List processing algorithms
- Recall that:
- The program
uses the
first
(or
head)
variable to
reference to the
first node of
a linked list
Therefore:
-
Only the
first node is
immediately
accessible by
a program...
|
|
-
Processing
data stored in
a linked list
(a.k.a. list processing)
often requires:
-
visiting
all
elements in the
linked list by
traversing the
chain
|
Graphically:
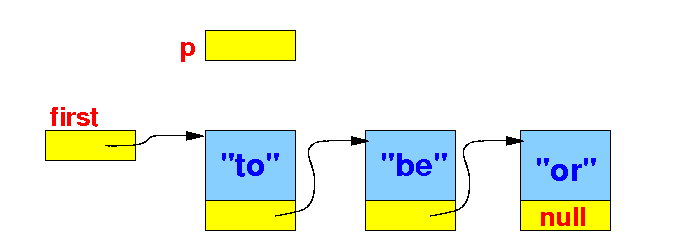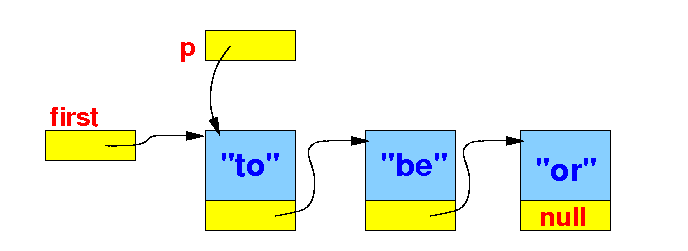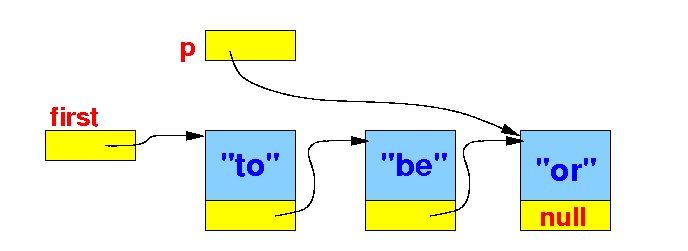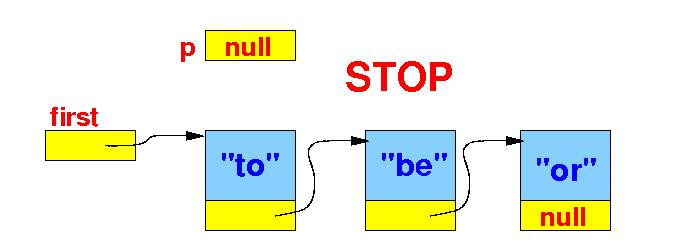
|
The standard list traversal algorithm
- Warning:
you must
never use
the variable
first
to traverse
the linked list:
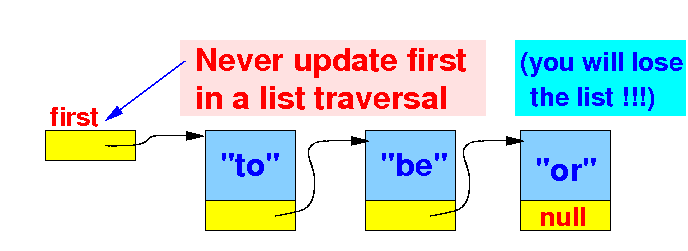
// The standard list traversal algorithm
Node p;
p = first;
while ( p != null )
{
// Process data in node p
p = p.next;
}
|
|
The standard list traversal algorithm
- Define a
helper reference
variable p
to traverse the
linked list:
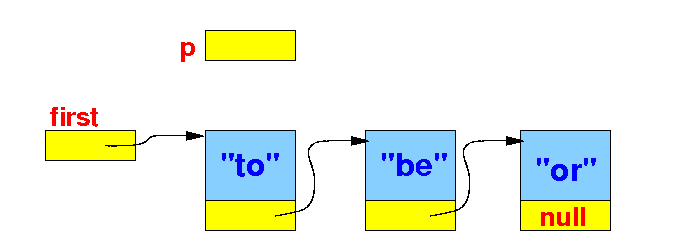
// The standard list traversal algorithm
Node p;
p = first;
while ( p != null )
{
// Process data in node p
p = p.next;
}
|
|
The standard list traversal algorithm
- Initialize the
helper reference
variable p
to point the
first node of the
linked list:
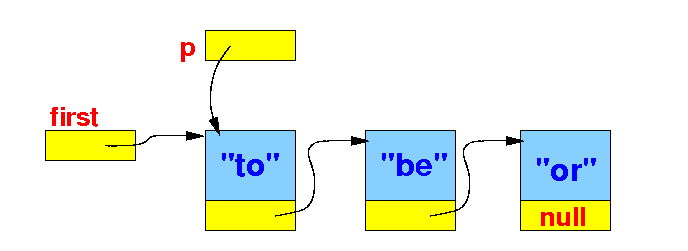
// The standard list traversal algorithm
Node p;
p = first; // P now points to the first node
while ( p != null )
{
// Process data in node p
p = p.next;
}
|
|
The standard list traversal algorithm
- When p
is pointing at a
certain node, we can
access its
data as
p.item:
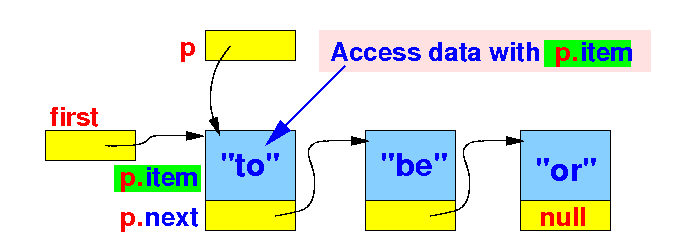
// The standard list traversal algorithm
Node p;
p = first; // P now points to the first node
while ( p != null )
{
// Process data (p.item) in node p
Notice: p.next is the address of the next Node !
}
|
|
The standard list traversal algorithm
