Prelude...
- Data structures created
with
references are
very flexible !
Consequently:
- There are
many varieties of
linked lists....
|
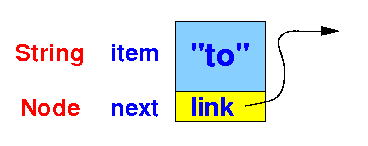
- We will first study the
singly linked
linked list where
each node
has a single reference (link):
- How to
approach the
material on
list manipulation:
-
Do not
memorize
(too many varieties of lists !)
- Understand
what an
operation must
achieve
-
Devise the
steps to
manipulate the
links to
achieve that
outcome
|
|
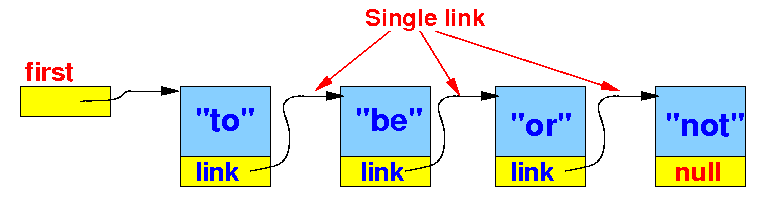
Operations on a Linked List
- The linked list is
a data structure used to
store
information
- To be useful as
a data structure,
the linked list must
support the following
operations:
- Create an
empty
linked list
- Insert
a data item into
the linked list
- Insert it at the
beginning of the
linked list
- Insert it at the
end of the
linked list
|
- Delete
a data item from
the linked list
- Insert the
element at the
beginning of the
linked list
- Insert the
element at the
end of the
linked list
|
- Searching for
some data item
in the linked list
- Search by its
index
- Seach by its
key value
|
|
|
Introduction to linked list
mainipulation
Constructing a linked list using
explicit helper reference variables
- Let's
create the
following
linked list:
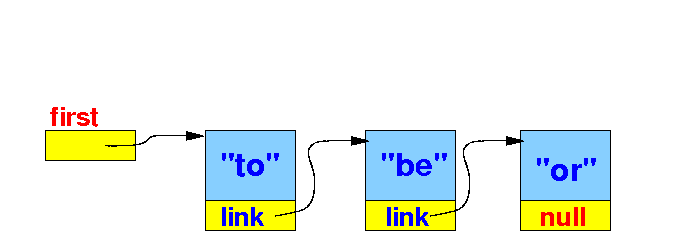
I will write staements here that achieves
the effect in the above diagram
Key: do not memorize the statements
understand why the statements will
achieve a particular effect
|
|
Constructing a linked list using
explicit helper reference variables
- Let's
start with
a
clean slate:

public class Demo
{
public static Node first; // Define the first variable
// first references to a Node object
// Therefore, its data type is Node
}
|
|
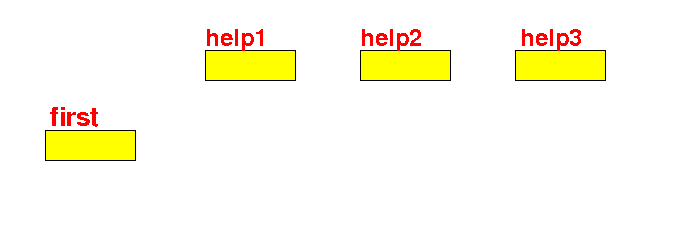
Constructing a linked list using
explicit helper reference variables
- Define some
helper variables
to hold
Node objects:
public class Demo
{
public static Node first; // Define the first variable
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node help1;
Node help2;
Node help3;
}
|
|
Constructing a linked list using
explicit helper reference variables
-
Create/allocate the
Node objects:
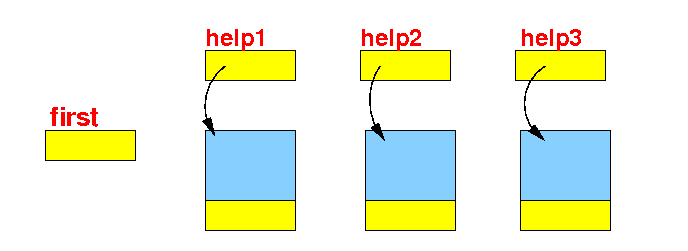
public class Demo
{
public static Node first; // Define the first variable
public static void main(String[] args)
{
Node help1 = new Node();
Node help2 = new Node();
Node help3 = new Node();
}
|
|
Constructing a linked list using
explicit helper reference variables
-
Store the
proper string in
each
Node:
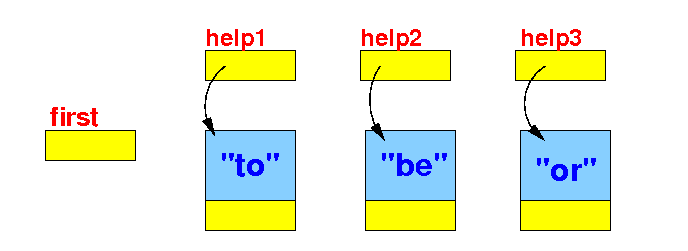
public class Demo
{
public static Node first; // Define the first variable
public static void main(String[] args)
{
...
