
the entry sought may
not be present:
- If the entry is
present,
put() will update
the corresponding value, and
- If the entry is not present, put() will insert a new entry.
- If the entry is
present,
put() will update
the corresponding value, and
- You should know by now that
all these 3 operations
must first find
the approriate entry
- Consequently, we will write a
shared findEntry()
method that does the following:
- findEntry(k) will
return
the entry (k,v)
if
the key k is
present (found)
Example:
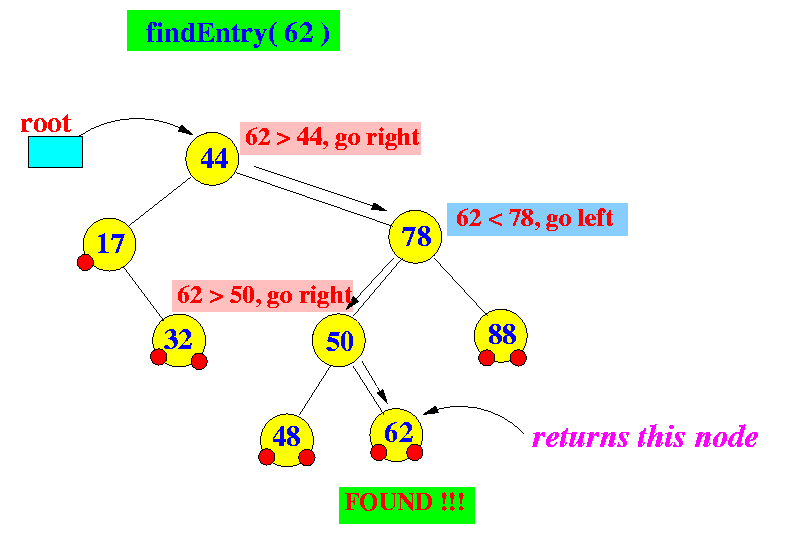
- findEntry(k) will
return
the parent entry of (k,v)
if
the key k is
not present (not found)
Example:
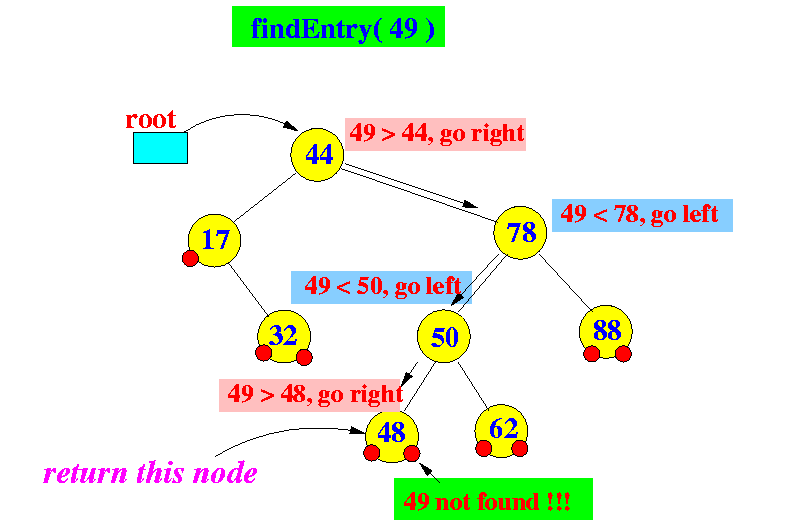
Consequently:
- The entry (k,v) can then be inserted as a child of the returned parent entry (for put())
- findEntry(k) will
return
the entry (k,v)
if
the key k is
present (found)
- The shared findEntry()
method:
/* ================================================================ findEntry(k): find entry with key k Return: reference to (k,v) IF k is in BST reference to parent(k,v) IF k is NOT in BST (for put) ================================================================ */ public BSTEntry findEntry(String k) { BSTEntry curr_node; // Current node in search BSTEntry prev_node; // The node BEFORE the curr node /* -------------------------------------------- Find the node with key == "k" in the BST -------------------------------------------- */ curr_node = root; // Always start at the root node prev_node = root; // Remember the previous node for insertion while ( curr_node != null ) { if ( k.compareTo( curr_node.key ) < 0 ) { prev_node = curr_node; // Remember prev. node curr_node = curr_node.left; // Continue search in left subtree } else if ( k.compareTo( curr_node.key ) > 0 ) { prev_node = curr_node; // Remember prev. node curr_node = curr_node.right; // Continue search in right subtree } else // k == current.key { // Found key in BST return curr_node; } } /* ====================================== When we reach here, k is NOT in BST ====================================== */ return prev_node; // Return the previous (parent) node }
- Fact:
- The running time of the findKey() (search) operation depends on the height of the search tree
- get(k):
/* ================================================================ get(k): find key k and return assoc. value ================================================================ */ public Integer get(String k) { BSTEntry p; // Help variable /* -------------------------------------------- Find the node with key == "key" in the BST -------------------------------------------- */ p = findEntry(k); if ( k.equals( p.key ) ) return p.value; else return null; }
- put(k,v):
/* ================================================================ put(k, v): store the (k,v) pair into the BST 1. if the key "k" is found in the BST, we replace the val that is associated with the key "k" 1. if the key "k" is NOT found in the BST, we insert a new node containing (k, v) ================================================================ */ public void put(String k, Integer v) { BSTEntry p; // Help variable /* ---------------------------------------------------------- Handle the EMPTY BST separately.... ---------------------------------------------------------- */ if ( root == null ) { // Insert into an empty BST root = new BSTEntry( k, v ); return; } /* -------------------------------------------- Find the node with key == "key" in the BST -------------------------------------------- */ p = findEntry(k); // If found, put() is update.... if ( k.equals( p.key ) ) { p.value = v; // Update value return; } /* ------------------------------------------------ Not found: Insert a new entry (k,v) under p !!! ------------------------------------------------ */ BSTEntry q = new BSTEntry( k, v ); q.parent = p; // p is the parent if ( k.compareTo( p.key ) < 0 ) p.left = q; // Add q as left child else p.right = q; // Add q as right child }
