- Splay tree:
- A splay tree is an
ordinary (no balance requirement)
binary (search) tree
- However:
a splay tree
is a self-adjusting
("self-changing")
binary search tree
- How does a splay tree adjusted itself:
- Recently accessed elements
are moved closer
to the root node
- In fact:
- the last access element is moved up the tree to become the root node of the (new) tree
- Recently accessed elements
are moved closer
to the root node
- A splay tree is an
ordinary (no balance requirement)
binary (search) tree
- The splay tree
was invented by Daniel Dominic Sleator
and Robert Endre Tarjan
in 1985.
Research Paper: click here
- Categories of the basic restructuring operations:
- The zig-zig restructuring operation
- The zig-zag restructuring operation
- The zig restructuring operation
- The zig-zig restructuring
operation:


Property:
- Node x
moves 2 level
up the binary search tree
- The zig-zig restructuring can only be performed when node x has a grand-parent node...
- Node x
moves 2 level
up the binary search tree
- The zig-zag restructuring
operation:
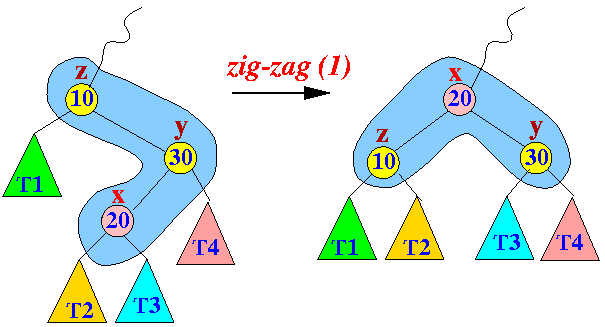
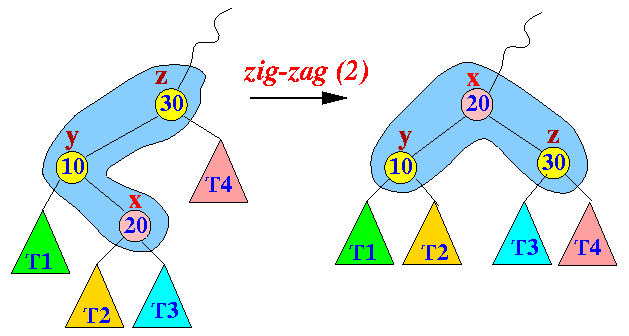
Property:
- Node x
moves 2 level
up the binary search tree
- The zig-zag restructuring can only be performed when node x has a grand-parent node...
- Node x
moves 2 level
up the binary search tree
- The zig restructuring
operation:
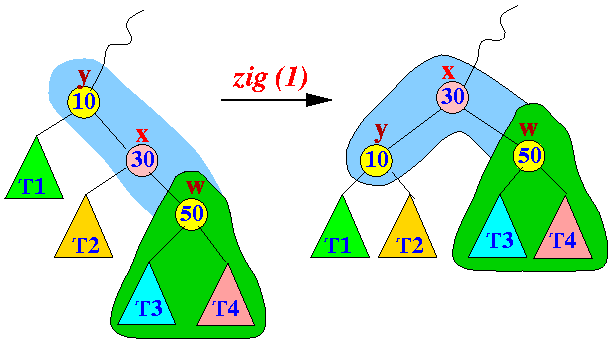

Property:
- Node x
moves 1 level
up the binary search tree
- The zig
restructuring is the last step
in the splaying operation
to move a
node x
towards the root node...
(The zig operation is only necessary when the depth of the node x is odd !)
- Node x
moves 1 level
up the binary search tree
- Terminology:
- Splaying a node x = apply the zig-zig, zig-zag and/or zig operation on the node x until node x become the root node of the binary (search) tree
- splay(88):
- Original binary tree:

- Step 1 in spray(88):
Zig-zig:
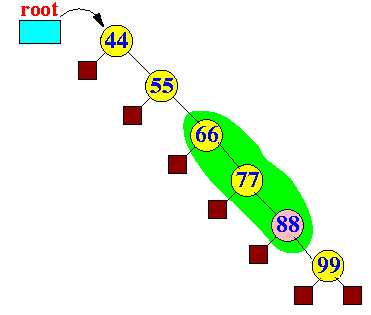
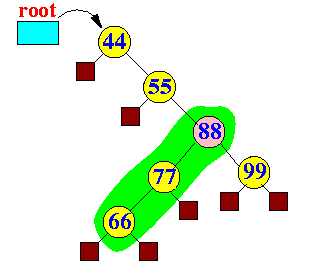
- Step 2 in spray(88):
Another zig-zig:

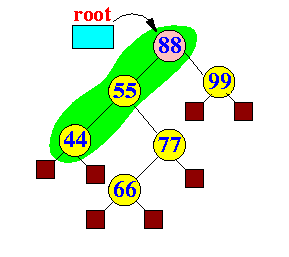
- Node 88 is the root: done...
- Original binary tree:
- Java:
/* ======================================================= Splay operation ======================================================= */ public void splay( BSTEntry x ) { while ( x != root ) { if ( x.parent == root ) { // height(x) = 1, can only move up 1 level... zig1(x); // Perform a zig operation } else { zig2( x ); // Perform a zig-zig or a zig-zag operation } } }
- The technique used in
similar to
implementing the
tri-node restructure operation.
Pseudo code:
Determine the configuration: 1. y 2. y / \ / \ T1 x x T4 / \ / \ T2 W W T3 setup the pointers x, y, T1, T2, T3 and T4 Depending on the configuration, construct the resulting tree Make x the root node (you only use zig in this case !)
- Java:
public void zig1( BSTEntry x ) { BSTEntry y = x.parent; // Find the parent node /* ******************************************************************* Determine the parent child relationships between (x,y)) ******************************************************************* */ boolean xIsLeftChild = (x == y.left); BSTEntry T1, T2, T3, T4, W; /* ======================================================= Determine the configuration and reconfigure ======================================================= */ if (xIsLeftChild) { /* Configuration zig 2 */ System.out.println("Use zig(2)"); // Prepare to link // y x // / \ / \ W = x.left; // x T4 W y T3 = x.right; // / \ / \ T4 = y.right; // W T3 T3 T4 // Link them up x.left = W; if ( W != null ) W.parent = x; x.right = y; y.parent = x; y.left = T3; if ( T3 != null ) T3.parent = y; y.right = T4; if ( T4 != null ) T4.parent = y; } else { /* Configuration zig(1) */ System.out.println("Use zig(1)"); // Prepare to link // y x T1 = y.left; // / \ / \ T2 = x.left; // T1 x y W // / \ / \ W = x.right; // T2 W T1 T2 // Link them up x.left = y; y.parent = x; x.right = W; if ( W != null ) W.parent = x; y.left = T1; if ( T1 != null ) T1.parent = y; y.right = T2; if ( T2 != null ) T2.parent = y; } root = x; // We only use zig1() when y is root !!! x.parent = null; }
- The code is very similar to
the zig-operation, so
I will just give you the
Java code:
public void zig2( BSTEntry x ) { BSTEntry y, z, zParent; BSTEntry T1, T2, T3, T4; y = x.parent; z = y.parent; zParent = z.parent; // Save the parent of z (link later) /* ******************************************************************* Determine the parent child relationships between (y,z) and (x,y)) z --> y --> x ******************************************************************* */ boolean yIsLeftChild = (y == z.left); boolean xIsLeftChild = (x == y.left); /* =========================================================== Determine the configuration and restructure accordingly =========================================================== */ if (xIsLeftChild && yIsLeftChild) { /* Configuration zig-zig 2 */ System.out.println("Use zig-zig(2)"); // z x // / \ / \ // y T4 T1 y T1 = x.left; // / \ / \ T2 = x.right; // x T3 T2 z T3 = y.right; // / \ / \ T4 = z.right; // T1 T2 T3 T4 x.left = T1; if ( T1 != null ) T1.parent = x; x.right = y; y.parent = x; y.left = T2; if ( T2 != null ) T2.parent = y; y.right = z; z.parent = y; z.left = T3; if ( T3 != null ) T3.parent = z; z.right = T4; if ( T4 != null ) T4.parent = z; } else if (!xIsLeftChild && yIsLeftChild) { /* Configuration zig-zag(2) */ System.out.println("Use zig-zag(2)"); // z x // / \ / \ // y T4 y z T1 = y.left; // / \ / \ / \ T2 = x.left; // T1 x T1 T2 T3 T4 T3 = x.right; // / \ T4 = z.right; // T2 T3 x.left = y; y.parent = x; x.right = z; z.parent = x; y.left = T1; if ( T1 != null ) T1.parent = y; y.right = T2; if ( T2 != null ) T2.parent = y; z.left = T3; if ( T3 != null ) T3.parent = z; z.right = T4; if ( T3 != null ) T4.parent = z; } else if (xIsLeftChild && !yIsLeftChild) { /* Configuration zig-zag(1) */ System.out.println("Use zig-zag(1)"); // z x // / \ / \ // T1 y z y T1 = z.left; // / \ / \ / \ T2 = x.left; // x T4 T1 T2 T3 T4 T3 = x.right; // / \ T4 = y.right; // T2 T3 x.left = z; z.parent = x; x.right = y; y.parent = x; y.left = T3; if ( T3 != null ) T3.parent = y; y.right = T4; if ( T4 != null ) T4.parent = y; z.left = T1; if ( T1 != null ) T1.parent = z; z.right = T2; if ( T2 != null ) T2.parent = z; } else { /* Configuration zig-zig(1) */ System.out.println("Use zig-zig(1)"); // z x // / \ / \ // T1 y y T4 T1 = z.left; // / \ / \ T2 = y.left; // T2 x z T3 T3 = x.left; // / \ / \ T4 = x.right; // T3 T4 T1 T2 x.left = y; y.parent = x; x.right = T4; if ( T4 != null ) T4.parent = x; y.left = z; z.parent = y; y.right = T3; if ( T3 != null ) T3.parent = y; z.left = T1; if ( T1 != null ) T1.parent = z; z.right = T2; if ( T2 != null ) T2.parent = z; } /* ============================================================= Link the resulting subtree to z's Parent (zParent) (Remember that prior to the restructuring, the tree is: z z \ / y y and so on... z was the root \ \ x x ============================================================== */ if ( root == z ) { /* If z is the root node, handle the replacement differently.... */ root = x; // x is now the new root x.parent = null; } else { // Link x to zParent (at left or at right, depending where z was) if ( zParent.left == z ) { /* Link x to the left branch of z's parent */ x.parent = zParent; zParent.left = x; } else { /* Link x to the right branch of z's parent */ x.parent = zParent; zParent.right = x; } } }
- Example Program:
(Demo above code)