help1.item = "to";
help2.item = "be";
help3.item = "or";
}
|
|
Constructing a linked list using
explicit helper reference variables
- Use the
next variable
in each
Node
to create this
chain:
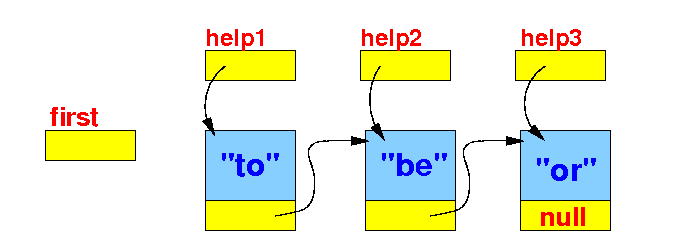
public class Demo
{
public static Node first; // Define the first variable
public static void main(String[] args)
{
...
help1.next = help2;
help2.next = help3;
help3.next = null ; // null marks the end
// Understand why this will create the above chain !
}
|
|
Constructing a linked list using
explicit helper reference variables
- We must use
the
first variable
to reference to
the
first Node
in the linked list:
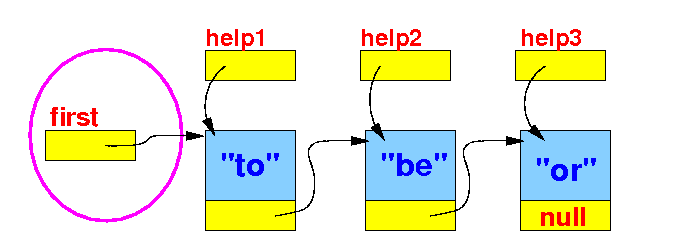
public class Demo
{
public static Node first; // Define the first variable
public static void main(String[] args)
{
...
help1.next = help2;
help2.next = help3;
help3.next = null ; // null marks the end
first = help1; // Done !
}
|
|
Constructing a linked list using
explicit helper reference variables
- If we
remove the
helper variables, you will
see the
linked list
clearer:
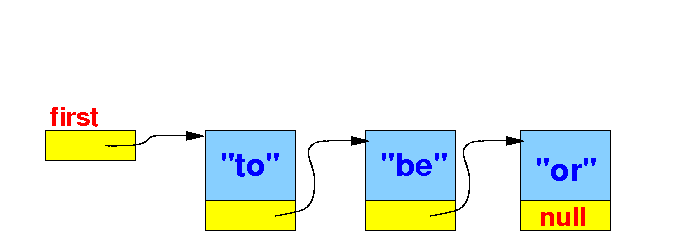
public class Demo
{
public static Node first; // Define the first variable
public static void main(String[] args)
{
...
help1.next = help2;
help2.next = help3;
help3.next = null ; // null marks the end
first = help1; // Done !
}
|
|
DEMO:
demo/11-linked-list/01-create/Demo.java
Summary and
insights
- Nodes of a
linked list can be
created
on demand
- A
linked list is
created by
chaining nodes
together using the
link field
(which is usually named
next)
- Node
addition and
removal
is
archieved by
manipulating
the links in
the
appropriate nodes
in the linked list !
- A comment and an
advice:
- There are many variations
possible
So:
- Do not
memorize
what to do
|
- Understand
what do you want to
achieve:
- How should the
new set of
links be ?
|
- Then device the
manipulation steps
to achieve the
result
|
|
❮
❯