- The remove() operation is
very complex
because it must
maintain the
properties of
a BST.
- Pseudo code of the remove(k)
algorithm:
if ( k not in BST ) { return; // Nothing to delete } /****** The "Hibbard deletion algorithm" ******/ if ( k has no subtrees ) // x x { // / \ ==> / unlink k from k's parent; // y k y return; // } if ( k has 1 tree ) // x x { // / \ ==> / \ make k's parent point to k's subtree; // y k y z return; // \ } z /* k has 2 subtrees - TOUGH */ (1) find the successor of k: go right once go left all the way down (2) Replace k with k's successor; (3) Make the successor's parent point to the successor's right subtree;
- remove(k) in Java:
(for your eyes only,
I will not explain it -
because this is CS171 material)
/* ======================================================= remove(k): delete entry containg key k ======================================================= */ public void remove(String k) { BSTEntry p; // Help variable BSTEntry parent; // parent node BSTEntry succ; // successor node /* -------------------------------------------- Find the node with key == "key" in the BST -------------------------------------------- */ p = findEntry(k); if ( ! k.equals( p.key ) ) return; // Not found ==> nothing to delete.... /* ======================================================== Hibbard's Algorithm ======================================================== */ if ( p.left == null && p.right == null ) // Case 0: p has no children { parent = p.parent; /* -------------------------------- Delete p from p's parent -------------------------------- */ if ( parent.left == p ) parent.left = null; // p was left child else parent.right = null; // p was the right child return; } if ( p.left == null ) // Case 1a: p has 1 (right) subtree { parent = p.parent; /* ---------------------------------------------- Link p's right child as p's parent child ---------------------------------------------- */ if ( parent.left == p ) parent.left = p.right; // p has a right subtree else parent.right = p.right; // p has a right subtree return; } if ( p.right== null ) // Case 1b: p has 1 (left) child { parent = p.parent; /* ---------------------------------------------- Link p's left child as p's parent child ---------------------------------------------- */ if ( parent.left == p ) parent.left = p.left; else parent.right = p.left; return; } /* ================================================================ Tough case: node has 2 children - find successor of p succ(p) is as as follows: 1 step right, all the way left Note: succ(p) has NOT left child ! ================================================================ */ // (1) Find successor(p) succ = p.right; // Go right once step // BTW, p has a right subtree // because p has 2 children.... while ( succ.left != null ) // Go all the way left downwards succ = succ.left; /* ----------------------------------------- Now: succ = the successor of p ----------------------------------------- */ // (2) Replace k with k's successor; p.key = succ.key; // Replace p with successor p.value = succ.value; // (3) Make the successor's parent point to // successor's right subtree; parent = succ.parent; // Prepare to delete parent.left = succ.right; // Link right tree to parent's left return; }
- I have implemented the
BST (my way).
