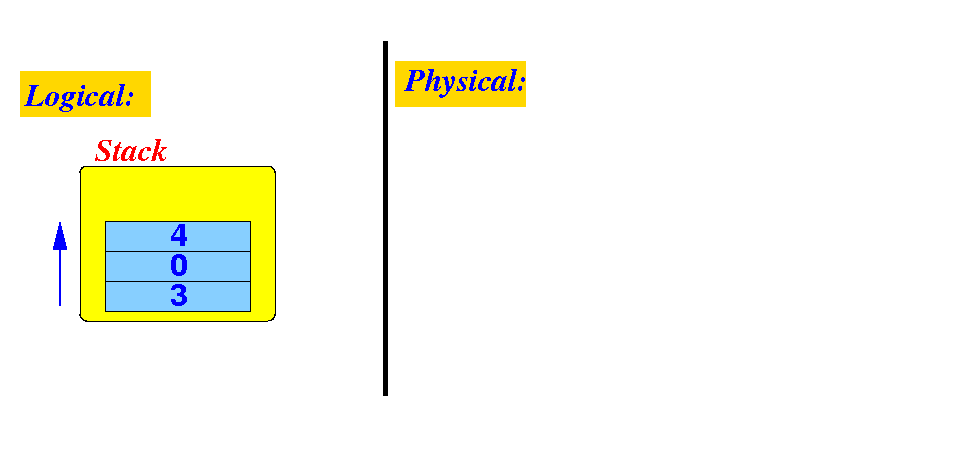
A basic implementation
of the Stack interface
- The basic implementation
of a Stack is
using:
Schematically:
|
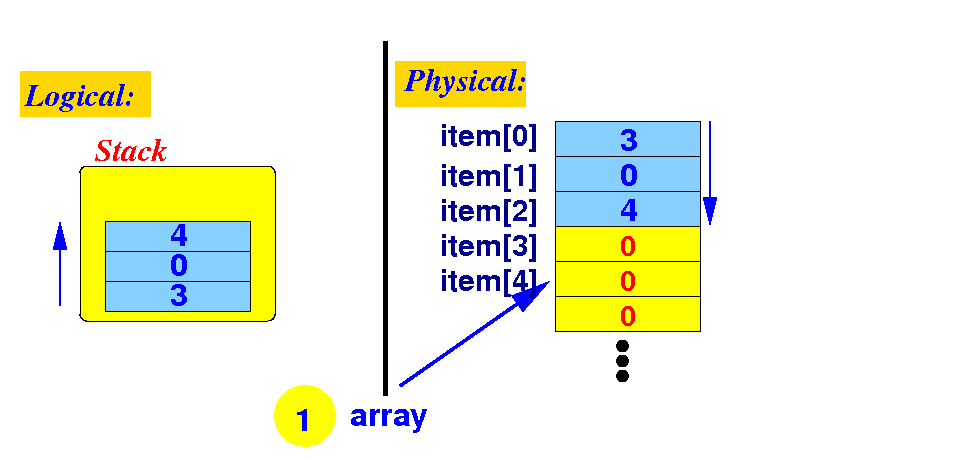
A basic implementation
of the Stack interface
- The basic implementation
of a Stack is
using:
- A fixed size
array to
store the
data items
-
|
Schematically:
|
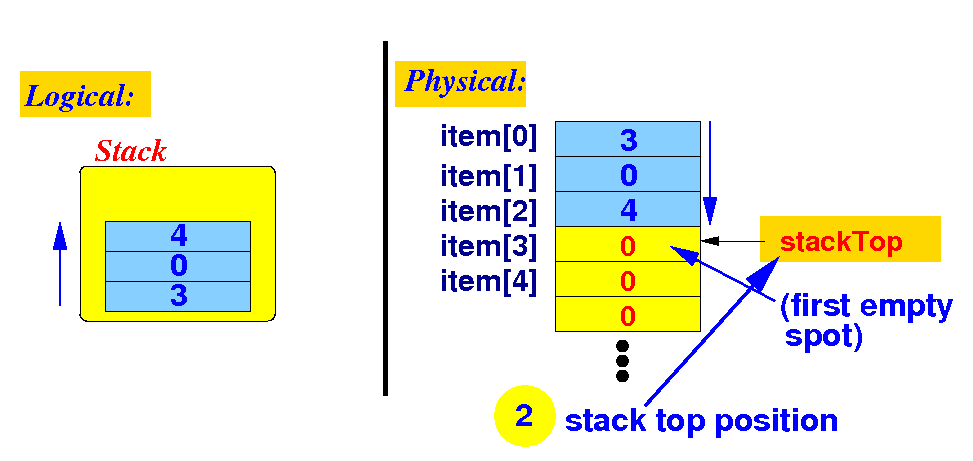
A basic implementation
of the Stack interface
- The basic implementation
of a Stack is
using:
- A fixed size
array to
store the
data items
- A
stackTop index variable
to record the
first open position
in
the array
|
Schematically:
|
A basic implementation
of the Stack interface
- The initial state of
the stack when it
is instantiated (= created):
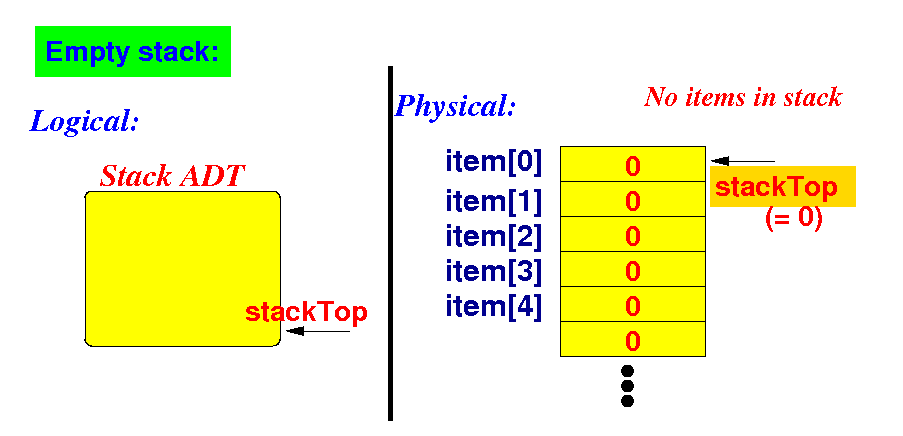
- Comment:
- I
choose to
initialize
stackTop = 0
to indicate and
empty stack
- An
alternate choice
can be
to use
stackTop = −1
|
|
A basic implementation
of the Stack interface
variables and constructor

- The
instance variables
and
the
constructor of an
Integer stack:
public class IntegerStack implements Stack<Integer>
{
private Integer[] item;
private int stackTop;
public IntegerStack(int N) // Create a stack of size N
{
item = new Integer[N];
stackTop = 0;