- After processing a
node, we
advance
p to point to
the next node with the
statement
p =
p.next:
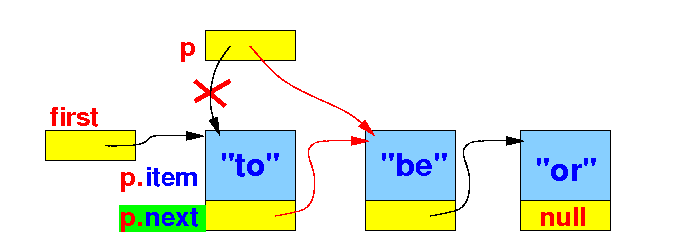
// The standard list traversal algorithm
Node p;
p = first; // P now points to the first node
while ( p != null )
{
// Process data (p.item) in node p
p = p.next; // Advances p to next node
}
|
|
The standard list traversal algorithm
-
Insight:
the reason
why
the variable p
"advances" to the
next node is because
p = p.next
assigns
the address in
p.next
to the variable
p:
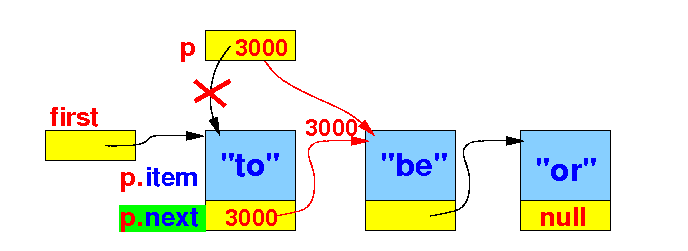
// The standard list traversal algorithm
Node p;
p = first; // P now points to the first node
while ( p != null )
{
// Process data (p.item) in node p
p = p.next; // Advances p to next node
}
|
|
The standard list traversal algorithm
- We repeat the
steps until
we have process the
data in the
last node, then
p will contain
null:
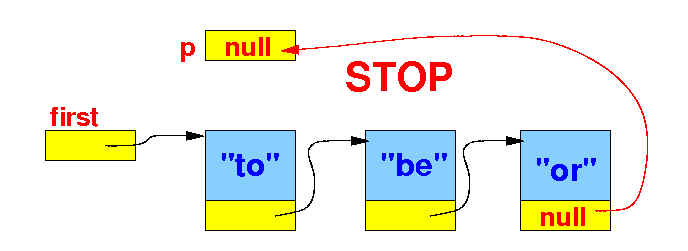
// The standard list traversal algorithm
Node p;
p = first; // P now points to the first node
while ( p != null )
{
// Process data (p.item) in node p
p = p.next; // Advances p to next node
}
|
|
Animation of
the standard list traversal algorithm
Use the list traversal algorithm
to
print out all items in a list
- Problem:
-
Print out
all the
item values
stored
in a linked list
|
- The list traversal
algorithm
will visit
every node
p:
// The standard list traversal algorithm
Node p;
p = first; // P now points to the first node
while ( p != null )
{
// Visiting node p (p.item = data store in p)
p = p.next; // Advances p to next node
}
|
|
Use the list traversal algorithm
to
print out all items in a list
DEMO:
demo/11-linked-list/01-create/Demo.java
Enhancements of the
list traversal algorithm
- The list traversal
algorithm is the
basis for
many other
list processing
algorithms.