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- The BSTEntry.java Prog file: click here
- The BST.java Prog file: click here
- The TestBST.java Prog file: click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link(s) and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac TestBST.java
- To run: java TestBST
Partial output: (the BST is printed side ways)
[zebra,1600] [tiger,8888] [owl,2000] [man,5000] [lion,9999] [jackal,4000] [horse,2000] [donkey,1900] [dog,1000] [cow,700] [cat,500] [ape,1500] ================================ BST after remove("lion"): [zebra,1600] [tiger,8888] [owl,2000] [man,5000] [jackal,4000] [horse,2000] [donkey,1900] [dog,1000] [cow,700] [cat,500] [ape,1500]
- Height of a node:
- A leaf node of
a tree has
height 1
- The height of a node is the largest number of links traversed towards a leaf node plus 1
Example:

- A leaf node of
a tree has
height 1
- Height of a tree:
- Height of a tree = height of the root node of the tree
- The smallest key value in a
subtree:
- The left most leaf node of a subtree is the node with the smallest key value in that subtree
Examples:
Example 1 Example 2 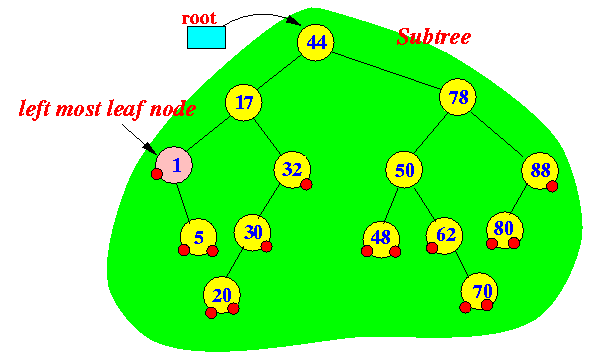
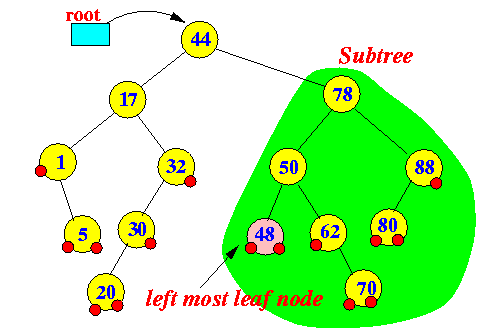
- The largest key value in a
subtree:
- The right most leaf node of a subtree is the node with the largest key value in that subtree
Examples:
Example 1 Example 2 

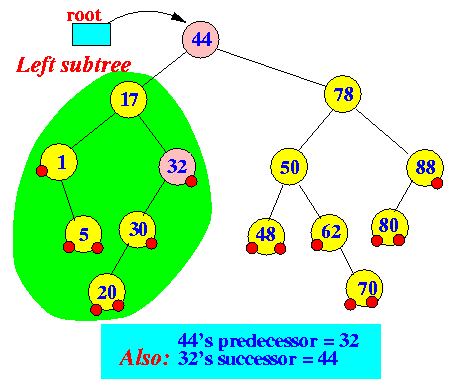
- In-order successor of x:
- successor(x) = the
smallest key that
is larger than x
(In other words: the "Next key")
How to find successor(x):
- If
x.right != null
(node has a right subtree),
then:
- succ(x) =
left most leaf node in
the right subtree of x
In other words:
- Go right exactly once
- Then, go left all the way down
- Go right exactly once
Examples:
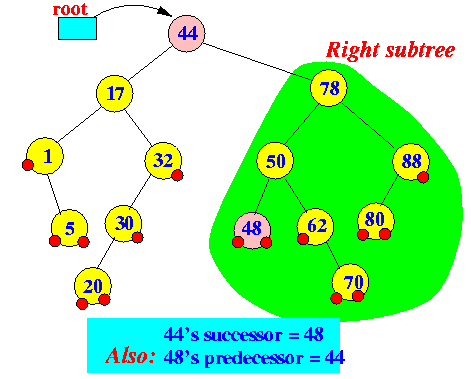

- succ(x) =