}
....
}
|
|
A basic implementation
of the Stack interface
isEmpty()

- The stack is
empty when
stackTop == 0:
public class IntegerStack implements Stack<Integer>
{
public boolean isEmpty( ) // Test if stack is empty
{
return stackTop == 0;
}
....
}
|
|
A basic implementation
of the Stack interface
push(x)
A basic implementation
of the Stack interface
push(x)
A basic implementation
of the Stack interface
push(x)
-
Basic implementaion of the
push( ) method:
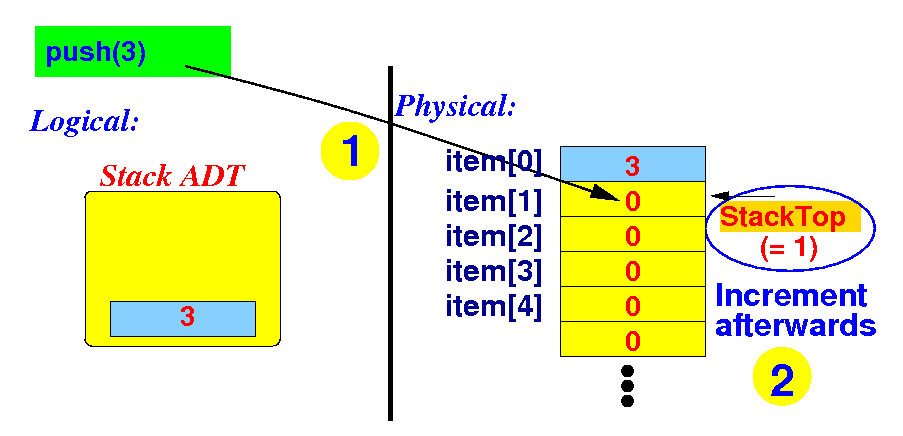
public void push(Integer e)
{
if ( isFull () )
{
System.out.println("Full");
return ;
}
item[ stackTop ] = e; // (1) store item
stackTop++; // (2) increment stackTop
}
|
|
A basic implementation
of the Stack interface
push(x)
-
Safer implementaion of the
push( ) method:

public void push(Integer e)
{
if ( isFull () ) // Implement this next
{
System.out.println("Full");
return ; // Or: throw an exception
}
item[ stackTop ] = e; // (1) store item
stackTop++; // (2) increment stackTop
}
|
|
A basic implementation
of the Stack interface
isFull()
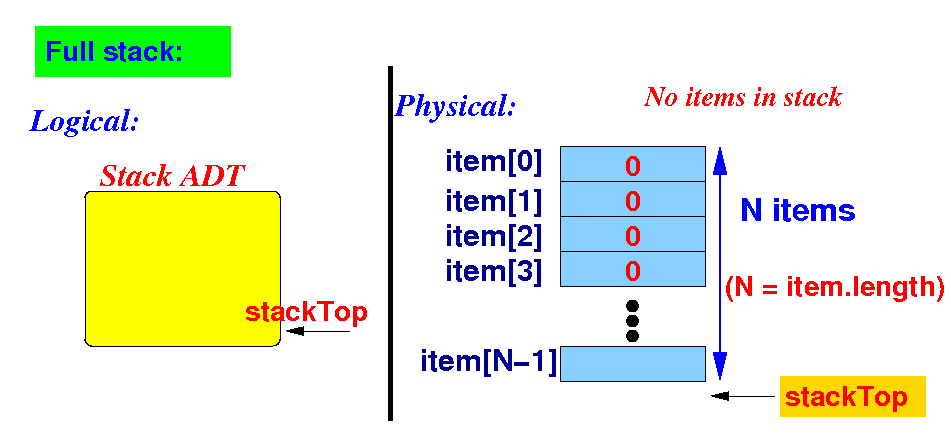
- The stack is
full when
stackTop == item.lenght:
public class IntegerStack implements Stack<Integer>
{
public boolean isFull( ) // Test if stack is empty