- The BSTEntry.java Prog file: click here
- The Splay_BST.java Prog file:
click here
- Test program (TestSplay.java): click here
How to run the program:
- Right click on link(s) and
save in a scratch directory
- To compile: javac TestSplay.java
- To run: java TestSplay
- In my demo program:
- I only perform
a splay operation in the
get() method
- ... and only when get() is successful (i.e., the entry was found)
- I only perform
a splay operation in the
get() method
- In general,
you can perform (if desired) a
splay operation in
these methods:
- lookup: get(k)
- If key k is
found:
splay(k)
Example:
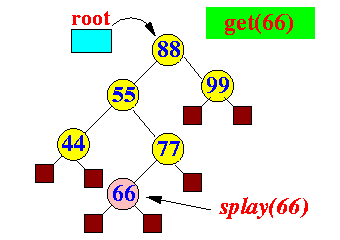
- If key k is
not found:
splay("parent(k)")
Example:
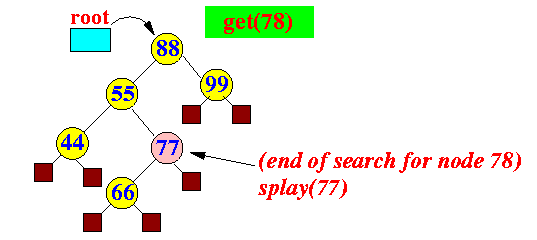
- If key k is
found:
splay(k)
- insert: put(k,v)
- If key k is
found:
splay(old k)
Example:
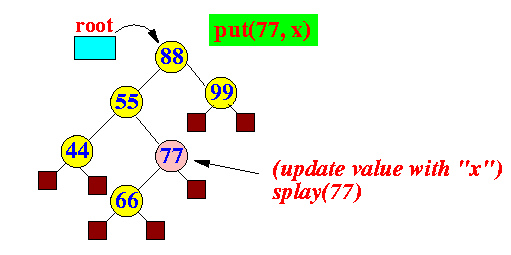
- If key k is
not found:
splay(new k)
Example:
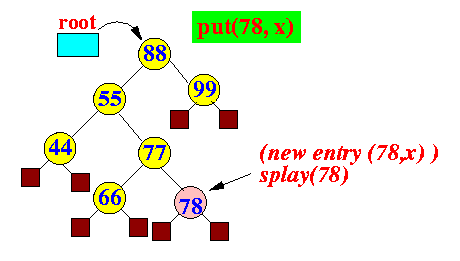
- If key k is
found:
splay(old k)
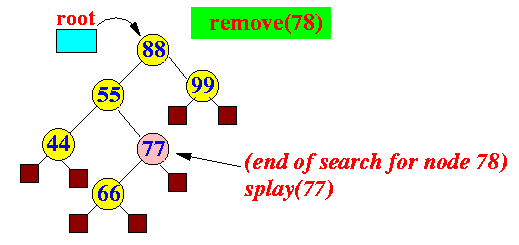
- delete: remove(k)
- If key k is
found:
splay(parent of the node that
got removed)
Example:

- If key k is
not found:
splay("parent(k)")
Example:
- If key k is
found:
splay(parent of the node that
got removed)
- lookup: get(k)
- $64,000 question:
- Suppose we perform a
splay operation
each time we perform one of the following operations:
- get(),
- put() and
- remove()
- What is the average
running time
of the
- get(),
- put() and
- remove()
operations ????
- Suppose we perform a
splay operation
each time we perform one of the following operations:
- Because the splay tree
changes structure continuously,
it looks like
this task is
impossible to perform...
One of the reason why I chose to study the splay tree is to introduce students to an interesting (novel) way to study performance evaluation:
- the Amortization technique
- Before we
discuss how to
perform the analysis on a splay tree,
I will first introduce
the
Amortization technique
by studying the
average running time
of:
- the push() operation in a doubling array stack