left most leaf node in
the right subtree of x
- Otherwise
(i.e., x.right == null,
(node has a no right subtree))
- successor(x) = the
first
"left-type" parent node of
node x
In other words:
- Keep going up in the BST
(Binary Search Tree) until you make a
"right" turn
- The node that you encounter when you make the "right" turn is the successor node
- Keep going up in the BST
(Binary Search Tree) until you make a
"right" turn
Example:
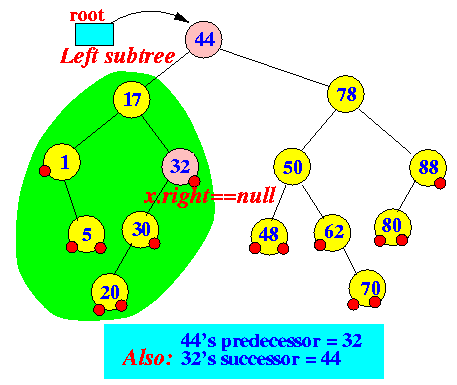
- successor(x) = the
first
"left-type" parent node of
node x
- successor(x) = the
smallest key that
is larger than x
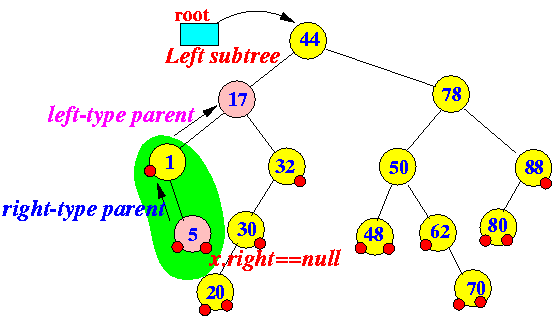
- In-order predecessor of x:
- predecessor(x) = the
largest key that
is smaller than x
(In other words: the previous key)
How to find predecessor(x):
- If
x.left != null,
then:
- predecessor(x) =
right most leaf node in
the left subtree of x
In other words:
- Go left exactly once
- Then, go right all the way down
- Go left exactly once
Example:
- predecessor(x) =
right most leaf node in
the left subtree of x
- Otherwise
(i.e., x.left == null)
- predecessor(x) = the
first
"right-type" parent node of
node x
In other words:
- Keep going up in the BST
(Binary Search Tree) until you make a
"left" turn
- The node that you encounter when you make the "left" turn is the successor node
- Keep going up in the BST
(Binary Search Tree) until you make a
"left" turn
Example:


- predecessor(x) = the
first
"right-type" parent node of
node x
- predecessor(x) = the
largest key that
is smaller than x
- firstEntry():
(returns entry with smallest key)
- Find the left most leaf node in the
Binary search tree
Example:

- Find the left most leaf node in the
Binary search tree
- lastEntry():
(returns entry with largest key)
- Find the right most leaf node in the
Binary search tree
Example:
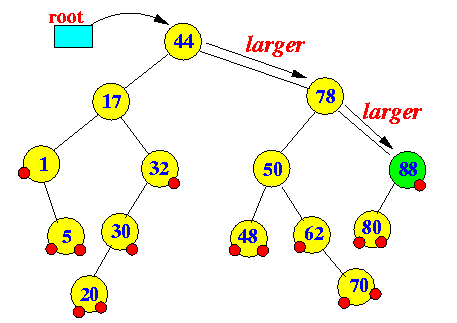