{
return stackTop == item.length;
}
....
}
|
|
A basic implementation
of the Stack interface
pop()
A basic implementation
of the Stack interface
pop()
-
Basic implementaion of the
pop( ) method:
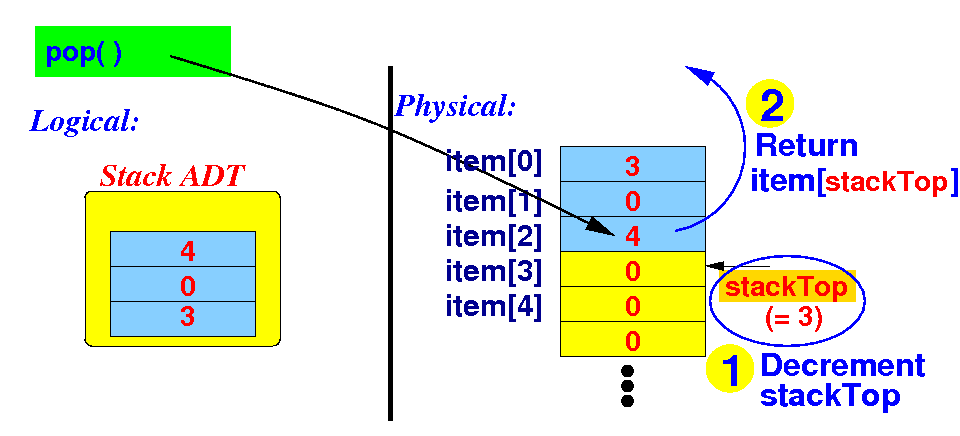
public Integer pop( )
{
if ( isEmpty () )
{
System.out.println("Full");
return ;
}
stackTop--; // (1) decrement stackTop
return item[ stackTop ]; // (2) return item
}
|
|
A basic implementation
of the Stack interface
pop()
-
Safer
implementaion of the
pop( ) method:

public Integer pop( )
{
if ( isEmpty () )
{
System.out.println("Empty");
return null; // Or: throw an exception
}
stackTop--; // (1) decrement stackTop
return item[ stackTop ]; // (2) return item
}
|
|
Demo program
- Demo program showing the
functionality of
the stack:
public class Demo
{
public static void main(String[] args)
{
IntegerStack s = new IntegerStack(5);
s.pop(); // Pops an empty stack !
s.push(1);
s.push(2);
s.push(3);
System.out.println( s );
System.out.println( s.pop() );
System.out.println( s );
System.out.println( s.pop() );
System.out.println( s );
System.out.println( s.pop() );
System.out.println( s );
}
}
|
|
DEMO:
demo/09-stack/01-array/Demo.java +
IntegerStack.java +
MyStackInterface.java
❮
❯