Example:
- Find a
node in the
list
that contains a special value
(say: X).
|
- Here is the
basic
list traversal
algorithm:
Node current = first;
while ( current != null )
{
// Process current node here
current = current.next; // Move to next node
}
|
|
Enhancements of the
list traversal algorithm
- The list traversal
algorithm is the
basis for
many other
list processing
algorithms.
Example:
- Find a
node in the
list
that contains a special value
(say: X).
|
- To find a
node that contains
X, we
exit the
loop when
the current contains
the X:
Node current = first;
while ( current != null ) // Find list element containing X
{
if ( current (node) contains X )
break;
current = current.next; // Move to next node
}
// Here:
// either current == null (no node contains X)
// or the current (node) contains X
|
|
Enhancements of the
list traversal algorithm
- The list traversal
algorithm is the
basis for
many other
list processing
algorithms.
Example:
- Find a
node in the
list
that contains a special value
(say: X).
|
- The search adaptation
of the list traversal
is often
written
as follows:
Node current = first;
while ( current != null && !(current (node) contains X) )
{
current = current.next; // Move to next node
}
// Here:
// either current == null (no node contains X)
// or the current (node) contains X
|
|
Use the list traversal algorithm
to
find a list element
that contains a certain key
- Problem:
- Write a method that
returns
a list element that
contains a certain value
|
- The method
findNode(f, s)
finds a node in
linked list f that
contains
the value s:
public static Node findNode( Node f, String s )
{
Node p = first;
while ( p != null )
{
// Visiting node p (p.item = data store in p)
p = p.next; // Advances p to next node
}
return null;
}
|
|
Use the list traversal algorithm
to
find a list element
that contains a certain key
- Problem:
- Write a method that
returns
a list element that
contains a certain value
|
- We test
every node
by (1)
visit the
node (using the variable
p):
public static Node findNode( Node f, String s )
{
Node p = f; // Start at the first node f
while ( p != null ) // Visit every node in list f
{
// Visiting node p (p.item = data store in p)
p = p.next; // Advances p to next node
}
return null;
}
|
|
Use the list traversal algorithm
to
find a list element
that contains a certain key
- Problem:
- Write a method that
returns
a list element that
contains a certain value
|
- (2) If
node p
contains the
search value,
we return
p:
public static Node findNode( Node f, String s )
{
Node p = f; // Start at the first node f
while ( p != null ) // Visit every node in list f
{
if ( p.item.equals( s ) )
return p; // Found s --> return p
p = p.next; // Advances p to next node
}
???
}
|
|
Use the list traversal algorithm
to
find a list element
that contains a certain key
- Problem:
- Write a method that
returns
a list element that
contains a certain value
|
- (3) If
we
exit the
loop, then
s is
not found in the
linked list f ---
we
return
null:
public static Node findNode( Node f, String s )
{
Node p = f; // Start at the first node f
while ( p != null ) // Visit every node in list f
{
if ( p.item.equals( s ) )
return p; // Found s --> return p
p = p.next; // Advances p to next node
}
return null; // Not found
}
|
|
DEMO:
demo/11-linked-list/01-create/Demo2.java
Postscript: list traversal
using a for-loop
DEMO:
demo/11-linked-list/01-create/Demo3.java
❮
❯