- Find the right most leaf node in the
Binary search tree
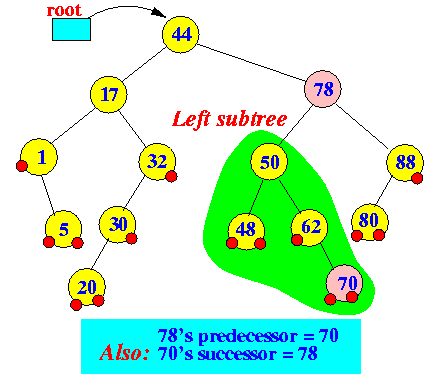
- ceilingEntry(k):
(returns the entry with the
smallest key value
that is ≥ k)
- Case 1: key "k" exists
⇒
return(k)
Example: ceilingEntry(30)

- Case 2: key "k" does
not exists
- Let node x = node the
findEntry(k) ends
- If x > k, then
return(x)
Example: ceilingEntry(18)
findEntry(18) ends at node 20 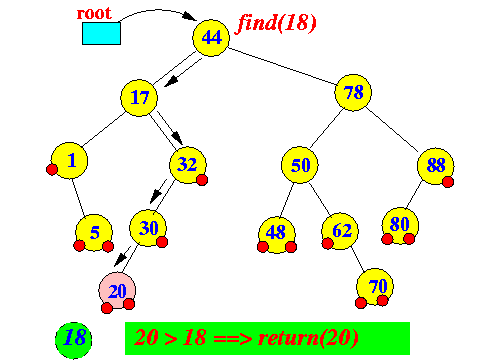
- If x < k, then:
return the successor of x
Example: ceilingEntry(75)
findEntry(75) ends at node 70 Return successor(70) 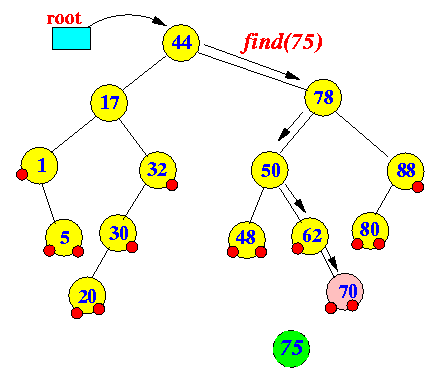
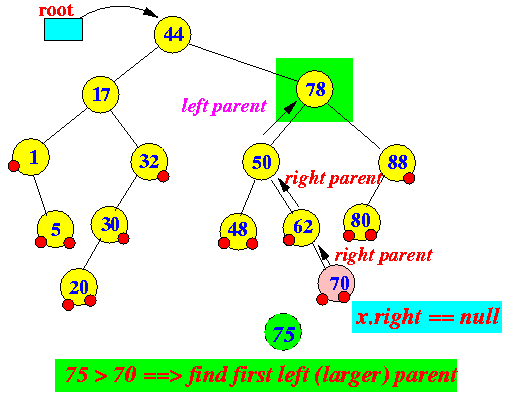
- Let node x = node the
findEntry(k) ends
- Case 1: key "k" exists
⇒
return(k)
- floorEntry(k):
(returns the entry with the
smallest key value
that is ≤ k)
- Case 1:
key "k" exists
- return(k)
- Case 2:
key "k" does not exists
- Let node x =
node where findEntry(k) ends
- If x < k, then
return(x)
- If x < k, then return(predecessor(x))
- Let node x =
node where findEntry(k) ends
-
(Similar
to ceilingEntry(x))
- Case 1:
key "k" exists
- upperEntry(k):
(returns the entry with the
smallest key value
that is > k)
- Let nodex x =
node where findEntry(k) ends
- If x > k, then
return(x)
Example: upperEntry(18)
findEntry(18) ends at node 20 
- If x ≤ k, then:
return the successor of x
Example: ceilingEntry(75)
findEntry(75) ends at node 70 Return successor(70) 

Note:
- The search for
ceilingEntry(70)
will also end in
node 70
- ceilingEntry(70) = 78
- The search for
ceilingEntry(70)
will also end in
node 70
- Let nodex x =
node where findEntry(k) ends
- lowerEntry(k):
(returns the entry with the
smallest key value
that is < k)
- Let nodex x =
node where
findEntry(k) ends
- If x > k,
then
return(x)
- If x ≤ k, then return(predecessor(x))
- Let nodex x =
node where
findEntry(k) ends